Bitcoin Halving 2025: When Is The Bitcoin Halving 2025
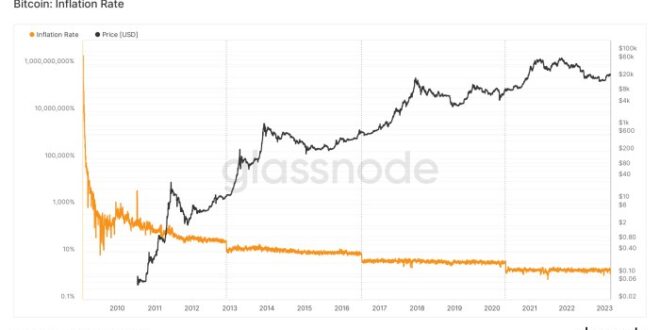
The Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. This occurs approximately every four years, and it’s a significant event that impacts both the price and the mining landscape of the cryptocurrency. Understanding the halving mechanism is key to grasping Bitcoin’s long-term economic model and potential future price movements.
Bitcoin Halving: A Reduction in Mining Rewards
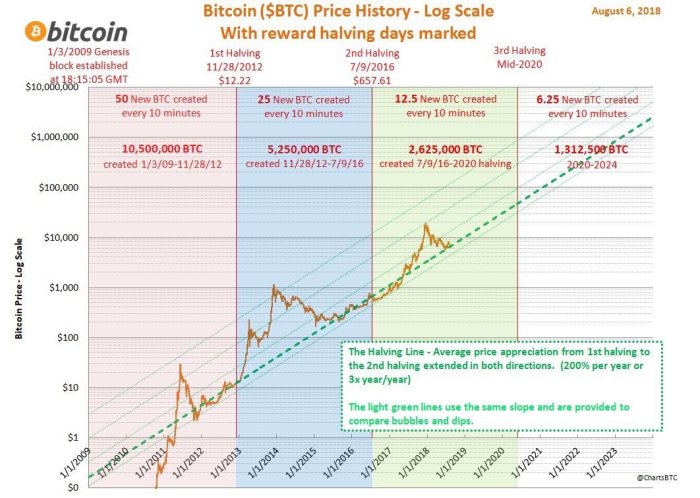
The Bitcoin halving mechanism is designed to control inflation. Every 210,000 blocks mined, the reward given to Bitcoin miners for verifying transactions is cut in half. This halving event directly affects the supply of new Bitcoins entering circulation, potentially impacting its value. The initial reward was 50 BTC per block. After each halving, this reward is halved, creating a progressively slower rate of new Bitcoin creation. This controlled inflation is a core tenet of Bitcoin’s design, intended to mimic the scarcity of precious metals like gold.
Historical Impact of Bitcoin Halvings
Previous halvings have demonstrated a correlation between the event and subsequent price increases, although the exact relationship is complex and influenced by various market factors. The halvings don’t directly cause price increases; rather, they influence the supply dynamics, which in turn can impact market sentiment and price. Mining activity also experiences shifts following a halving, with miners needing to adjust their operations to maintain profitability in the face of reduced rewards.
Timeline of Past Halvings and Price Movements
The following table summarizes the past Bitcoin halvings and their subsequent price movements. It’s crucial to remember that correlation does not equal causation; other market factors significantly influence Bitcoin’s price.
| Halving Date | Block Height | Reward Before Halving | Reward After Halving | Approximate Price Before Halving (USD) | Approximate Price After Halving (USD) (Peak) | Time to Peak Price (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| November 28, 2012 | 210,000 | 50 BTC | 25 BTC | ~13 USD | ~1,147 USD | ~12 |
| July 9, 2016 | 420,000 | 25 BTC | 12.5 BTC | ~650 USD | ~19,783 USD | ~18 |
| May 11, 2020 | 630,000 | 12.5 BTC | 6.25 BTC | ~8,700 USD | ~64,863 USD | ~6 |
Note: These price figures represent approximate values at specific points in time and the time to peak price is a general approximation. The actual price movements are far more complex and involve many other variables. For precise data, refer to reputable cryptocurrency price tracking websites.
Predicting the 2025 Halving Date
Predicting the exact date of the Bitcoin halving in 2025 requires understanding the core mechanism behind it: the reduction of the block reward given to miners for successfully adding a block to the blockchain. This reward is halved approximately every four years, aiming for a consistent schedule. However, several factors can subtly influence the precise timing, leading to variations from a purely theoretical calculation.
The Bitcoin protocol dictates that a new block is added to the blockchain approximately every ten minutes. This target block time is not strictly enforced; the actual time can fluctuate due to network conditions and mining difficulty adjustments. The halving occurs after a predetermined number of blocks have been mined (currently 210,000 blocks between each halving). Therefore, accurately predicting the halving date hinges on accurately estimating the average block time leading up to the event.
Calculating the Halving Date
Several methods exist for estimating the halving date. The most straightforward approach involves extrapolating from the current block height and the average block time. This calculation assumes a consistent average block time going forward, which is a simplification. For example, if we know the current block height and the average block time over the last year, we can project when the next 210,000 blocks will be mined. However, this method’s accuracy is limited by the inherent variability of the block time. Significant changes in the network’s hashrate or other unforeseen circumstances could alter the average block time, impacting the prediction’s accuracy. A more sophisticated approach might involve statistical modeling that accounts for historical block time variability, potentially incorporating factors like hash rate fluctuations and network congestion. Such models aim to provide a more robust prediction but still remain susceptible to unforeseen events. The historical data from previous halvings can also be used to refine these models, comparing the predicted dates with the actual dates to identify potential biases and improve predictive accuracy. However, past performance is not always indicative of future results.
Factors Influencing Halving Timing
The most significant factor affecting the halving date is the variability in the average block time. This variability is influenced by several factors, including the total hash rate of the Bitcoin network, the difficulty adjustment algorithm, and even network congestion. A sudden increase in the hash rate could lead to blocks being mined faster than expected, potentially accelerating the halving. Conversely, a decrease in the hash rate would slow down block creation, delaying the halving. The difficulty adjustment algorithm, designed to maintain a roughly ten-minute block time, plays a crucial role in mitigating these fluctuations, but it cannot perfectly eliminate them. Unexpected events, such as major network upgrades or regulatory changes, could also introduce unpredictable shifts in the block time and therefore influence the halving date.
Market Anticipation and Price Predictions
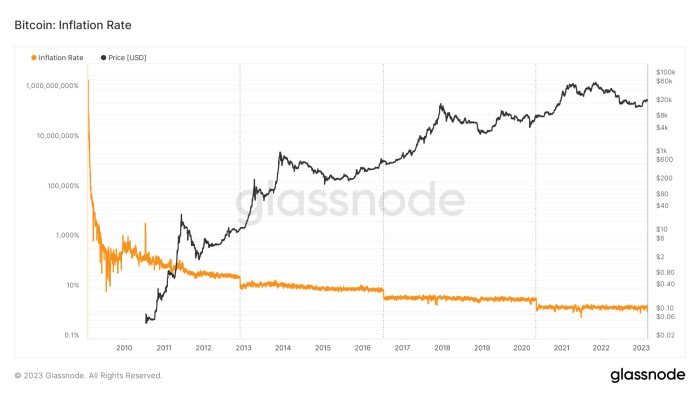
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation, consistently generates significant market anticipation. This anticipation stems from the historical correlation between halving events and subsequent price increases, although the extent and timing of these increases remain subjects of debate and speculation. Understanding this anticipation and analyzing past trends is crucial for navigating the volatile cryptocurrency market.
Historical Price Trends Following Previous Halvings
Bitcoin has undergone three previous halvings (2012, 2016, and 2020). Following each event, the price experienced a period of growth, although the duration and magnitude varied significantly. The 2012 halving was followed by a gradual price increase over the next year. The 2016 halving saw a more dramatic price surge, peaking in late 2017. The 2020 halving resulted in a substantial price increase, though the market experienced periods of volatility and correction before reaching its peak. These historical trends fuel speculation about a similar price surge following the 2025 halving. However, it’s crucial to remember that past performance is not indicative of future results, and various other factors influence Bitcoin’s price.
Bitcoin Price Predictions Post-2025 Halving: A Comparison
Numerous analysts and firms offer price predictions for Bitcoin after the 2025 halving, ranging from cautiously optimistic to extremely bullish. These predictions employ various models, incorporating factors like supply and demand dynamics, adoption rates, macroeconomic conditions, and regulatory developments. Some predictions suggest a modest price increase, while others project exponential growth to significantly higher price levels. The disparity highlights the inherent uncertainty and complexity of forecasting cryptocurrency prices.
Price Prediction Models and Underlying Assumptions
The following table compares different price prediction models and their underlying assumptions. Note that these are illustrative examples and not exhaustive. The actual price movement will depend on a complex interplay of various factors.
| Model | Assumptions | Predicted Price (USD) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative Model | Gradual adoption, moderate macroeconomic stability, some regulatory headwinds. | $100,000 – $150,000 | Based on historical trends, accounting for potential market corrections. |
| Moderate Model | Increased institutional adoption, positive macroeconomic conditions, relatively stable regulatory environment. | $200,000 – $300,000 | Considers a more optimistic scenario of increased demand and limited regulatory interference. |
| Aggressive Model | Widespread global adoption, significant institutional investment, favorable regulatory developments. | $500,000+ | Assumes a highly optimistic scenario with exponential growth in demand and limited supply. |
| PlanB’s Stock-to-Flow Model (Example) | Focuses primarily on Bitcoin’s scarcity, comparing it to precious metals. | Highly variable, historically inaccurate in recent years. | This model’s accuracy has been debated extensively; its past predictions have not consistently materialized. |
Impact on Bitcoin Mining
The Bitcoin halving, a pre-programmed event reducing the block reward for miners by half, significantly impacts the profitability and operational landscape of the Bitcoin mining industry. This event forces miners to adapt their strategies to maintain profitability in a changed economic environment. The consequences ripple through the entire mining ecosystem, influencing everything from energy consumption to the geographical distribution of mining power.
The halving directly affects miners’ profitability by reducing their revenue stream. Before the halving, miners receive a certain number of Bitcoins for successfully validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain. After the halving, this reward is cut in half, meaning miners earn less Bitcoin for the same amount of work. To maintain profitability, miners must either reduce their operational costs or see the price of Bitcoin increase to compensate for the reduced reward. Failure to do so could lead to miners shutting down operations, impacting the network’s security and hashrate.
Miner Profitability and Operational Costs
The halving creates a pressure on miners to optimize their operations. Reduced Bitcoin rewards necessitate a careful examination of all operational expenses, including electricity costs, hardware maintenance, and personnel salaries. Miners with access to cheaper electricity, more efficient mining hardware, and lower overhead costs are better positioned to weather the halving’s impact. Those with higher operational costs might be forced to shut down their operations if the Bitcoin price doesn’t rise sufficiently to offset the reduced block reward. For example, miners in regions with high electricity prices, like some parts of the United States, might find themselves at a disadvantage compared to those in regions with abundant hydroelectric power, such as some parts of China or Central Asia, before the stricter regulations were implemented in China. This competitive pressure leads to a consolidation of the mining industry, with larger, more efficient operations surviving while smaller, less efficient ones are forced to exit the market.
Changes in Mining Strategies and Distribution of Mining Power
The halving often triggers changes in mining strategies. Miners may invest in more energy-efficient hardware, optimize their mining pools, or explore alternative revenue streams, such as staking other cryptocurrencies. The distribution of mining power can also shift geographically, with miners relocating to regions with more favorable regulatory environments and lower energy costs. The 2020 halving, for instance, saw a significant shift in mining activity towards the United States due to the regulatory uncertainty in China. This redistribution of mining power can have implications for network decentralization and security.
Impact on the Environmental Sustainability of Bitcoin Mining
The halving’s impact on the environmental sustainability of Bitcoin mining is complex. While the halving reduces the rate at which new Bitcoin are created, it doesn’t directly address the energy consumption associated with mining. The long-term impact on the environment depends on several factors, including the adoption of more energy-efficient mining hardware and the increasing use of renewable energy sources by miners. If miners fail to adopt more sustainable practices, the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining could remain a concern. Conversely, a rise in the Bitcoin price following the halving might incentivize the adoption of greener energy sources as profitability allows for such investments.
Impact of Halving on the Bitcoin Mining Lifecycle
The following flowchart illustrates the impact of the Bitcoin halving on the lifecycle of Bitcoin mining:
[Flowchart Description: The flowchart begins with “Bitcoin Halving.” This leads to two branches: “Reduced Block Reward” and “Increased Mining Difficulty.” “Reduced Block Reward” leads to “Decreased Miner Revenue.” “Decreased Miner Revenue” branches into “Increased Operational Efficiency” and “Miners Exit Market.” “Increased Operational Efficiency” leads to “Improved Profitability” and then back to the “Bitcoin Halving” start point, creating a cycle. “Miners Exit Market” leads to “Reduced Network Hashrate.” “Increased Mining Difficulty” leads to “Higher Energy Consumption” and “Increased Competition.” “Higher Energy Consumption” connects to “Environmental Concerns,” while “Increased Competition” connects to “Consolidation of Mining Power,” which then connects to “Improved Profitability” and back to the “Bitcoin Halving” start point, completing the cycle.]Long-Term Implications for Bitcoin
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation by half, is anticipated to have profound and lasting effects on Bitcoin’s trajectory and the broader cryptocurrency market. Understanding these long-term implications requires considering its impact on adoption, market dynamics, and the competitive landscape within the crypto ecosystem. The event’s influence will likely extend beyond price fluctuations, shaping the future of digital currencies in significant ways.
The halving’s primary long-term effect will be on Bitcoin’s scarcity. As the supply of newly mined Bitcoin diminishes, its inherent value proposition as a deflationary asset is reinforced. This increased scarcity could drive further adoption, particularly among investors seeking inflation hedges and long-term store-of-value assets. Increased institutional investment, fueled by this scarcity and growing regulatory clarity in certain jurisdictions, is a likely outcome. This could, in turn, lead to greater mainstream acceptance and integration into traditional financial systems. Conversely, a lack of substantial regulatory clarity or a significant negative event in the overall economic climate could dampen adoption.
Bitcoin’s Adoption and Use
The reduced supply of newly minted Bitcoin post-halving will likely increase its value, potentially making it less accessible for everyday transactions. This could push Bitcoin towards its intended role as a store of value rather than a medium of exchange. We might see a rise in the use of second-layer scaling solutions like the Lightning Network to facilitate smaller, more frequent transactions, mitigating the impact of higher transaction fees that could result from increased value. This evolution could enhance Bitcoin’s functionality and broaden its appeal to a wider range of users. The success of this transition, however, depends on the continued development and adoption of these second-layer solutions. For example, if the Lightning Network proves scalable and user-friendly, it could significantly increase Bitcoin’s utility as a payment method despite its higher value.
Implications for the Cryptocurrency Market
The 2025 halving’s impact extends beyond Bitcoin. Other cryptocurrencies, particularly those with similar scarcity models, might experience positive spillover effects. Increased investor interest in Bitcoin could lead to a broader resurgence in the entire cryptocurrency market, boosting the prices of altcoins as well. However, this effect could be unevenly distributed, with some altcoins benefiting more than others based on their underlying technology, market capitalization, and community support. For instance, cryptocurrencies with established ecosystems and strong community engagement are more likely to ride the wave of increased investor interest. Conversely, cryptocurrencies with weak fundamentals could struggle to maintain their value in the face of increased competition.
Comparison with Other Cryptocurrencies
Comparing Bitcoin’s market capitalization post-halving with other cryptocurrencies requires considering various factors, including their respective supply mechanisms, technological advancements, and market sentiment. Bitcoin’s dominance in the market, largely due to its first-mover advantage and established brand recognition, means its market capitalization response to a halving will likely be disproportionately larger than that of other cryptocurrencies. However, the relative performance of other cryptocurrencies will depend on their individual characteristics and market dynamics. For example, a cryptocurrency with a similar scarcity model but superior technology could potentially outperform Bitcoin in the long run, even after a Bitcoin halving.
Risks and Opportunities Associated with the Halving, When Is The Bitcoin Halving 2025
The halving presents both significant opportunities and risks. It is important to consider both sides of this equation for a complete understanding of its potential impact.
When Is The Bitcoin Halving 2025 – Before listing the risks and opportunities, it’s important to remember that these are potential outcomes, not guaranteed results. The actual impact of the halving will depend on a complex interplay of factors, including macroeconomic conditions, regulatory developments, and technological advancements.
- Opportunity: Increased Bitcoin value and adoption leading to higher returns for long-term holders.
- Opportunity: Attracting new investors and institutional capital into the Bitcoin ecosystem.
- Opportunity: Stimulating innovation in Bitcoin’s scaling solutions and related technologies.
- Risk: Increased price volatility in the short term, potentially leading to market corrections.
- Risk: A potential decrease in Bitcoin’s transactional usability due to higher transaction fees.
- Risk: Increased regulatory scrutiny and potential government intervention.
Factors Affecting Bitcoin’s Price Beyond the Halving
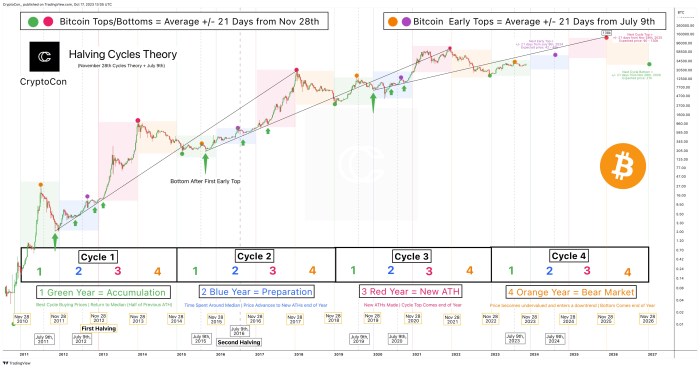
The Bitcoin halving, while a significant event, is not the sole determinant of Bitcoin’s price trajectory. Numerous other factors, both internal and external to the cryptocurrency ecosystem, exert considerable influence on its value. Understanding these factors is crucial for navigating the complexities of the Bitcoin market and forming informed predictions.
Macroeconomic Factors Influencing Bitcoin Price
Global macroeconomic conditions significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. Periods of high inflation, for instance, can drive investors towards Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation, increasing demand and potentially boosting its price. Conversely, periods of economic uncertainty or recession can lead to risk-aversion, causing investors to sell assets like Bitcoin, thereby decreasing its price. The performance of traditional markets, such as the stock market, also correlates with Bitcoin’s price; a downturn in the stock market might see investors move their capital into Bitcoin, and vice versa. Examples include the correlation observed between Bitcoin’s price movements and the performance of the S&P 500 index during various economic cycles. Similarly, changes in interest rates set by central banks globally can affect the attractiveness of Bitcoin relative to other investment options. Higher interest rates may make traditional bonds more appealing, potentially drawing investment away from Bitcoin.
Regulatory Changes and Governmental Policies
Governmental regulations and policies play a pivotal role in shaping Bitcoin’s price. Favorable regulatory frameworks, such as those that provide clarity on taxation and legal status, can increase investor confidence and attract institutional investment, thus driving up the price. Conversely, restrictive regulations, bans, or uncertainty surrounding the legal landscape can lead to price volatility and potential downturns. The contrasting approaches of countries like El Salvador, which has adopted Bitcoin as legal tender, and China, which has banned cryptocurrency trading, exemplify the significant impact of governmental policies on Bitcoin’s value. These contrasting approaches have resulted in vastly different price reactions within their respective markets.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
Technological advancements within the Bitcoin ecosystem itself can also significantly affect its price. Improvements in scalability, such as the implementation of the Lightning Network, can enhance Bitcoin’s usability and transaction speed, potentially increasing its adoption and driving price appreciation. Conversely, major security breaches or significant protocol vulnerabilities could erode investor confidence and negatively impact the price. The development and adoption of second-layer scaling solutions directly impacts transaction fees and speeds, thereby influencing Bitcoin’s practical usability and appeal to a wider range of users and businesses.
Impact of Institutional Investment
The entry of institutional investors, such as large corporations and hedge funds, into the Bitcoin market has been a significant driver of price increases in the past. These large-scale investments bring substantial capital into the market, increasing demand and pushing prices upwards. The growing acceptance of Bitcoin as an asset class by major financial institutions indicates a shift in the perception of Bitcoin from a niche speculative asset to a potential component of diversified investment portfolios. Examples include the investments made by MicroStrategy and Tesla, which have significantly impacted Bitcoin’s price and overall market sentiment. However, the extent of institutional investment is also subject to broader market trends and economic conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section addresses common queries regarding the Bitcoin halving event, focusing on its mechanics, predicted timing, price impact, and associated risks and opportunities. Understanding these aspects is crucial for navigating the cryptocurrency market effectively around this significant event.
Bitcoin Halving Explained
The Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. Every four years, or roughly every 210,000 blocks mined, the reward given to Bitcoin miners for verifying transactions is cut in half. This process is designed to control inflation and maintain the scarcity of Bitcoin. Initially, the reward was 50 BTC per block. After the first halving, it became 25 BTC, then 12.5 BTC, and the next halving in 2025 will reduce it to 6.25 BTC.
Bitcoin Halving Expected Date in 2025
Predicting the exact date of the 2025 Bitcoin halving requires monitoring the block creation time. While approximately every four years, the actual date fluctuates slightly due to variations in the time it takes to mine a block. This variation is influenced by factors like the overall network hash rate (the computational power dedicated to mining) and the difficulty adjustment algorithm. Based on current block times, the halving is expected to occur around April 2025. However, this is just an estimate, and the actual date might vary by a few days or even weeks.
The Halving’s Effect on Bitcoin’s Price
Historically, Bitcoin’s price has tended to increase in the period leading up to and following a halving. This is largely attributed to the reduced supply of new Bitcoins entering circulation, potentially increasing demand and driving up the price. The 2012 and 2016 halvings saw significant price increases following the event, although other factors undoubtedly contributed to these price movements. It is important to note, however, that past performance is not indicative of future results. Market conditions and investor sentiment play a significant role in determining price, and the 2025 halving’s impact remains uncertain.
Risks and Opportunities Associated with the Halving, When Is The Bitcoin Halving 2025
The Bitcoin halving presents both opportunities and risks. A potential opportunity lies in the anticipated price increase, offering investors a chance for significant returns. However, there’s also a risk of a price correction or even a prolonged bear market after the initial price surge, as seen in some past instances. Furthermore, the halving could impact Bitcoin mining profitability, potentially leading to consolidation within the mining industry. The reduced block reward might make mining less profitable for smaller operations, resulting in a more centralized mining landscape. Conversely, the anticipated price increase could offset the reduced block reward, ensuring continued profitability for miners. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial for both investors and miners.
Visual Representation of Bitcoin Halving Data
Understanding the relationship between Bitcoin halving events and its price requires a visual approach. Charts and diagrams can effectively communicate complex data, making trends and patterns more readily apparent. This section presents two visual representations to illustrate key aspects of Bitcoin halving.
Bitcoin Price and Halving Events Chart
This chart would use a line graph to display the historical Bitcoin price (in USD) on the y-axis against time (in years) on the x-axis. Each halving event would be clearly marked on the x-axis with a vertical dashed line and a labeled annotation indicating the date of the halving. The price data points immediately preceding and following each halving would be highlighted, perhaps with different colored markers to distinguish them. The y-axis would use a logarithmic scale to better visualize the significant price fluctuations over time. The chart title would be “Bitcoin Price and Halving Events (2009-Present)”. A legend would clearly define the line representing the Bitcoin price and the annotations representing halving events. For example, the chart would show a clear upward trend in Bitcoin’s price generally following each halving event, although it’s important to note that other market factors significantly influence price movements. The chart would help to visually confirm the historical correlation between halvings and subsequent price increases, though not causation.
Bitcoin Flow Diagram
This diagram would be a simplified flowchart illustrating the path of Bitcoin from miners to exchanges to users. It would begin with a large rectangle labeled “Bitcoin Miners,” representing the source of newly mined Bitcoin. Arrows would then flow from this rectangle to two smaller rectangles: “Miners’ Wallets” and “Exchanges.” The arrow leading to “Miners’ Wallets” would be labeled “Bitcoin Mining Rewards,” representing the newly mined Bitcoin kept by miners. The arrow leading to “Exchanges” would be labeled “Bitcoin Sales,” representing the Bitcoin sold by miners. From “Exchanges,” arrows would flow to a large rectangle labeled “Users,” representing individuals and institutions that buy and hold Bitcoin. These arrows would be labeled “Bitcoin Purchases.” The diagram would visually represent the flow of Bitcoin from its creation through miners to its ultimate users via exchanges, showing how miners introduce new Bitcoin into circulation. The visual elements would be color-coded for clarity: for instance, “Miners” could be green, “Exchanges” blue, and “Users” purple. The thickness of the arrows could represent the approximate volume of Bitcoin moving along each path, although this would be a simplification given the fluctuating nature of market activity. The diagram’s title would be “Bitcoin Flow: Miners to Exchanges to Users.”