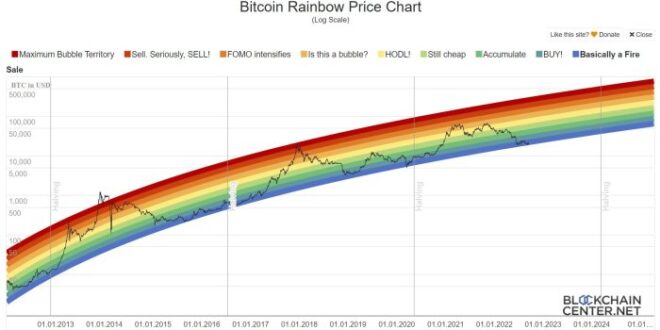
Bitcoin Price Prediction 2025
Bitcoin, launched in 2009, has experienced a tumultuous journey, marked by periods of explosive growth and dramatic crashes. Its decentralized nature and limited supply have fueled its appeal as a potential store of value and hedge against inflation, but its price remains incredibly volatile, subject to significant swings driven by various factors. Understanding these factors is crucial when attempting any price prediction, even for a relatively near-term forecast like 2025.
Bitcoin’s price is influenced by a complex interplay of market sentiment, regulatory actions, technological developments, and broader macroeconomic conditions. Investor confidence, fueled by news, social media trends, and adoption by major institutions, directly impacts trading volume and price. Regulatory clarity or uncertainty in different jurisdictions significantly affects accessibility and investor appetite. Technological upgrades to the Bitcoin network, such as the Lightning Network, can improve scalability and transaction speed, potentially increasing adoption and price. Finally, global economic factors like inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical events all play a significant role, often impacting investor risk tolerance and the appeal of alternative assets like Bitcoin.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price
The inherent volatility of Bitcoin makes accurate price prediction extremely challenging. Numerous unpredictable events can dramatically shift market sentiment and price. For instance, a sudden surge in institutional investment could lead to a rapid price increase, while a major security breach or regulatory crackdown could trigger a sharp decline. Furthermore, the relatively young age of Bitcoin and the lack of a long historical price record limit the reliability of traditional forecasting models. Predictive models often rely on historical data, and Bitcoin’s short history provides a limited dataset. Additionally, the influence of unpredictable news cycles and social media trends makes quantitative analysis particularly difficult. While technical analysis and on-chain metrics can provide insights, they are not foolproof predictors of future price movements. Past performance is not indicative of future results, and this is particularly true for an asset as volatile as Bitcoin. Consider the 2017 bull run, followed by a significant correction; this highlights the unpredictable nature of the market and the difficulty in making accurate long-term forecasts.
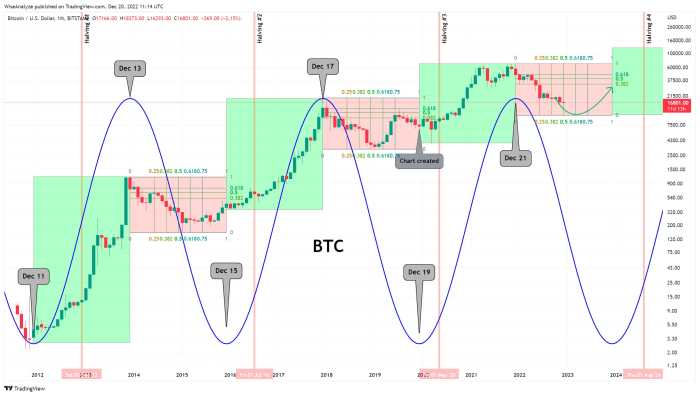
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Future Price: Bitcoin Price 2025 Prediction
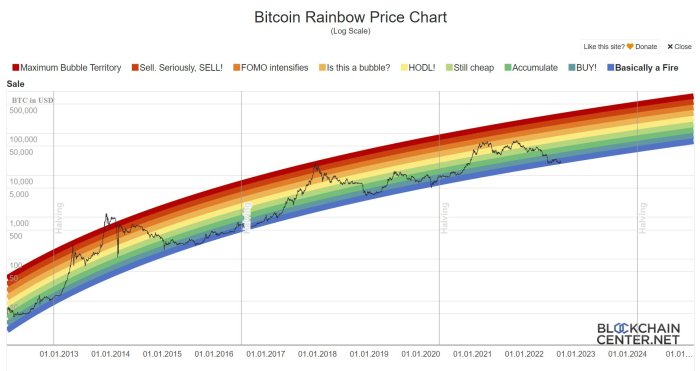
Predicting Bitcoin’s price in 2025, or any year for that matter, is inherently complex. Numerous interconnected factors influence its value, making any forecast inherently uncertain. However, by examining these key drivers, we can gain a better understanding of the potential price trajectories.
Technological Advancements and Adoption
Technological advancements play a crucial role in Bitcoin’s scalability, security, and overall usability, directly impacting its adoption rate and, consequently, its price. The Lightning Network, for example, aims to drastically improve transaction speeds and reduce fees, making Bitcoin more suitable for everyday transactions. Taproot, a significant upgrade to Bitcoin’s scripting language, enhances privacy and smart contract capabilities, potentially attracting further developers and users. Increased efficiency and functionality lead to wider adoption, boosting demand and, in turn, price. The successful implementation and widespread adoption of such upgrades are likely to positively impact Bitcoin’s price. For example, the successful launch of the Lightning Network has already seen a rise in the number of users and transactions, suggesting a positive correlation between technological improvements and price appreciation.
Institutional Investment and Price Stability
The entry of institutional investors, such as large corporations and investment funds, has significantly influenced Bitcoin’s price stability and volatility. Initially, Bitcoin’s price was highly volatile due to its relatively small market capitalization and primarily retail-driven trading. However, the growing involvement of institutional investors, seeking diversification and exposure to a potentially high-growth asset, has contributed to increased liquidity and potentially more stable price movements. Large-scale institutional buying can drive up prices, while their selling can lead to corrections. The long-term impact, however, is likely to be a gradual reduction in volatility as institutional investors tend to take a longer-term perspective than individual traders. For instance, the investment strategies of firms like MicroStrategy, which have made substantial Bitcoin purchases, have influenced market sentiment and potentially stabilized the price during periods of uncertainty.
Government Regulations and Legal Frameworks
Government regulations and legal frameworks significantly shape the perception and accessibility of Bitcoin. Clear and favorable regulations can boost investor confidence and encourage wider adoption. Conversely, restrictive or unclear regulations can hinder growth and potentially suppress prices. The regulatory landscape varies considerably across countries, with some embracing Bitcoin as a legitimate asset class while others maintain a cautious or even hostile stance. The ongoing evolution of regulatory frameworks globally will continue to play a major role in determining Bitcoin’s future price trajectory. For example, the increasing acceptance of Bitcoin as a payment method in El Salvador has positively impacted its price, while concerns over stringent regulations in China have led to price corrections.
Bitcoin’s Price Trajectory Compared to Other Assets
Comparing Bitcoin’s price trajectory to other cryptocurrencies and traditional assets provides valuable context. While Bitcoin remains the dominant cryptocurrency by market capitalization, its price movements are not always perfectly correlated with altcoins. Similarly, its price can be influenced by macroeconomic factors affecting traditional assets like gold, stocks, and bonds, but the correlation is not always consistent. The unique characteristics of Bitcoin, such as its limited supply and decentralized nature, differentiate it from traditional assets, leading to independent price dynamics. For example, while traditional markets might experience downturns due to economic recession, Bitcoin’s price might fluctuate independently based on factors such as adoption rates and technological developments.
Macroeconomic Factors and Bitcoin’s Price
Macroeconomic factors, such as inflation and economic growth, significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. During periods of high inflation, Bitcoin is often viewed as a hedge against inflation due to its limited supply. Conversely, during periods of economic uncertainty or recession, investors may move towards safer assets, potentially impacting Bitcoin’s price negatively. Economic growth, on the other hand, can boost investor confidence and increase risk appetite, potentially leading to higher demand for Bitcoin. The interplay of these macroeconomic factors makes predicting Bitcoin’s price even more challenging. For example, during periods of high inflation, as seen in some countries recently, the demand for Bitcoin as a store of value has increased, leading to price appreciation.
Different Prediction Models and Methodologies
Predicting the price of Bitcoin in 2025, or any future date, is inherently complex and uncertain. No model can guarantee accuracy, but various methodologies attempt to forecast future price movements based on different assumptions and data sets. These models offer diverse perspectives, each with strengths and limitations that must be carefully considered. Understanding these methodologies is crucial for interpreting any Bitcoin price prediction.
Predicting Bitcoin’s price relies on a combination of approaches, each offering unique insights. Technical analysis focuses on historical price and volume data to identify patterns and trends, while fundamental analysis assesses factors impacting Bitcoin’s underlying value. Quantitative modeling employs statistical and mathematical techniques to build predictive models based on historical data and various influencing factors.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis utilizes historical price and volume data to identify trends and patterns, projecting these into the future. Common tools include moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and candlestick charts. Analysts look for support and resistance levels, charting patterns like head and shoulders or double tops/bottoms, to anticipate price reversals or continuations. While visually intuitive, its reliance on past performance doesn’t account for unforeseen events like regulatory changes or technological breakthroughs. For example, predicting a price surge based solely on a bullish trend line might fail if a major exchange is hacked, impacting market sentiment.
Fundamental Analysis, Bitcoin Price 2025 Prediction
Fundamental analysis evaluates factors impacting Bitcoin’s intrinsic value. This includes considering factors such as adoption rates, network effects, mining difficulty, regulatory developments, macroeconomic conditions, and overall market sentiment. Unlike technical analysis, fundamental analysis seeks to understand the underlying forces driving price movements. A strong increase in institutional adoption, for example, could be considered a bullish fundamental factor, potentially leading to price appreciation. However, predicting the impact of these factors and their interplay is challenging and often subjective.
Quantitative Modeling
Quantitative modeling employs statistical and mathematical techniques to forecast Bitcoin’s price. These models use historical price data and potentially other relevant factors to create predictive algorithms. Examples include Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) models and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. These models can capture complex relationships and patterns in data, but their accuracy relies heavily on the quality and relevance of the input data and the model’s assumptions. Overfitting, where a model performs well on historical data but poorly on new data, is a significant risk.
Comparison of Prediction Models
| Model | Assumptions | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARIMA | Stationarity of the time series, linear relationships between data points. | Relatively simple to implement, widely understood. | Assumes linear relationships, may not capture complex non-linear patterns in Bitcoin’s price. Sensitive to outliers. |
| LSTM | Non-linear relationships exist in the data, sufficient historical data is available. | Can capture complex non-linear patterns, handles sequential data well. | Requires significant computational resources, prone to overfitting if not carefully trained. Difficult to interpret model parameters. |
| Prophet (Facebook) | Data contains seasonality and trend, potential for holiday effects. | Handles seasonality and trend well, robust to outliers and missing data. | Assumes additive seasonality, may not accurately capture all non-linear patterns. Requires sufficient historical data. |
Examples of Past Predictions and Their Accuracy
Many predictions for Bitcoin’s price have been made, with varying degrees of success. For instance, some analysts predicted a price of $100,000 by the end of 2021, a target that was not reached. Others accurately predicted significant price increases in previous years, but these successes often don’t translate to accurate long-term forecasts. The inherent volatility of the cryptocurrency market and the influence of unpredictable external factors severely limit the accuracy of any long-term price prediction. The limitations stem from the inability to perfectly foresee events such as regulatory changes, technological advancements, or shifts in market sentiment, which can significantly impact Bitcoin’s price.