Predicting the Next Bitcoin Halving Date: When Is Next Bitcoin Halving After 2025
Predicting the precise date of the next Bitcoin halving requires understanding the core mechanics of Bitcoin’s blockchain and accounting for potential variations in its behavior. While not perfectly predictable, a reasonable estimate can be made based on established parameters.
The Bitcoin halving event occurs approximately every four years, reducing the block reward paid to miners by 50%. This is a crucial element in Bitcoin’s design, intended to control inflation. The timing, however, isn’t tied to a calendar date but rather to the number of blocks mined.
Factors Determining the Halving Date
The primary factor determining the halving date is the time it takes to mine a block. Bitcoin’s protocol aims for a block time of approximately 10 minutes. However, this is not a fixed value; it fluctuates due to variations in mining hash rate and network congestion. The cumulative number of blocks mined, rather than a specific time frame, dictates the halving event. Once 210,000 blocks have been mined after the previous halving, the next one is triggered. This makes precise prediction challenging.
Calculating the Approximate Halving Date
Calculating the approximate halving date involves estimating the average block generation time over a significant period. Let’s assume, for example, that the average block time following the 2024 halving remains consistently around 10 minutes. To reach the next halving (210,000 blocks), the calculation would be:
210,000 blocks * 10 minutes/block = 2,100,000 minutes
Converting this to days and years provides a rough estimate:
2,100,000 minutes / 60 minutes/hour / 24 hours/day / 365 days/year ≈ 3.99 years
This calculation indicates the next halving would occur approximately four years after the previous one. However, the reality is more complex.
Influencing Factors on Halving Timing
Several factors can influence the actual halving date, altering the average block generation time. A significant increase in the mining hash rate, for instance, would lead to faster block generation, potentially accelerating the halving. Conversely, a decrease in the hash rate would slow down block generation, delaying the halving. Network congestion, caused by high transaction volumes, can also impact block generation times. These variables make precise prediction challenging, requiring ongoing monitoring of network conditions.
Predicting the Halving Date: A Flowchart
A flowchart illustrating the prediction process could be designed as follows:
1. Start: Obtain the block height at the last halving.
2. Determine Target Blocks: Add 210,000 to the current block height.
3. Monitor Block Generation Time: Track the average block generation time over a substantial period (e.g., several months).
4. Calculate Estimated Time: Multiply the target number of blocks (210,000) by the average block generation time.
5. Convert to Date: Convert the calculated time into a calendar date.
6. Consider Variables: Account for potential variations in mining hash rate and network congestion.
7. Output: Provide an estimated halving date, acknowledging inherent uncertainties.
8. End:
This flowchart illustrates a simplified approach. More sophisticated models might incorporate machine learning algorithms to analyze historical data and predict future block generation times with greater accuracy.
Halving Date Prediction Models and Methodologies
Several models and methodologies exist for predicting the halving date. These range from simple calculations based on average block times, as described above, to more complex models that incorporate machine learning algorithms and incorporate various factors like mining difficulty adjustments. While precise prediction is difficult, these models aim to provide more accurate estimates than simple extrapolations. The accuracy of any model depends heavily on the stability of the network and the assumptions made regarding future conditions. Real-world examples show variations in the actual halving date compared to initial predictions, highlighting the inherent complexities.
Market Impact of the Next Halving
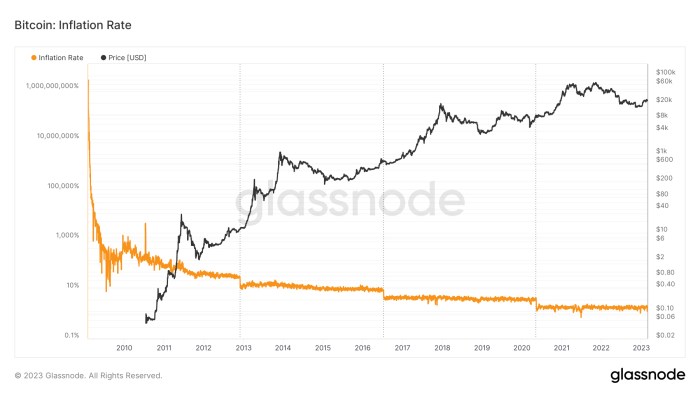
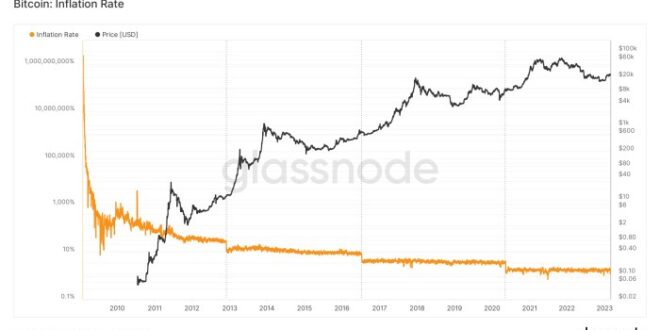
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation, has historically shown a significant impact on the cryptocurrency market. While not a guaranteed predictor of price movements, the halving significantly alters the supply dynamics of Bitcoin, influencing investor sentiment and potentially driving price volatility in both the short and long term. Analyzing past halvings provides valuable insights into potential future market reactions.
Short-Term Price Reactions to the Halving
The short-term market reaction to a Bitcoin halving is typically characterized by increased volatility. The period leading up to the event often sees a surge in speculative trading activity as investors anticipate the potential price impact. Immediately following the halving, the price may experience a temporary increase or decrease, depending on the prevailing market sentiment and other macroeconomic factors. For example, the halving in 2020 saw a period of price consolidation followed by a significant bull run, whereas the 2016 halving was followed by a period of slower price growth. The short-term price movement is highly influenced by the interplay of supply and demand, along with broader market trends and investor expectations.
Long-Term Price Reactions to the Halving
The long-term impact of a Bitcoin halving is often considered more significant than the short-term fluctuations. The reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin creates a deflationary pressure, potentially increasing its scarcity and perceived value. Historically, the halvings have been followed by periods of substantial price appreciation, although the timeline and magnitude of these increases vary. The 2012 halving, for instance, was followed by a significant price rally, while the time frame after the 2016 halving showed more gradual growth. The long-term price trajectory is a complex interplay of several factors, including technological advancements, regulatory changes, and overall market adoption.
Comparison with Previous Halvings
Comparing the anticipated market reaction to the next halving with previous events reveals both similarities and differences. While all halvings have led to increased scarcity of Bitcoin, the macroeconomic environment and overall market sentiment at the time of each halving significantly influenced the resulting price action. Factors like the overall state of the global economy, regulatory pressures, and technological developments play a crucial role. Therefore, predicting the precise market response solely based on past halvings is inherently limited. A comprehensive analysis must consider these contextual factors to create a more accurate projection.
Influence of Halving on Bitcoin’s Scarcity and Value Proposition
The halving directly impacts Bitcoin’s scarcity, a key element of its value proposition. By reducing the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation, the halving reinforces its deflationary nature. This scarcity, coupled with increasing demand, theoretically leads to higher prices. The limited supply acts as a powerful catalyst, attracting investors who see Bitcoin as a store of value, similar to gold. However, this is not a guaranteed outcome; market sentiment and other factors play a crucial role in determining the actual impact on Bitcoin’s price. The scarcity factor, however, remains a fundamental aspect of Bitcoin’s appeal and long-term value proposition.
Categorization of Potential Market Responses
The market’s response to the next Bitcoin halving can be broadly categorized into three potential scenarios:
* Bullish: A significant price increase, potentially exceeding previous halving cycles, driven by strong investor demand and anticipation of increased scarcity. This scenario assumes a positive macroeconomic environment and sustained investor confidence.
* Bearish: A relatively muted price reaction or even a price decline. This scenario could occur if the overall market sentiment is negative, or if other factors overshadow the impact of the halving.
* Neutral: A period of price consolidation or relatively minor price fluctuations. This scenario suggests a balance between bullish and bearish pressures, with the halving’s impact being partially offset by other market dynamics. This is often observed in the short-term period immediately following the halving, before a clearer trend emerges.
Factors Influencing Post-Halving Price
While the Bitcoin halving significantly reduces the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation, it’s not the sole determinant of its price afterward. Numerous other factors interact to shape the post-halving price trajectory, creating a complex interplay of influences. Understanding these factors is crucial for navigating the market’s volatility.
Macroeconomic Conditions
Broad economic trends significantly influence Bitcoin’s price, regardless of the halving. Periods of high inflation, recessionary fears, or geopolitical instability can drive investors towards Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation or a safe haven asset. Conversely, periods of economic growth and stability might lead investors to favor more traditional assets, potentially impacting Bitcoin’s price negatively. For example, the 2022 bear market coincided with rising inflation and interest rates globally, dampening investor enthusiasm for riskier assets like Bitcoin. The strength of the US dollar, a global reserve currency, also plays a significant role; a strengthening dollar often correlates with a weakening Bitcoin price, as investors shift their holdings.
Regulatory Developments
Government regulations and policies concerning cryptocurrencies exert considerable influence on Bitcoin’s price. Favorable regulations, such as clear legal frameworks and the acceptance of Bitcoin as a legitimate asset class, tend to boost investor confidence and drive price increases. Conversely, stricter regulations, bans, or ambiguous legal environments can lead to uncertainty and price drops. The regulatory landscape varies widely across countries; China’s crackdown on cryptocurrency mining and trading in 2021 significantly impacted Bitcoin’s price, while the increasing regulatory clarity in some jurisdictions like El Salvador has had a comparatively positive effect.
Technological Advancements
Technological improvements within the Bitcoin ecosystem and broader blockchain technology can impact the price. Upgrades to the Bitcoin network, such as the implementation of the Lightning Network to enhance transaction speed and scalability, can attract more users and increase demand. Developments in related technologies, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) applications built on blockchains, could indirectly influence Bitcoin’s price through increased adoption and overall market growth. The introduction of Taproot, a significant upgrade enhancing transaction privacy and smart contract functionality, is an example of a positive technological development that, while not immediately causing a price surge, contributes to long-term network health and adoption.
Relative Importance of Factors
The relative importance of these factors varies over time. In the short term, macroeconomic conditions and regulatory developments often have a more immediate and pronounced impact on Bitcoin’s price. However, in the long term, technological advancements and the inherent scarcity of Bitcoin itself (due to the halving) play a more crucial role in shaping its value. The interplay between these factors is dynamic and unpredictable, making it challenging to accurately predict post-halving price movements.
Historical Examples
Following the 2012 halving, Bitcoin’s price experienced a gradual increase over several years, although other factors, such as increased adoption and media attention, also contributed to this growth. After the 2016 halving, the price initially remained relatively stable, before experiencing a significant surge in 2017 due to a confluence of factors, including increased institutional interest and broader market enthusiasm for cryptocurrencies. The period after the 2020 halving saw a significant price increase, but this was later followed by a substantial correction, illustrating the complexity of the interplay between the halving and other market forces. These examples highlight the importance of considering multiple factors beyond the halving itself when analyzing Bitcoin’s price performance.
Investor Sentiment and Strategies
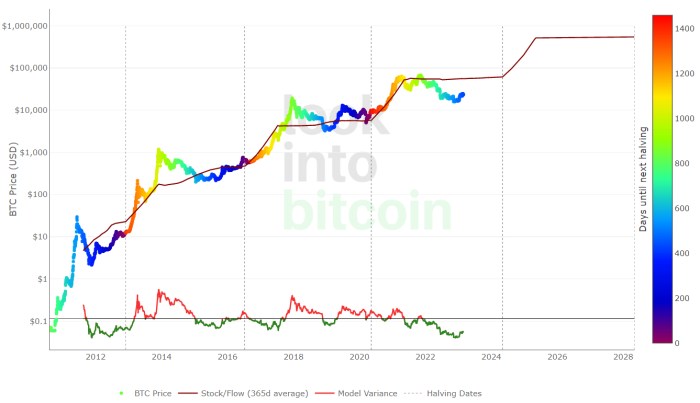
Bitcoin halving events are significant occurrences in the cryptocurrency market, often generating considerable excitement and speculation among investors. The anticipation surrounding these events stems from the historical correlation between halvings and subsequent price increases, although this is not guaranteed to repeat. Understanding investor sentiment and the strategies employed is crucial for navigating the inherent volatility.
Investor Sentiment Surrounding Bitcoin Halvings
Investor sentiment leading up to and following a Bitcoin halving is typically characterized by a mix of optimism and caution. The reduction in new Bitcoin supply often fuels bullish sentiment, with many believing the scarcity will drive up demand and, consequently, the price. However, a degree of skepticism always exists, with some investors wary of potential market corrections or the possibility that the halving’s impact might be less pronounced than anticipated. This duality in sentiment often leads to price fluctuations and heightened market activity.
Common Investment Strategies, When Is Next Bitcoin Halving After 2025
Investors employ a variety of strategies to capitalize on the potential opportunities presented by Bitcoin halvings. Some adopt a long-term “HODL” (Hold On for Dear Life) strategy, accumulating Bitcoin and holding it for an extended period, anticipating significant price appreciation over time. Others employ more active trading strategies, attempting to time the market by buying before the halving and selling after a perceived price surge. Still others might use derivatives like futures or options contracts to speculate on price movements without directly holding Bitcoin.
Risk and Reward Comparison
The HODL strategy minimizes transaction costs and capital gains taxes but exposes investors to potential long-term price stagnation or even a significant price drop. Active trading strategies, while offering the potential for higher returns, carry increased risk due to market volatility and the difficulty of accurately predicting price movements. Using derivatives involves leverage, magnifying both profits and losses; it’s a high-risk, high-reward approach. The choice of strategy depends heavily on individual risk tolerance and investment goals.
Risk Management in Bitcoin Halving Volatility
Effective risk management is paramount when navigating the volatility surrounding Bitcoin halvings. Diversification across different asset classes is crucial to mitigate losses should the Bitcoin price decline unexpectedly. Setting stop-loss orders can help limit potential losses on individual trades. Thorough due diligence and a realistic understanding of market risks are essential before committing significant capital. It’s also important to avoid emotional decision-making, sticking to a pre-defined investment plan.
Investor Profile Approaches
Different investor profiles approach investing around halvings differently. Long-term investors with a high risk tolerance might view a halving as an opportunity to accumulate more Bitcoin, confident in its long-term potential. Short-term traders, on the other hand, might focus on shorter-term price swings, aiming to profit from the anticipated volatility. Conservative investors might prefer to remain on the sidelines, waiting for greater market clarity before committing any funds. The optimal strategy depends on individual financial circumstances, risk tolerance, and investment timeline.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common queries regarding Bitcoin halvings, focusing on their mechanics, market impact, and investment implications. Understanding these aspects is crucial for navigating the complexities of Bitcoin’s cyclical nature.
Bitcoin Halving Explained
A Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created (mined) by 50%. This occurs approximately every four years, or every 210,000 blocks mined. The halving mechanism is designed to control Bitcoin’s inflation rate, mimicking the scarcity of precious metals like gold. Essentially, it cuts the reward miners receive for verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain in half.
The Next Bitcoin Halving’s Timing
Predicting the precise date of the next halving requires monitoring the block creation rate, which can fluctuate slightly. However, based on the current block generation time, the next halving is projected to occur sometime in April 2024. This prediction is based on the consistent and predictable nature of Bitcoin’s block generation algorithm, barring any significant unexpected changes or disruptions to the network. Any deviations from this projection would be due to minor variations in block times.
Halving’s Impact on Bitcoin Price
Historically, Bitcoin halvings have been associated with periods of price appreciation, both in the short-term and long-term. The short-term effect often manifests as increased volatility and price fluctuations as the market anticipates the reduced supply. In the long-term, the reduced inflation rate can contribute to increased scarcity, potentially driving up demand and, consequently, the price. The 2012 and 2016 halvings, for instance, were followed by significant price increases, though the timeframe varied. However, it’s crucial to remember that other factors also influence price, and past performance is not indicative of future results.
Investing in Bitcoin Before a Halving: Risks and Rewards
Investing in Bitcoin before a halving presents both potential rewards and substantial risks. The reward lies in the possibility of capital appreciation as the price potentially rises leading up to and following the event. However, the risk stems from the increased volatility surrounding halvings. The market can experience sharp price corrections, leading to significant losses for investors who enter the market too close to the halving without a robust risk management strategy. It is crucial to understand that the market’s reaction to a halving is not guaranteed, and other market forces can significantly influence the price.
Risks Associated with Investing Around a Halving
The primary risk associated with investing around a halving is heightened market volatility. The anticipation surrounding the event can lead to speculative trading and price swings, making it challenging to time the market effectively. Moreover, a halving doesn’t automatically guarantee price increases; other macroeconomic factors and market sentiment can significantly influence the price trajectory. Corrections after periods of significant price increases are also common. For example, the price of Bitcoin surged significantly after the 2017 halving, only to experience a substantial correction in 2018. This underscores the importance of careful risk assessment and diversification in any investment strategy.
Illustrative Examples (Visual Aids)
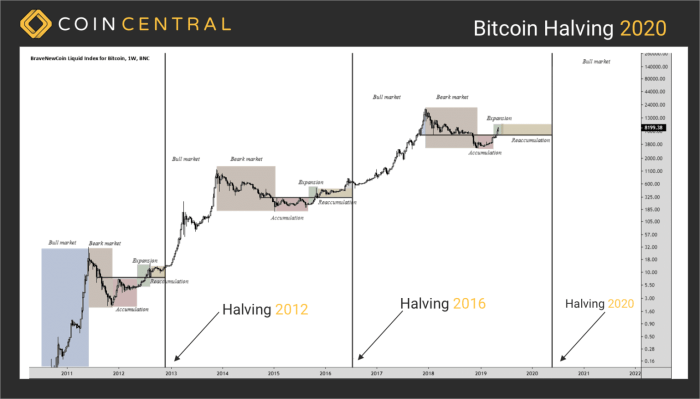
Visual aids can significantly enhance understanding of complex concepts like Bitcoin halving. The following examples use textual descriptions to create mental images that clarify the mechanics of halving and its relationship with Bitcoin’s price.
Bitcoin Halving: A Visual Representation
Imagine a vibrant, three-dimensional bar graph. Each bar represents a Bitcoin block reward. The first bar, a towering, deep blue structure, represents the initial block reward of 50 BTC. As we move to the right along the x-axis, representing time, the bars progressively shrink in height and change color. The second bar, slightly shorter and a lighter shade of blue, is 25 BTC. The third bar, even smaller and a pale blue, is 12.5 BTC. This continues, with each subsequent bar halving in size and gradually transitioning to a light, almost white blue, signifying the diminishing reward. The bars are clearly labeled with their corresponding BTC values, and the x-axis is marked with the approximate dates of each halving event. The overall image creates a powerful visual metaphor for the gradual reduction of block rewards over time.
Halving Events and Bitcoin Price: A Chart Representation
A line graph effectively illustrates the correlation between Bitcoin halving events and price fluctuations. The x-axis represents time, marked with significant dates, including each Bitcoin halving event. These dates are clearly highlighted. The y-axis represents the price of Bitcoin in US dollars. The graph plots the Bitcoin price over time, showing a series of data points connected by a line. Each halving event is marked with a distinct vertical line, intersecting the price line. Ideally, the graph would show a noticeable price increase following each halving, although the magnitude of this increase varies. To enhance understanding, we can include shaded areas to represent periods of bull and bear markets. For example, a period of rapid price increase could be highlighted in green, representing a bull market, while a period of decline could be shaded in red, representing a bear market. The graph should clearly demonstrate the general trend of price increases following halving events, even while acknowledging the volatility of the market. The inclusion of specific price points for key dates, such as the dates before and after each halving event, will provide a more concrete understanding of the price fluctuations. For example, we could show the price before the 2012 halving, the price immediately after, and the peak price achieved during the subsequent bull run. This would allow viewers to visualize the impact of each halving on price action.
When Is Next Bitcoin Halving After 2025 – Determining the precise date of the next Bitcoin halving after 2025 requires careful consideration of the blockchain’s block generation time. To fully understand the halving mechanism itself, it’s helpful to review what it entails; a great resource for this is Que Es El Halving Bitcoin 2025 , which provides a clear explanation. With that understanding, we can then more accurately project the timing of future halvings and their potential impact on the Bitcoin market.
Determining the next Bitcoin halving after 2025 requires understanding the previous one. To clarify the timing of the 2025 halving, a helpful resource is this article: When Bitcoin Halving 2025. Once we have a firm grasp on the 2025 event, calculating the subsequent halving, approximately four years later, becomes straightforward.
The next Bitcoin halving after 2025 is projected for 2028, reducing the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation. Understanding the potential impact on price is crucial, and for insights into the anticipated market behavior, you might find the analysis at Bitcoin 2025 Halving Price Prediction helpful. This prediction serves as a foundation for speculating about the price trajectory leading up to and following the 2028 halving event.
Determining when the next Bitcoin halving occurs after 2025 requires understanding the previous halving cycles. To accurately predict the 2025 halving’s impact, it’s helpful to consult resources like this insightful analysis on Bitcoin Halving 2025 Prediction. This information helps clarify the timeline and allows for better forecasting of subsequent halvings, ultimately answering the question of when the next one will take place after 2025.
Determining the next Bitcoin halving after 2025 requires understanding the four-year cycle. While researching this, it’s helpful to note that other cryptocurrencies have their own halving schedules; for instance, the Bitcoin Cash Halving 2025 is a significant event in its own right. Returning to Bitcoin, the next halving will likely occur sometime in 2028, but precise timing depends on block generation rates.
Determining when the next Bitcoin halving occurs after 2025 requires understanding the halving cycle. The next scheduled reduction in Bitcoin’s block reward is covered in detail on this helpful resource: Next Bitcoin Halving Date 2025. Following this event, the subsequent halving will take place approximately four years later, assuming the current block generation time remains consistent. Therefore, we can project the next halving after 2025 based on this information.