Bitcoin’s Price History and Market Trends: Prediction For Bitcoin 2025
Bitcoin’s journey since its inception in 2009 has been marked by extreme volatility, punctuated by periods of explosive growth and sharp corrections. Understanding this price history and the underlying market forces is crucial for any attempt to predict its future trajectory. This analysis will examine Bitcoin’s price fluctuations, key influencing events, and comparative performance against other assets.
Bitcoin’s Price Volatility Timeline
Bitcoin’s early years saw relatively low prices and trading volumes. Its value remained largely insignificant until the late 2010s, when it began attracting wider attention. The following table provides a simplified overview of key milestones in Bitcoin’s price history, highlighting significant highs and lows. Note that these are approximate figures and the actual daily price fluctuated significantly.
| Year | Significant Event | Approximate Price (USD) | Market Commentary |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | Bitcoin’s Genesis Block | ~$0 | Initial release; minimal trading activity. |
| 2010 | First Real-World Transaction | ~$0.003 | Early adoption; low volume. |
| 2011 | First Major Price Surge | ~$30 | Increased media attention and early investor interest. |
| 2013 | Significant Price Increase and First Major Correction | ~$1,000 (high) / ~$200 (low) | Growing institutional interest and market speculation. |
| 2017 | Historic Bull Run | ~$20,000 (high) | Mainstream media coverage; significant retail investor influx. |
| 2018-2019 | Significant Bear Market | ~$3,000 (low) | Regulatory uncertainty and market correction. |
| 2020-2021 | Another Bull Run | ~$65,000 (high) | Increased institutional adoption and DeFi growth. |
| 2022-Present | Market Consolidation and Volatility | Variable | Macroeconomic factors and regulatory scrutiny impact price. |
Major Market Events Influencing Bitcoin’s Price
Several significant events have profoundly impacted Bitcoin’s price. These include:
- Halving Events: The halving, which reduces the rate of new Bitcoin creation approximately every four years, has historically been followed by periods of price appreciation, although the impact varies. The reduced supply often creates upward pressure on demand.
- Regulatory Changes: Government regulations and pronouncements concerning cryptocurrencies have significantly influenced Bitcoin’s price. Positive regulatory developments often lead to price increases, while negative news can trigger sharp drops.
- Technological Advancements: Improvements in blockchain technology, such as the Lightning Network (for faster transactions), can boost investor confidence and lead to price appreciation. Conversely, major security breaches or technical failures can negatively impact the price.
- Macroeconomic Factors: Global economic events, such as inflation, recession fears, and geopolitical instability, can significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. Bitcoin is often seen as a hedge against inflation or a safe haven during times of uncertainty.
Bitcoin’s Performance Compared to Other Assets
Bitcoin’s performance has been compared to both other cryptocurrencies and traditional assets like gold and the US dollar. While Bitcoin has exhibited higher volatility than gold, it has also shown periods of outperformance. Compared to other cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin’s market dominance has fluctuated, with altcoins occasionally experiencing periods of rapid growth. The correlation between Bitcoin’s price and traditional assets is complex and not always consistent. Its performance is influenced by a unique set of factors, including its limited supply, technological characteristics, and perceived status as a digital gold.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Future Price
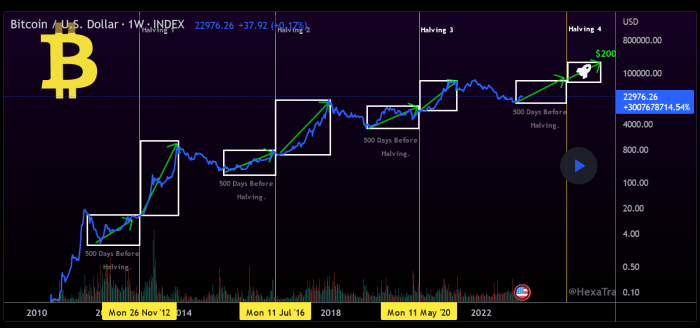
Predicting Bitcoin’s price in 2025 requires considering a complex interplay of macroeconomic conditions, technological advancements, regulatory landscapes, and adoption rates. While no one can definitively say what the price will be, analyzing these factors provides a framework for informed speculation.
Macroeconomic Factors
Macroeconomic factors significantly influence Bitcoin’s price, often acting as a counter-cyclical asset. High inflation, for example, can drive investors towards Bitcoin as a hedge against currency devaluation. Conversely, rising interest rates, which increase the attractiveness of traditional, yield-bearing assets, could decrease Bitcoin’s appeal. A positive global economic outlook might lead investors to allocate more capital to riskier assets, potentially boosting Bitcoin’s price, while a recessionary environment could trigger a sell-off. The overall global economic health, therefore, acts as a significant backdrop against which Bitcoin’s value fluctuates. For example, the 2022 bear market coincided with rising inflation and interest rate hikes by central banks globally.
Technological Advancements
Technological progress within the Bitcoin ecosystem is crucial for its long-term viability and price appreciation. Layer-2 scaling solutions, such as the Lightning Network, aim to improve transaction speed and reduce fees, thereby enhancing Bitcoin’s usability for everyday transactions. Improvements in security protocols, including enhanced wallet security and the ongoing development of robust consensus mechanisms, also contribute to increased investor confidence and potential price growth. The successful implementation and widespread adoption of these technologies could significantly impact Bitcoin’s scalability and attractiveness, driving up demand. Conversely, significant security breaches or unforeseen technical limitations could negatively affect its price.
Regulatory Developments
Government regulations play a pivotal role in shaping Bitcoin’s trajectory. Increased regulatory clarity and acceptance, such as the establishment of clear legal frameworks for cryptocurrency trading and taxation, could legitimize Bitcoin and attract institutional investment, leading to price appreciation. Conversely, stricter regulations, including outright bans or excessively burdensome compliance requirements, could stifle innovation and limit adoption, potentially depressing the price. The contrasting regulatory approaches of countries like El Salvador (which adopted Bitcoin as legal tender) and China (which banned cryptocurrency trading) highlight the significant impact of government policies on Bitcoin’s price.
Adoption Rates
The rate of Bitcoin adoption by both institutional and retail investors is a key determinant of its future price. Increased institutional investment, particularly from large corporations and hedge funds, signifies a growing acceptance of Bitcoin as an asset class and can drive up demand. Similarly, wider retail adoption, fueled by increased accessibility and user-friendliness, contributes to a broader base of holders, potentially leading to price appreciation. Conversely, a slowdown in adoption rates or a significant loss of investor confidence could negatively impact Bitcoin’s price. The growing number of publicly traded companies holding Bitcoin on their balance sheets illustrates the increasing institutional interest.
| Factor | Positive Influence on Price (2025) | Negative Influence on Price (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Macroeconomic Factors | High inflation, positive global economic outlook | Rising interest rates, global recession |
| Technological Advancements | Successful implementation of Layer-2 solutions, enhanced security | Significant security breaches, technological limitations |
| Regulatory Developments | Increased regulatory clarity and acceptance, government adoption | Stricter regulations, outright bans |
| Adoption Rates | Increased institutional and retail adoption | Slowdown in adoption rates, loss of investor confidence |
Bitcoin Adoption and Use Cases

Bitcoin’s increasing adoption extends beyond its initial role as a speculative asset, encompassing institutional investment, corporate integration, and diverse applications in various sectors. This broadening of use cases significantly influences Bitcoin’s long-term value proposition and future price trajectory.
The growing acceptance of Bitcoin as a legitimate asset class is evident in the increasing number of institutional investors, including large corporations and hedge funds, allocating a portion of their portfolios to Bitcoin. This institutional adoption provides a level of legitimacy and stability not seen in the early days of the cryptocurrency market, bolstering its price and reducing volatility. Furthermore, the development of regulated Bitcoin-related financial products, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs), further enhances institutional participation and accessibility.
Institutional Adoption of Bitcoin
Several notable examples showcase the growing institutional interest in Bitcoin. MicroStrategy, a publicly traded business intelligence company, has made significant investments in Bitcoin, holding it as a long-term treasury reserve asset. Similarly, Tesla, under the leadership of Elon Musk, briefly accepted Bitcoin as payment for its vehicles, demonstrating a willingness to integrate cryptocurrency into mainstream business operations. These high-profile adoptions signal a shift in perception, suggesting that Bitcoin is no longer viewed solely as a speculative asset but as a potential store of value and a hedge against inflation. The growing number of publicly traded companies holding Bitcoin on their balance sheets reinforces this trend.
Bitcoin Use Cases Beyond Speculation
Bitcoin’s utility extends far beyond mere speculation. Its inherent properties, such as decentralization and immutability, support a variety of applications:
- Payments: While transaction fees and processing speeds can be limitations, Bitcoin’s borderless nature and pseudonymous transactions offer a compelling alternative to traditional payment systems, particularly in cross-border transactions. Companies like Strike are actively developing solutions to address scalability issues and make Bitcoin payments more user-friendly.
- Store of Value: Bitcoin’s limited supply of 21 million coins, combined with its decentralized nature and resistance to censorship, positions it as a potential store of value, comparable to gold or other precious metals. Its scarcity and decentralized nature make it attractive to individuals and institutions seeking to protect their wealth from inflation and potential government overreach.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Bitcoin is increasingly integrated into DeFi protocols, enabling users to leverage its value for lending, borrowing, and other financial applications. This integration expands Bitcoin’s utility and provides new avenues for generating returns.
Comparison with Other Digital Assets
Bitcoin’s adoption rate, while significant, is not uniform across all digital assets. While it maintains its position as the most widely adopted cryptocurrency, altcoins have carved out niches based on specific features and functionalities. For example, Ethereum’s smart contract capabilities have led to its adoption in the DeFi space, while other cryptocurrencies focus on scalability and privacy. However, Bitcoin’s established network effect, brand recognition, and first-mover advantage continue to provide a substantial advantage in terms of market capitalization and overall adoption.
Emerging Trends in Bitcoin Usage and Applications
The landscape of Bitcoin usage is constantly evolving. The Lightning Network, a second-layer scaling solution, aims to improve transaction speeds and reduce fees, making Bitcoin more practical for everyday payments. Furthermore, the growing integration of Bitcoin into custodial solutions and institutional investment vehicles is further driving adoption. The increasing use of Bitcoin as collateral for loans and other financial instruments also represents a significant trend.
Bitcoin Use Cases and Their Potential Impact
| Use Case | Potential Impact on Bitcoin’s Future Value |
|---|---|
| Payments | Increased demand and transaction volume could drive up price. Widespread adoption could lead to significant price appreciation. |
| Store of Value | Growing institutional adoption and demand as a hedge against inflation could lead to long-term price appreciation. |
| Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Integration into DeFi protocols could unlock new sources of demand and increase utility, potentially boosting price. |
| Corporate Treasury Reserves | Large-scale corporate adoption as a treasury asset could significantly increase demand and drive up the price. |
Technological Advancements and Bitcoin’s Scalability
Bitcoin’s inherent design, prioritizing security and decentralization, has resulted in limitations regarding transaction speed and scalability. This has led to higher transaction fees during periods of high network activity and longer confirmation times, impacting the user experience and hindering widespread adoption. Addressing these challenges is crucial for Bitcoin’s continued growth and relevance as a global payment system.
Bitcoin’s Scalability Limitations
Bitcoin’s current architecture processes a limited number of transactions per second (TPS), significantly lower than many other payment systems. This constraint arises from its block size limit and the time required for block creation and propagation across the network. High transaction volume leads to congestion, resulting in increased fees and slower confirmation times. For example, during periods of intense market activity, users have experienced transaction fees exceeding several dollars, making Bitcoin impractical for small, frequent transactions. The average transaction confirmation time can also fluctuate, sometimes exceeding an hour during peak network congestion.
Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
Layer-2 scaling solutions offer a pathway to improve Bitcoin’s scalability without compromising its underlying security model. These solutions process transactions off-chain, reducing the load on the main Bitcoin blockchain. This allows for faster transaction processing and lower fees. Several prominent layer-2 solutions are currently being developed and implemented, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Impact of Technological Improvements on Transaction Fees and Usability
Successful implementation of layer-2 scaling solutions and other technological advancements promises to significantly reduce Bitcoin’s transaction fees and improve its usability. By offloading transaction processing to secondary networks, the main blockchain’s capacity is freed up, resulting in lower congestion and, consequently, lower fees. This makes Bitcoin more accessible for everyday transactions, potentially boosting its adoption among individuals and businesses. The improved speed and reduced cost would make Bitcoin a more viable alternative to traditional payment systems. For instance, if transaction fees consistently remain below $1, Bitcoin’s utility as a micropayment system would be greatly enhanced.
Comparison of Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
Several layer-2 scaling solutions are vying for dominance, each employing different approaches. The Lightning Network, for instance, utilizes micropayment channels to facilitate fast and inexpensive transactions off-chain. Other solutions, such as the Liquid Network, focus on providing faster settlement times and enhanced privacy features. Each solution offers unique advantages and disadvantages regarding transaction throughput, security, complexity, and user experience. A comprehensive comparison requires careful consideration of these factors to determine the most effective and widely adopted solution. The ongoing development and competition among these solutions will ultimately determine which ones best meet the needs of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Upcoming Technological Advancements Affecting Bitcoin’s Scalability, Prediction For Bitcoin 2025
Ongoing research and development focus on improving Bitcoin’s scalability through various avenues. These include exploring alternative consensus mechanisms, enhancing block propagation techniques, and developing more sophisticated layer-2 solutions. Further improvements in the efficiency of the underlying cryptography and network protocols could also contribute to increased transaction throughput and reduced latency. The potential for significant improvements in Bitcoin’s scalability remains high, driven by continuous innovation within the community. The successful integration of these advancements could transform Bitcoin into a far more efficient and widely usable payment system.