Bitcoin Halving 2025
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol, is anticipated to occur in early 2025. This event significantly impacts the rate at which new Bitcoins are introduced into circulation, historically influencing its price and market dynamics. Understanding the mechanics and historical context of this event is crucial for navigating the cryptocurrency market.
Bitcoin Halving Mechanics and Historical Price Impact
The Bitcoin halving reduces the block reward – the amount of Bitcoin miners receive for verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain – by half. This occurs approximately every four years, or every 210,000 blocks mined. Historically, halvings have been followed by periods of increased Bitcoin price, although this is not guaranteed and other market factors significantly influence price movements. The reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin, combined with consistent demand, theoretically pushes the price upwards. However, the actual impact is complex and depends on various macroeconomic conditions, regulatory changes, and overall market sentiment. The price surge after a halving isn’t instantaneous; it often takes months or even years to fully manifest.
Projected Bitcoin Supply After the 2025 Halving
After the 2025 halving, the block reward will decrease from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC. The total supply of Bitcoin is capped at 21 million coins. The halving event doesn’t change this cap; it merely slows down the rate at which new coins enter circulation. This controlled supply is a core tenet of Bitcoin’s deflationary model, contributing to its perceived value as a store of value. The exact circulating supply at the time of the halving will depend on the precise date and mining activity, but it will be significantly closer to the 21 million cap than it was before.
Comparison of Market Conditions Leading Up to Previous Halvings
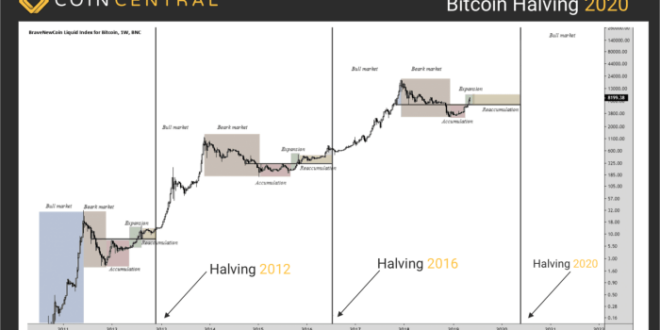
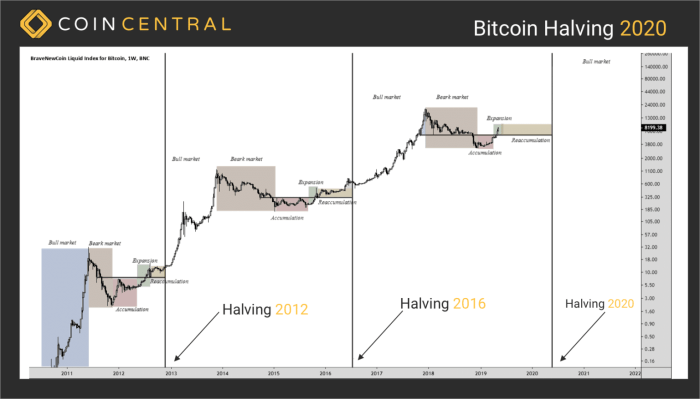
The market conditions leading up to each Bitcoin halving have varied significantly. The first halving in 2012 occurred during the early days of Bitcoin, with a relatively small market capitalization and limited mainstream awareness. The second halving in 2016 took place amidst growing institutional interest and increasing adoption. The third halving in 2020 coincided with a global pandemic and a surge in institutional investment, leading to significant price volatility. The upcoming 2025 halving occurs in a market characterized by increased regulatory scrutiny, macroeconomic uncertainty, and a broader adoption of blockchain technology beyond just Bitcoin. While previous halvings have shown a correlation with price increases, extrapolating this to 2025 requires caution given the different contexts.
Timeline of Significant Events Surrounding Past Halvings
A detailed timeline illustrating significant events around each halving would provide a valuable context. For example, the period leading up to the 2020 halving saw a considerable rise in institutional interest and investment, while the period after saw increased price volatility and market consolidation. Analyzing these timelines for each halving can reveal patterns and potentially informative trends, although they don’t predict future events.
Key Metrics Before and After Previous Halvings
| Halving Date | Block Reward (Before) | Circulating Supply (Before) | Price (Before – Approximate USD) | Price (After – Approximate USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| November 2012 | 50 BTC | 10.5 Million BTC (approx.) | $13 | $1000+ (over time) |
| July 2016 | 25 BTC | 15.5 Million BTC (approx.) | $650 | $20,000+ (over time) |
| May 2020 | 12.5 BTC | 18 Million BTC (approx.) | $9,000 | $60,000+ (over time) |
Predicting Bitcoin’s Price Post-Halving 2025
Predicting Bitcoin’s price after the 2025 halving is a complex undertaking, fraught with uncertainty. Numerous factors, often intertwined and difficult to isolate, influence its value. While no one can definitively say what the price will be, analyzing these factors allows for informed speculation and the development of various price prediction models.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price
Several key factors significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. Adoption rates, encompassing both individual investors and institutional players, are crucial. Widespread institutional adoption could drive significant price increases, while a decline in new users could exert downward pressure. Regulatory landscapes vary globally, with stricter regulations potentially dampening enthusiasm and looser ones fostering growth. Macroeconomic conditions, including inflation rates, interest rates, and overall economic stability, also play a significant role. A period of high inflation might push investors towards Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation, increasing demand and price. Conversely, a strong dollar and low inflation could decrease demand.
Price Prediction Models and Their Limitations
Various models attempt to forecast Bitcoin’s price, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some models utilize historical price data and technical indicators, identifying trends and patterns to project future movements. Others incorporate on-chain metrics, such as transaction volume and the number of active addresses, to gauge network activity and assess potential price changes. Quantitative models, incorporating economic variables and statistical methods, attempt to quantify the influence of macroeconomic factors on Bitcoin’s price. However, all models have limitations. Bitcoin’s relatively short history limits the reliability of historical data-based predictions. Unforeseen events, such as major regulatory changes or technological breakthroughs, can significantly disrupt even the most sophisticated models. Furthermore, the inherent volatility of the cryptocurrency market makes precise predictions exceptionally challenging.
Insights from Prominent Cryptocurrency Analysts
Prominent cryptocurrency analysts offer diverse perspectives on Bitcoin’s post-halving price. While specific numerical predictions vary widely, a common theme is the significant influence of the halving event itself. Many analysts anticipate a period of price consolidation or even a slight dip immediately following the halving, as the reduced supply is initially absorbed by the market. However, a long-term bullish outlook is frequently expressed, with the expectation that scarcity will eventually drive prices upward. The level of adoption and the overall macroeconomic environment are frequently cited as key determinants of the magnitude of this price increase. It is important to note that these are opinions, and not financial advice.
Hypothetical Price Trajectory Post-Halving
Let’s consider two hypothetical scenarios. A bullish scenario might see a gradual price increase in the months leading up to the halving, followed by a period of consolidation immediately after. As the reduced supply begins to tighten, price could then experience a significant surge, potentially reaching new all-time highs within 12-18 months post-halving. Conversely, a bearish scenario could involve a prolonged period of sideways trading or even a price decline before the halving, followed by a relatively muted response to the reduced supply. This scenario might be influenced by negative macroeconomic conditions or increased regulatory scrutiny. These scenarios are illustrative, not predictive.
Comparison of Price Prediction Models
| Model Type | Methodology | Assumptions | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Analysis | Uses charts and indicators to identify trends | Past price patterns will repeat | Susceptible to manipulation, lacks fundamental analysis |
| On-Chain Analysis | Analyzes blockchain data to gauge network activity | Network activity correlates with price | Correlation doesn’t equal causation, difficult to predict future activity |
| Quantitative Models | Uses statistical methods and economic variables | Economic factors significantly influence price | Requires accurate data and assumptions, complex and difficult to validate |
| Analyst Forecasts | Expert opinions and market sentiment | Analysts have accurate insights into market dynamics | Subjective, prone to biases, lacks quantitative rigor |
The Impact of the 2025 Halving on Bitcoin Mining
The Bitcoin halving event of 2025, scheduled to occur in approximately April, will significantly impact the Bitcoin mining landscape. This reduction in the block reward, from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC, will alter the economics of mining and potentially reshape the industry’s structure. The consequences are multifaceted, impacting profitability, network security, and the strategies employed by miners.
Challenges Faced by Bitcoin Miners Due to Reduced Block Reward
The immediate challenge for miners post-halving is the diminished profitability per block mined. With half the reward, miners will need to generate significantly more revenue from transaction fees to maintain profitability. This necessitates either increased mining efficiency or a sustained rise in Bitcoin’s price. The reduced income could force less-efficient or higher-cost miners to shut down operations, potentially leading to consolidation within the industry. Miners will face a pressure to optimize energy consumption and hardware efficiency to stay competitive.
Potential Impact on Hashrate and Network Security
The reduced profitability will likely cause a decrease in the Bitcoin hashrate in the short term. Hashrate refers to the total computational power dedicated to securing the network. A lower hashrate can theoretically make the network more vulnerable to 51% attacks, although the extent of this vulnerability is debatable and depends on other factors such as the distribution of mining power. However, historically, the hashrate has generally recovered after previous halvings, driven by technological advancements and price increases. The long-term effect on network security remains uncertain but is a crucial aspect to consider.
Profitability of Bitcoin Mining Before and After the Halving
Comparing mining profitability before and after the halving requires a multifaceted analysis. Before the halving, miners enjoy a higher block reward, leading to potentially higher profits, even with higher electricity costs. After the halving, the reduced block reward will directly impact profitability. Profitability is largely determined by the interplay between the Bitcoin price, mining hardware efficiency (measured in hashes per joule), electricity costs, and mining difficulty. A higher Bitcoin price can offset the reduced block reward, maintaining profitability for efficient miners. However, less efficient miners might find it unsustainable to continue operations.
Strategies Miners Might Adopt to Adapt to the Changing Landscape
Miners will need to adopt various strategies to remain profitable in the post-halving environment. These could include: upgrading to more energy-efficient hardware, optimizing mining operations to reduce costs, diversifying revenue streams by engaging in activities like providing staking services or participating in other blockchain networks, and strategically relocating to regions with lower electricity costs. Consolidation through mergers and acquisitions among mining firms is also a plausible outcome. Further, increased focus on renewable energy sources might become a key differentiator and a strategic advantage for miners.
Influence of Electricity Costs on Mining Profitability After the Halving
Electricity costs play a crucial role in mining profitability. Higher electricity prices directly reduce the margin for profit. The following table illustrates a simplified scenario showing how changes in electricity cost influence profitability after the halving, assuming a constant Bitcoin price and mining hardware efficiency. These are hypothetical examples and actual results will vary significantly.
| Electricity Cost ($/kWh) | Profit per Block (USD) – Before Halving (6.25 BTC Reward) | Profit per Block (USD) – After Halving (3.125 BTC Reward) | Profitability Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | $25,000 (Example) | $12,500 (Example) | -50% |
| 0.15 | $20,000 (Example) | $10,000 (Example) | -50% |
| 0.20 | $15,000 (Example) | $7,500 (Example) | -50% |
Long-Term Implications of the 2025 Halving
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, reducing the block reward for miners by half, is a significant event with potentially profound long-term implications for Bitcoin’s trajectory and the broader cryptocurrency landscape. While short-term price volatility is expected, the enduring effects on scarcity, value proposition, and market dynamics are what truly shape Bitcoin’s future.
The halving’s most immediate impact is on Bitcoin’s scarcity. By reducing the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation, the halving intensifies the already limited supply. This inherent scarcity is a cornerstone of Bitcoin’s value proposition, often compared to precious metals like gold, which derive value partly from their limited supply. This increased scarcity could potentially drive up demand, leading to price appreciation over the long term.
Bitcoin’s Role as a Store of Value and Medium of Exchange
The halving’s impact on Bitcoin’s functionality as a store of value and medium of exchange is intertwined with its scarcity. Increased scarcity strengthens its appeal as a store of value, making it a more attractive hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty for investors seeking long-term asset preservation. However, its role as a medium of exchange remains dependent on factors like transaction fees, network scalability, and wider adoption. The halving itself doesn’t directly improve transaction speeds or reduce fees, so improvements in these areas are crucial for broader transactional use. For example, the Lightning Network aims to address these scalability issues and could contribute significantly to Bitcoin’s usability as a daily payment method.
Impact on the Broader Cryptocurrency Market
The 2025 halving is unlikely to be isolated in its effects. The ripple effects could be felt throughout the broader cryptocurrency market. A significant price increase in Bitcoin could lead to increased investor confidence in the cryptocurrency market as a whole, potentially driving up the prices of altcoins. Conversely, a lack of significant price movement after the halving might negatively impact sentiment across the entire market. The interconnectedness of cryptocurrencies suggests that the halving’s impact will extend beyond Bitcoin’s own price action.
Institutional Investor Adoption
The halving could influence institutional investment in Bitcoin. The increased scarcity and potential price appreciation could make Bitcoin a more attractive asset for large investors, pension funds, and endowments looking for long-term, inflation-hedging investments. However, regulatory clarity and infrastructure development remain critical factors. The successful integration of Bitcoin into existing financial systems is essential for broader institutional adoption. For example, the establishment of regulated Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) could significantly boost institutional investment.
Key Long-Term Implications of the Halving, What Date Is The Bitcoin Halving 2025
The long-term implications of the 2025 Bitcoin halving are complex and depend on several interacting factors. However, some key potential effects can be summarized as follows:
- Increased Bitcoin scarcity, potentially driving long-term price appreciation.
- Strengthened position of Bitcoin as a store of value, attracting long-term investors.
- Potential for increased volatility in the short term, followed by a period of relative price stability.
- Ripple effects across the broader cryptocurrency market, impacting investor sentiment and altcoin prices.
- Increased institutional investment, contingent on regulatory clarity and infrastructure development.
- Potential acceleration of Bitcoin adoption as a medium of exchange, driven by Layer-2 solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Bitcoin Halving 2025: What Date Is The Bitcoin Halving 2025
The Bitcoin halving is a significant event in the cryptocurrency’s lifecycle, impacting its supply and potentially its price. Understanding the mechanics and implications of the 2025 halving is crucial for anyone interested in Bitcoin. This section addresses some common questions surrounding this event.
Bitcoin Halving Explained
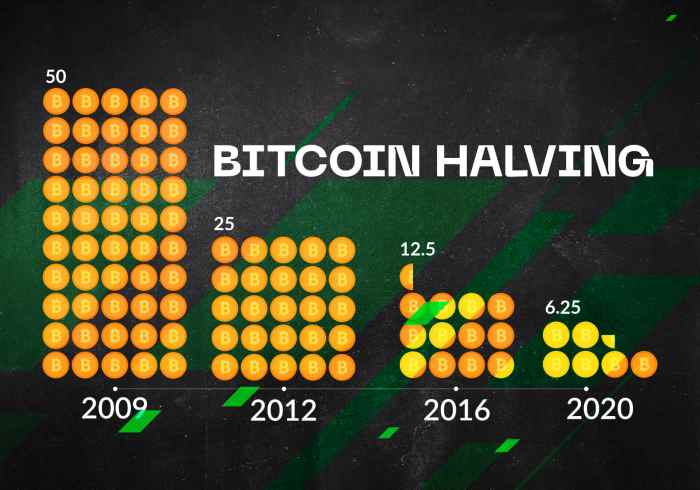
The Bitcoin halving is a programmed reduction in the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. Approximately every four years, the reward given to Bitcoin miners for verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain is cut in half. This mechanism is designed to control inflation and maintain the scarcity of Bitcoin. Initially, miners received 50 BTC per block. After the first halving, this dropped to 25 BTC, then to 12.5 BTC, and the next halving in 2025 will reduce it to 6.25 BTC.
Bitcoin Halving Date in 2025
While the halving is approximately every four years, the precise date depends on the time it takes to mine blocks. The target block time is 10 minutes, but this fluctuates due to mining difficulty adjustments. Currently, estimates place the 2025 halving around April 2025, but this date is subject to minor variations depending on the network’s hash rate and block creation times. Previous halvings have shown slight deviations from predicted dates.
The Halving’s Effect on Bitcoin Price
Historically, Bitcoin’s price has tended to increase in the period leading up to and following a halving. This is often attributed to the reduced supply of new Bitcoins entering the market, potentially increasing scarcity and driving demand. However, it’s crucial to remember that correlation doesn’t equal causation. Other market factors, such as regulatory changes, macroeconomic conditions, and overall investor sentiment, significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. The 2012 and 2016 halvings were followed by substantial price increases, though the timeframes varied. Predicting the precise price impact of the 2025 halving remains speculative.
Comparing the 2025 Halving to Previous Halvings
The 2025 halving shares similarities with previous events: a reduction in the block reward and a consequent decrease in the rate of Bitcoin inflation. However, key differences exist. The Bitcoin ecosystem is significantly larger and more mature now compared to 2012 or 2016. The level of institutional adoption, regulatory scrutiny, and overall market awareness are all substantially higher. These factors could influence the price reaction differently than in previous cycles. Furthermore, the macroeconomic environment in 2025 will undoubtedly differ from previous halving years, potentially affecting investor behavior and Bitcoin’s price trajectory.
Risks of Investing in Bitcoin Around the Halving
Investing in Bitcoin carries inherent risks, amplified around halving events due to increased volatility. The price could rise significantly, leading to substantial profits, but it could also fall sharply, resulting in significant losses. Market manipulation, regulatory uncertainty, and unforeseen technological developments are all potential risks. Furthermore, the hype surrounding halving events can create speculative bubbles, leading to sharp corrections afterward. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research, understand your risk tolerance, and only invest what you can afford to lose. Diversification within your investment portfolio is also a prudent strategy to mitigate risk.
Illustrative Example
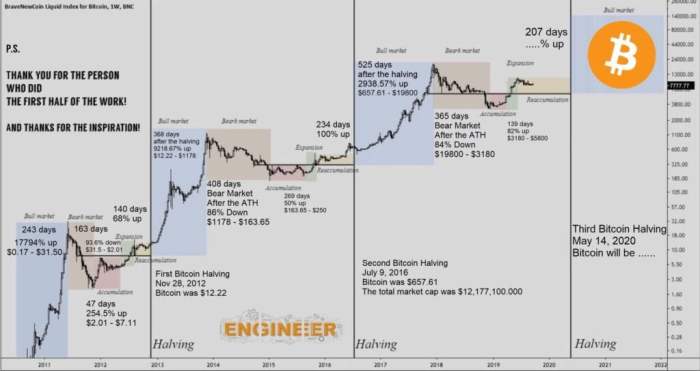
Predicting Bitcoin’s price trajectory after a halving is inherently speculative, as numerous factors influence its value. However, we can create a hypothetical model based on historical data and reasonable assumptions to illustrate a potential price path. This example should not be interpreted as a financial prediction but rather as an exploration of possible scenarios.
This illustrative example uses a simplified model to depict a potential Bitcoin price trajectory following the 2025 halving, scheduled for approximately April 2025. The model incorporates historical data from previous halvings, market sentiment indicators, and assumptions about overall macroeconomic conditions. It’s crucial to remember that this is a hypothetical scenario and actual price movements may differ significantly.
Bitcoin Price Trajectory Post-2025 Halving
The following description details a hypothetical chart depicting Bitcoin’s price movement after the 2025 halving. The x-axis represents time, measured in months, starting from the halving date (April 2025) and extending for 24 months. The y-axis represents the Bitcoin price in USD.
The chart would show an initial period of price consolidation or slight decline immediately following the halving. This is represented by a relatively flat line or a gentle downward slope for the first 3-6 months. This period reflects the market’s absorption of the halving event and the time it takes for the reduced supply to impact the market dynamics.
Following the initial consolidation, the chart would depict a gradual upward trend. This upward trajectory is based on the assumption that the reduced inflation rate caused by the halving, coupled with continued institutional and retail investor interest, would drive increased demand for Bitcoin. This upward trend would not be linear; rather, it would likely involve periods of volatility and price corrections, represented by short-term dips and rebounds. These corrections would be shown as smaller downward fluctuations along the overall upward trendline.
After approximately 12-18 months, the chart could show a period of more significant price appreciation. This acceleration is based on the assumption that the market begins to fully recognize the long-term scarcity of Bitcoin and the impact of the halving on its future value. This period could be represented by a steeper upward slope in the chart.
Finally, after 24 months, the chart would show a price that is significantly higher than the price at the time of the halving. The exact price point would depend on the specific assumptions made about market conditions and investor sentiment, but a significant increase would be a reasonable projection based on the historical impact of previous halvings.
Assumptions Used in the Model
The model incorporates several key assumptions:
* Historical Precedent: The model draws upon the price movements observed after the previous Bitcoin halvings, assuming a similar pattern, albeit potentially scaled differently given the evolving market maturity.
* Market Sentiment: The model assumes continued, albeit potentially fluctuating, positive investor sentiment towards Bitcoin. This assumes ongoing institutional adoption, increasing retail investor interest, and a general belief in Bitcoin’s long-term value proposition.
* Macroeconomic Conditions: The model assumes a relatively stable or mildly positive macroeconomic environment. A significant global recession or other major economic disruption could drastically alter the projected trajectory.
* Technological Advancements: The model assumes no major technological disruptions or breakthroughs that would significantly impact Bitcoin’s network or its adoption rate.
* Regulatory Environment: The model assumes a relatively stable and predictable regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies, with no major regulatory crackdowns that could negatively impact the market.
It’s important to reiterate that this is a simplified model and the actual price trajectory of Bitcoin post-2025 halving could deviate significantly from this hypothetical illustration. Numerous unforeseen events and market forces could influence the actual price movement.