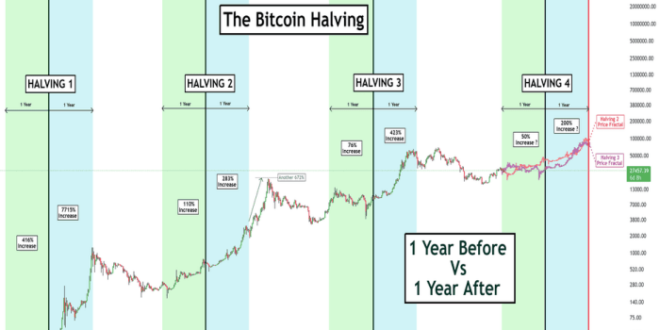
Bitcoin Halving 2025
The Bitcoin halving, a pre-programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol, is set to occur in 2025. This event, anticipated with considerable interest within the cryptocurrency community, significantly impacts the rate at which new Bitcoins are introduced into circulation. Understanding its mechanics, historical context, and projected effects is crucial for navigating the potential market volatility surrounding this event.
Bitcoin Halving Mechanics and Historical Price Impact
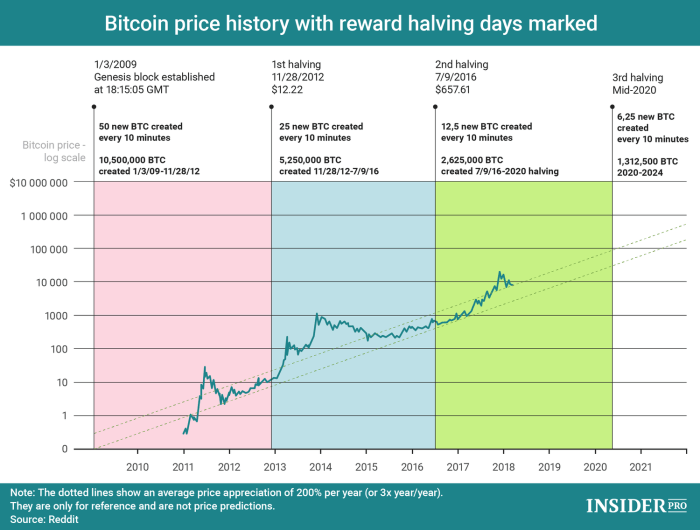
The Bitcoin halving reduces the reward given to Bitcoin miners for successfully verifying and adding new blocks to the blockchain by half. This process, designed to control inflation, occurs approximately every four years, or every 210,000 blocks mined. Historically, halvings have been followed by periods of significant price appreciation, although the timing and magnitude of these price increases have varied. The reduced supply of newly minted Bitcoin, coupled with sustained or increased demand, is generally considered the primary driver of these price movements. The impact isn’t solely determined by the halving itself; market sentiment, regulatory changes, and overall economic conditions play a substantial role.
Projected Bitcoin Supply After the 2025 Halving
After the 2025 halving, the block reward will decrease from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC. This will further reduce the rate of Bitcoin inflation, bringing the total supply closer to its hard cap of 21 million coins. While the precise timing of reaching the 21 million limit is uncertain due to variations in block mining times, it’s expected to occur sometime after the year 2140. The scarcity inherent in this finite supply is a key factor underpinning Bitcoin’s value proposition.
Comparison of Market Conditions Leading Up to Previous Halvings
The market conditions leading up to the 2025 halving differ from those preceding previous halvings. The 2012 and 2016 halvings occurred during periods of relative obscurity for Bitcoin. The 2020 halving, however, took place against a backdrop of increased institutional interest and mainstream media attention. The current environment is characterized by heightened regulatory scrutiny, macroeconomic uncertainty, and significant technological advancements in the broader cryptocurrency landscape. Therefore, while historical trends offer valuable insights, they don’t provide a definitive prediction for the 2025 halving’s impact. The increased awareness and institutional participation may lead to different outcomes compared to previous cycles.
Timeline of Significant Events Expected Around the 2025 Halving
Predicting precise dates for market events is inherently speculative, but a plausible timeline could include:
Increased speculation and price volatility in the months leading up to the halving. A surge in on-chain activity, potentially driven by anticipation of the event. Post-halving price adjustments, which could be positive or negative, depending on prevailing market sentiment. Continued regulatory developments impacting the cryptocurrency market globally.
Key Metrics of Previous Bitcoin Halvings
| Date | Block Height | Price Before (USD) | Price After (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| November 28, 2012 | 210,000 | ~13 | ~100 (approx. 1 year later) |
| July 9, 2016 | 420,000 | ~650 | ~20,000 (approx. 2 years later) |
| May 11, 2020 | 630,000 | ~8,700 | ~65,000 (approx. 1 year later) |
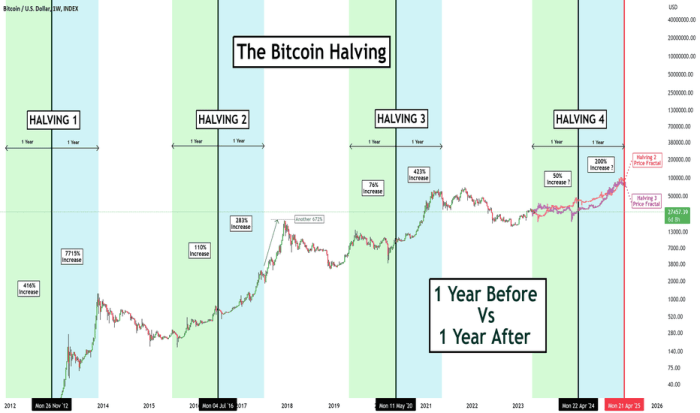
The 2025 Halving’s Impact on Bitcoin Price: Halving Bitcoin 2025 Fecha
The Bitcoin halving, scheduled for 2025, is a significant event anticipated to influence Bitcoin’s price. This event, occurring approximately every four years, reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created, fundamentally altering the supply dynamics of the cryptocurrency. While past halvings have been followed by price increases, predicting the exact impact of the 2025 halving remains complex and subject to numerous variables.
The halving’s impact on Bitcoin’s price is a multifaceted issue. Short-term effects are likely to involve increased price volatility, driven by speculative trading and anticipation of the event. Long-term effects, however, are more difficult to ascertain and are heavily dependent on broader economic conditions and market sentiment. The reduced supply of newly minted Bitcoin could create a scarcity effect, potentially pushing prices upwards, but this effect is not guaranteed and may be counteracted by other factors.
Short-Term Price Effects
The period immediately surrounding the 2025 halving is expected to be characterized by heightened volatility. Traders often engage in speculative buying in anticipation of a post-halving price surge, leading to price increases in the months preceding the event. Conversely, profit-taking after the price increase could lead to a short-term correction. The magnitude of these short-term fluctuations will depend on the prevailing market sentiment and overall economic conditions. For example, a period of general market uncertainty might dampen the price increase, while a bullish market could amplify it. Historically, the price volatility has been significant in the months surrounding halving events.
Long-Term Price Effects
The long-term price trajectory after the 2025 halving is less predictable. While reduced supply generally supports higher prices, macroeconomic factors like inflation, interest rates, and global economic growth play crucial roles. Regulatory changes in major jurisdictions also exert significant influence. Increased regulatory clarity could boost investor confidence, driving prices higher, while stricter regulations might lead to price suppression. Furthermore, the adoption rate of Bitcoin by institutions and individual investors will significantly impact long-term price trends. A surge in adoption could lead to sustained price growth, while a slowdown in adoption might limit the impact of the halving.
Expert Opinions on Price Volatility
Expert opinions on the post-halving price volatility vary significantly. Some analysts predict a substantial price increase, citing the historical precedent of previous halvings and the anticipated scarcity effect. Others express caution, emphasizing the uncertainty surrounding macroeconomic factors and regulatory developments. For example, some analysts compare the situation to the 2016 halving, where the price saw a significant increase in the following year, while others point to the fact that market conditions are considerably different in 2025 than they were in 2016. The divergence in opinions highlights the complexity of accurately forecasting Bitcoin’s price.
Potential Price Scenarios
Several potential price scenarios can be envisioned, ranging from optimistic to pessimistic. An optimistic scenario could see Bitcoin’s price exceeding $100,000 within a year or two after the halving, driven by strong adoption and positive macroeconomic conditions. A more conservative scenario might project a more moderate price increase, perhaps reaching $50,000-$75,000. A pessimistic scenario, considering significant regulatory headwinds or a global economic downturn, could see the price remaining relatively flat or even experiencing a decline after the halving.
Illustrative Price Trajectories
Imagine three lines on a graph representing price over time. The first, optimistic trajectory, shows a steep upward curve immediately following the halving, reaching significantly higher prices within a year or two. The second, moderate trajectory, shows a more gradual incline, reaching a higher price but at a slower pace. The third, pessimistic trajectory, shows either a flat line or a slight downward trend after the halving, before potentially resuming an upward trajectory at a later date. These represent simplified visualizations of the potential price movements.
Mining and the 2025 Halving
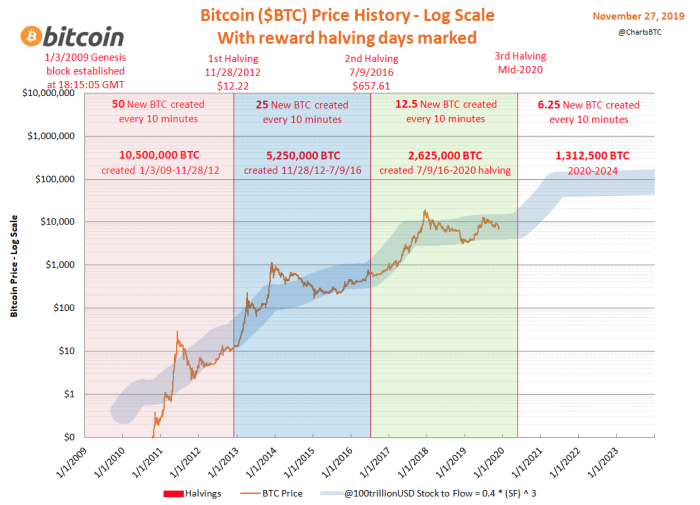
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, reducing the block reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC, will significantly impact Bitcoin mining. This reduction in newly minted coins directly affects miners’ profitability, forcing them to adapt or potentially exit the market. Understanding these impacts is crucial for assessing the future health and security of the Bitcoin network.
The halving’s primary effect is a decrease in miners’ revenue. With fewer coins awarded per block, miners must rely more heavily on transaction fees to maintain profitability. This necessitates a reevaluation of operational costs, including electricity, hardware maintenance, and personnel. The response from miners will vary; some may increase efficiency, upgrade equipment, or seek cheaper energy sources. Others, especially those operating at higher costs, might be forced to shut down operations, leading to a reshaping of the mining landscape.
Miner Profitability and Responses, Halving Bitcoin 2025 Fecha
The halving creates a challenging environment for miners. Profitability hinges on the interplay between the Bitcoin price, mining difficulty, and energy costs. A rising Bitcoin price can offset the reduced block reward, while a stagnant or falling price will exacerbate the pressure. Miners will respond in several ways: some will consolidate, merging operations to achieve economies of scale; others will adopt more energy-efficient hardware, such as ASICs with improved hash rates and power consumption ratios; some may relocate to regions with lower electricity costs, potentially leading to geographical shifts in mining activity. The 2012 and 2016 halvings witnessed similar scenarios, with many less efficient miners exiting the market and the remaining miners adopting more sophisticated and efficient technologies. For example, after the 2016 halving, we saw a significant increase in the adoption of more energy-efficient ASICs and a shift towards large-scale mining operations.
Impact on Hash Rate and Network Security
The hash rate, representing the total computational power securing the Bitcoin network, is directly influenced by miner profitability. A decrease in profitability could lead to a temporary decline in the hash rate as less-efficient miners shut down. However, the network’s security is intrinsically linked to the hash rate. A sustained drop could theoretically make the network more vulnerable to attacks, although the Bitcoin network has historically proven resilient to such events. The overall effect on the hash rate after previous halvings has been mixed. While there might be a temporary dip, the long-term trend has generally been upward, driven by technological advancements and increased participation from larger mining pools.
Comparison of Mining Landscapes Before and After Previous Halvings
Before the previous halvings, the mining landscape was often more fragmented, with a greater number of smaller, independent miners. After the halvings, we have seen a trend towards consolidation, with larger, more sophisticated mining operations dominating the market. This is largely due to economies of scale, access to cheaper energy, and advanced technological capabilities. This consolidation, while potentially leading to centralization concerns, also generally results in a more efficient and resilient network. The 2012 halving, for example, saw a significant shift towards larger mining pools and the emergence of specialized mining hardware. Similarly, the 2016 halving further solidified this trend.
Energy Consumption Implications
The halving’s impact on energy consumption is complex. While a decrease in the number of miners could reduce overall energy usage, the remaining miners may invest in more powerful, albeit potentially less energy-efficient, hardware to maintain profitability. Furthermore, the increased adoption of renewable energy sources by some mining operations could partially offset the impact. The overall effect on energy consumption is difficult to predict precisely and depends on various factors, including the price of Bitcoin, the technological advancements in mining hardware, and the adoption of sustainable energy practices. Previous halvings have shown that while initial energy consumption may fluctuate, the long-term trend is often upward, reflecting growth in the overall network’s hash rate. However, the increasing use of renewable energy sources in certain mining regions could mitigate some of this increase.
The long-term impact of the halving on energy consumption will depend on the balance between the reduction in the number of miners and the increase in the efficiency of remaining operations.