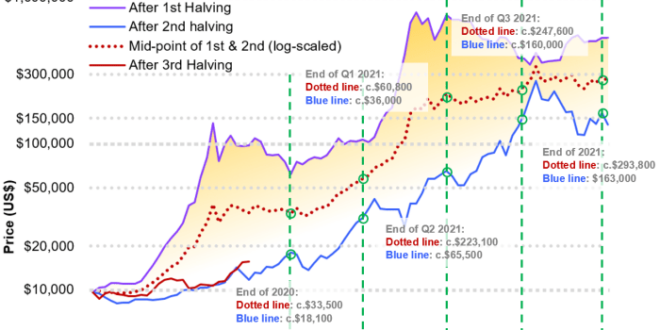
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price in 2030: What Will Bitcoin Price Be In 2030
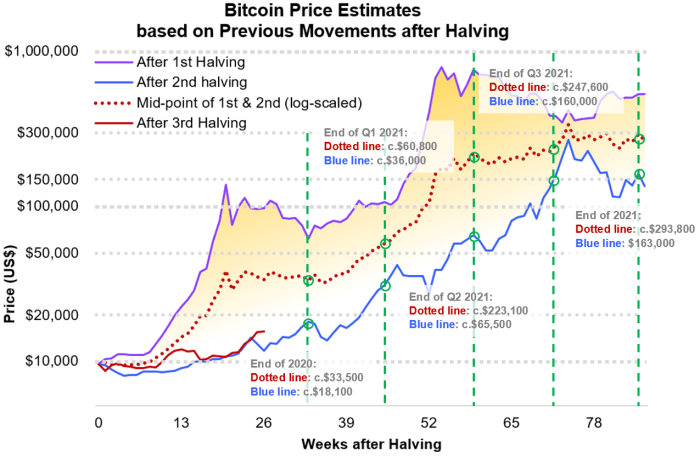
Predicting Bitcoin’s price in 2030 is inherently speculative, yet understanding the key factors influencing its trajectory is crucial. Several interconnected forces – technological advancements, regulatory landscapes, macroeconomic conditions, and institutional adoption – will play significant roles in shaping its value.
Widespread Institutional Adoption’s Impact on Bitcoin’s Price
Increased institutional investment, encompassing large corporations, hedge funds, and pension funds, is likely to significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. As these entities allocate substantial capital to Bitcoin, demand will surge, potentially driving up the price. This increased demand is driven by diversification strategies, a hedge against inflation, and the potential for long-term growth. For example, MicroStrategy’s significant Bitcoin holdings have already demonstrated the market impact of large-scale institutional investment. Further substantial institutional adoption could lead to a substantial price increase, potentially exceeding current market valuations by a considerable margin, depending on the scale and pace of adoption.
Government Regulations and Their Effects on Bitcoin’s Price
Government regulations represent a double-edged sword for Bitcoin. Favorable regulatory frameworks, providing clarity and legal certainty, could boost investor confidence and attract further investment, thereby increasing the price. Conversely, overly restrictive or unclear regulations could stifle innovation, limit adoption, and potentially depress the price. The regulatory landscape varies significantly across jurisdictions, with some countries embracing Bitcoin as a legitimate asset class while others maintain a cautious or even hostile stance. The evolution of these regulatory frameworks will significantly influence Bitcoin’s price trajectory in 2030. A clear, consistent global regulatory framework would likely be the most positive outcome for price stability and growth.
Technological Advancements Shaping Bitcoin’s Future Value
Technological advancements, particularly the scaling solutions like the Lightning Network, are vital for Bitcoin’s long-term viability and price appreciation. The Lightning Network, by enabling faster and cheaper transactions, addresses one of Bitcoin’s current limitations – transaction speed and fees. Widespread adoption of the Lightning Network and similar technologies could dramatically increase Bitcoin’s usability and appeal, potentially leading to higher demand and price increases. Further innovations in areas like privacy enhancing technologies and improved wallet security will also play a role in bolstering confidence and driving adoption.
Macroeconomic Factors and Their Influence on Bitcoin’s Price
Macroeconomic factors, including inflation and global economic trends, significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. High inflation, eroding the value of fiat currencies, could drive investors towards Bitcoin as a store of value, increasing its demand and price. Conversely, periods of economic stability or growth might reduce the appeal of Bitcoin as a safe haven asset, potentially leading to price corrections. Global economic uncertainty, such as geopolitical instability or major economic downturns, could also influence Bitcoin’s price, potentially leading to either increased demand (as a safe haven) or decreased demand (due to risk aversion). The correlation between Bitcoin’s price and macroeconomic indicators is complex and not always straightforward, but it remains a significant influence.
Key Technological Hurdles Affecting Bitcoin’s Price
Technological hurdles, such as scalability issues beyond the Lightning Network, quantum computing threats, and the ongoing debate about energy consumption, could either hinder or boost Bitcoin’s price. Successful resolution of these challenges would foster increased confidence and broader adoption, potentially driving up the price. Conversely, failure to address these issues effectively could negatively impact investor sentiment and limit Bitcoin’s growth potential. The ongoing development and improvement of Bitcoin’s underlying technology will be a critical factor determining its long-term price. For instance, successful mitigation of quantum computing threats through cryptographic upgrades would be a significant positive factor.
Different Price Prediction Models
Predicting Bitcoin’s price in 2030, or any future date, is inherently speculative. However, various models attempt to forecast its trajectory, each with its own strengths, weaknesses, and underlying assumptions. These models offer different perspectives and can lead to vastly different conclusions. Understanding their methodologies and limitations is crucial for interpreting any price prediction.
Predicting the future price of Bitcoin relies on several distinct approaches, each with its own set of tools and assumptions. These methodologies, while offering valuable insights, are not foolproof and often yield conflicting predictions. The inherent volatility of Bitcoin and the influence of external factors further complicate the forecasting process.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis focuses on historical price and volume data to identify patterns and predict future price movements. Analysts use charts, indicators (like moving averages and RSI), and candlestick patterns to spot trends, support and resistance levels, and potential breakout points. For example, a strong upward trend line might suggest continued price appreciation, while a bearish head-and-shoulders pattern could signal a price decline. However, technical analysis is subjective and relies heavily on interpretation; what one analyst sees as a bullish signal, another might view as bearish. Past performance is not indicative of future results, a crucial caveat for this method. A notable example of a failed technical prediction would be many analysts’ inability to accurately predict the sharp drop in Bitcoin’s price in 2018, despite using various technical indicators.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis assesses the intrinsic value of Bitcoin based on factors affecting its adoption and utility. This involves considering factors such as network adoption rate, transaction volume, regulatory changes, technological advancements, and macroeconomic conditions. For instance, a growing number of institutional investors adopting Bitcoin could be interpreted as a positive fundamental signal, potentially driving price increases. Conversely, increased regulatory scrutiny might exert downward pressure. A limitation is the difficulty in quantifying the impact of these factors and accurately predicting their future trajectory. Predicting the impact of regulatory changes, for instance, is particularly challenging due to their often unpredictable nature. Many predictions in 2017 based on the increasing adoption rate and network effects overestimated the subsequent price stability.
Quantitative Models
Quantitative models utilize statistical and mathematical methods to predict Bitcoin’s price. These models often incorporate various factors from both technical and fundamental analysis, creating complex algorithms to forecast future price movements. Some models might incorporate machine learning techniques to analyze vast datasets and identify patterns not easily discernible through traditional methods. These models, while potentially more objective, are still susceptible to errors stemming from flawed data, incorrect model specifications, or the inherent unpredictability of the cryptocurrency market. For example, a quantitative model that heavily weighs historical volatility might significantly underestimate the potential for extreme price swings in the future. The accuracy of these models depends heavily on the quality and comprehensiveness of the data used and the underlying assumptions built into the model. Many sophisticated quantitative models failed to accurately predict the rapid price increases in 2020 and 2021, highlighting the limitations of even the most advanced approaches.
Comparison of Prediction Models
| Model | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Analysis | Relatively easy to understand and apply; identifies short-term trends | Subjective; relies on past performance; prone to false signals |
| Fundamental Analysis | Considers underlying factors affecting value; provides long-term perspective | Difficult to quantify factors; subject to unpredictable events |
| Quantitative Models | Objective; can incorporate large datasets; potentially more accurate | Complex; requires expertise; susceptible to data errors and model limitations |
Impact of Different Assumptions
Different assumptions within each model can lead to vastly different price predictions. For example, a technical analyst assuming a continuation of an upward trend might predict a much higher price than one who anticipates a reversal. Similarly, a fundamental analyst who anticipates widespread adoption might forecast a significantly higher price than one who believes adoption will be limited. Quantitative models are especially sensitive to the assumptions made about the input variables and the weighting given to each factor. A model that assumes high volatility might predict a much wider range of potential outcomes than one that assumes low volatility. This highlights the importance of critically evaluating the assumptions underlying any price prediction. A prediction of $1 million per Bitcoin based on the assumption of widespread global adoption might be significantly different from a prediction of $100,000 based on a more conservative adoption scenario.
Potential Scenarios for Bitcoin’s Price in 2030
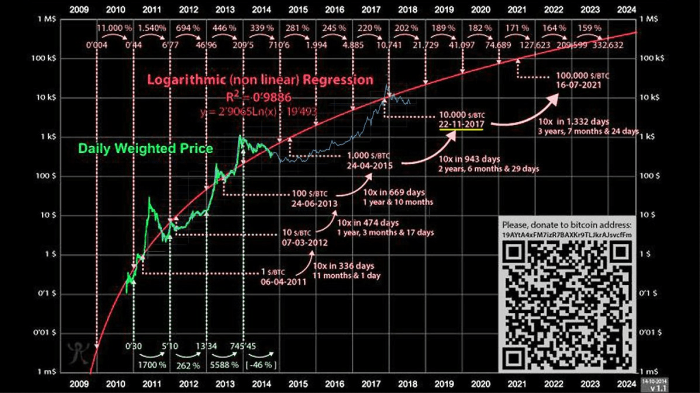
Predicting Bitcoin’s price a decade out is inherently speculative, relying on numerous interconnected factors. However, by considering various potential developments, we can Artikel plausible scenarios for its value in 2030. These scenarios are not exhaustive, but they represent a range of possibilities based on current trends and potential future events. It’s crucial to remember that these are hypothetical projections and should not be interpreted as financial advice.
Bitcoin’s Price Surge: Mass Adoption and Positive Regulation
This scenario envisions a future where Bitcoin experiences widespread adoption as a store of value and a medium of exchange. Positive regulatory developments, such as clearer guidelines and increased institutional acceptance, contribute to this growth. Imagine a world where major corporations integrate Bitcoin into their payment systems, governments establish regulatory frameworks that encourage its use, and everyday consumers utilize Bitcoin for transactions. This increased demand, coupled with a limited supply of 21 million Bitcoin, would likely drive the price significantly higher. For example, if Bitcoin becomes a widely accepted global currency alongside fiat, its value could be driven by increased demand and scarcity, potentially reaching prices in the hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars per Bitcoin. This scenario assumes a continued narrative of Bitcoin as a safe haven asset, further amplified by global economic uncertainty or inflation.
Bitcoin’s Price Stability: Moderate Growth and Continued Use
In this scenario, Bitcoin’s price remains relatively stable, fluctuating within a defined range. While adoption continues to grow, it does so at a more moderate pace than in the previous scenario. Regulatory uncertainty persists, preventing widespread institutional investment and hindering mass adoption. However, Bitcoin maintains its position as a digital gold, attracting investors seeking diversification and protection against inflation. In this case, the price might hover around a specific price range, perhaps between $100,000 and $200,000, experiencing fluctuations based on market sentiment and technological advancements. This stability reflects a mature market where price volatility is less extreme than in its earlier years. This scenario assumes a balance between continued adoption and persistent regulatory uncertainty.
Bitcoin’s Price Decline: Negative Regulation and Technological Disruption
This pessimistic scenario Artikels a future where Bitcoin’s price significantly decreases. This decline could stem from several factors, including harsh regulatory crackdowns that restrict its use, the emergence of superior cryptocurrencies with more efficient technologies, or a major security breach that undermines trust in the network. Imagine a scenario where governments worldwide impose strict regulations, effectively limiting Bitcoin’s functionality and accessibility. Concurrently, a new cryptocurrency emerges with superior scalability and transaction speeds, attracting investors and users away from Bitcoin. This combined effect could lead to a substantial price drop, potentially below its current value. This scenario also considers the possibility of a significant security flaw that erodes confidence in the Bitcoin network, triggering a sell-off.
Scenario Summary Table, What Will Bitcoin Price Be In 2030
| Scenario Name | Price Range (USD) | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Mass Adoption & Positive Regulation | $100,000 – $1,000,000+ | Widespread adoption, positive regulatory environment, increased institutional investment, scarcity |
| Moderate Growth & Continued Use | $100,000 – $200,000 | Gradual adoption, persistent regulatory uncertainty, Bitcoin as a digital gold |
| Negative Regulation & Technological Disruption | Below current value | Harsh regulatory crackdowns, emergence of superior cryptocurrencies, major security breach |