Bitcoin Halving 2025
The Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. This occurs approximately every four years, and significantly impacts the supply of Bitcoin entering the market, influencing its price and overall market dynamics. Understanding the halving mechanism and its historical effects is crucial for navigating the cryptocurrency landscape.
Bitcoin Halving: A Supply Shock Mechanism
The Bitcoin halving is a core component of Bitcoin’s deflationary monetary policy. Every 210,000 blocks mined, the reward given to Bitcoin miners for verifying transactions is cut in half. This programmed scarcity is designed to control inflation and maintain Bitcoin’s long-term value proposition. The halving event doesn’t directly cause price increases, but it significantly reduces the influx of new Bitcoin into circulation, potentially leading to increased scarcity and, consequently, price appreciation. This effect is often amplified by market speculation and investor sentiment.
Historical Bitcoin Halvings and Their Impact
The Bitcoin halving has occurred three times previously, each time generating considerable market interest and price fluctuations. Analyzing these events provides valuable insights into potential future market behavior, though past performance is not indicative of future results.
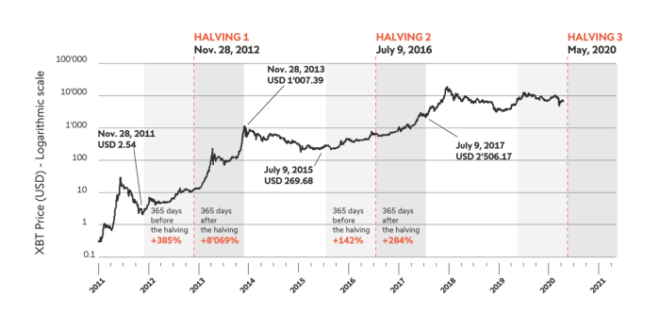
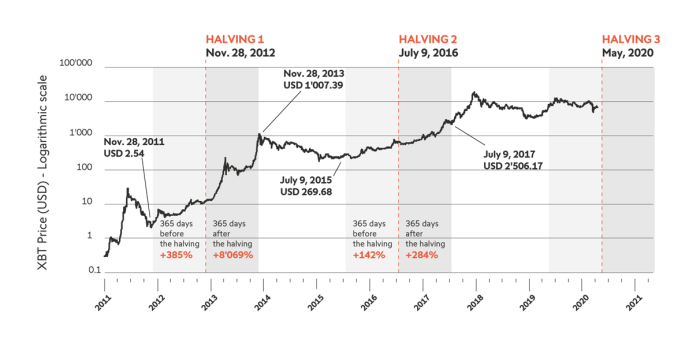
The first halving took place in November 2012, reducing the block reward from 50 BTC to 25 BTC. This event coincided with a period of increasing Bitcoin adoption and price appreciation, though the direct causal link between the halving and price movements is debated. Following the halving, Bitcoin’s price experienced a gradual but significant increase over the subsequent years.
The second halving occurred in July 2016, halving the block reward again to 12.5 BTC. Similar to the first halving, this event was followed by a period of substantial price growth, though this growth was not immediate and involved periods of consolidation and volatility. The price surge started gradually and accelerated later, demonstrating the complex interplay between halving and other market factors.
The third halving took place in May 2020, reducing the block reward to 6.25 BTC. This halving event was followed by a significant price surge, although this was followed by a period of price correction. The price increase was influenced by a number of factors, including increased institutional investment and global macroeconomic conditions.
Timeline of Past Halvings and Their Effects
The following table summarizes the key dates and observable effects of past Bitcoin halvings:
| Halving Date | Block Reward Before Halving | Block Reward After Halving | Subsequent Price Movement (General Trend) |
|---|---|---|---|
| November 2012 | 50 BTC | 25 BTC | Gradual but significant price increase over several years. |
| July 2016 | 25 BTC | 12.5 BTC | Substantial price growth after a period of consolidation and volatility. |
| May 2020 | 12.5 BTC | 6.25 BTC | Significant price surge followed by a correction. |
Predicting the 2025 Halving Date
The Bitcoin halving, a crucial event in the cryptocurrency’s lifecycle, occurs approximately every four years. It’s a programmed reduction in the rate at which new Bitcoins are created, effectively decreasing the inflation rate of the Bitcoin network. Predicting the precise date of the 2025 halving requires understanding the underlying mechanism.
The Bitcoin protocol dictates that the block reward, the amount of Bitcoin awarded to miners for successfully adding a block to the blockchain, is halved at regular intervals. This halving event is designed to control the supply of Bitcoin and maintain its long-term value.
The Halving Calculation
The halving date isn’t determined by a specific calendar date but rather by the number of blocks mined. Bitcoin’s blockchain is designed to add a new block approximately every 10 minutes. Therefore, the halving occurs after a specific number of blocks have been mined since the previous halving. The formula used is relatively straightforward: The target block count for a halving is 210,000 blocks multiplied by the number of halvings that have occurred.
The formula is not explicitly stated in the code, but rather implied by the halving mechanism. It’s derived from the known block reward reduction and the approximate block time.
For the 2025 halving, this translates to 210,000 blocks * 4 halvings (since the genesis block) = 840,000 blocks. This assumes that block times remain consistently close to the target of 10 minutes.
Factors Affecting the Halving Schedule
While the halving is programmed to occur after approximately 210,000 blocks, several factors could potentially influence the exact date. The most significant is the mining difficulty adjustment. This mechanism dynamically adjusts the difficulty of mining new blocks to maintain the approximately 10-minute block time target. Periods of increased mining power (more miners joining the network) lead to faster block creation, while decreased mining power leads to slower block creation. These fluctuations impact the time it takes to reach the 840,000 block target.
Another factor is potential unforeseen events affecting the Bitcoin network, such as major protocol upgrades or network congestion. These events, while rare, could potentially disrupt the mining process and subtly affect the time until the halving. The historical halvings have largely adhered to the predicted schedule, however, demonstrating the robustness of the system. For example, the third halving in May 2020, despite significant market volatility, occurred very close to the predicted date. This indicates that while external factors can influence the exact date slightly, the underlying mechanism remains highly predictable.
Anticipated Market Effects of the 2025 Halving
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation, is anticipated to have significant effects on the cryptocurrency market in 2025. While predicting precise market movements is impossible, analyzing past halvings and current market conditions offers insights into potential short-term and long-term impacts on Bitcoin’s price. The reduced supply coupled with potential increased demand often creates a scenario of price appreciation. However, other macroeconomic factors and market sentiment also play crucial roles.
The impact of Bitcoin halvings on price is a complex interplay of supply and demand dynamics. Historically, halvings have been followed by periods of price increases, though the timing and magnitude of these increases have varied. Understanding these past patterns, while acknowledging the unique circumstances of each halving event, is crucial for forming reasonable expectations for 2025. The effect is not instantaneous; it unfolds over time, influenced by various market forces beyond the halving itself.
Short-Term Price Effects
The short-term effects of the 2025 halving are likely to be characterized by increased volatility. In the months leading up to the event, we might observe a period of price anticipation, with investors potentially accumulating Bitcoin in expectation of future price appreciation. Immediately following the halving, the market could experience a period of uncertainty as traders assess the actual impact of the reduced supply on demand. This could lead to price fluctuations, potentially including both upward and downward movements. The 2012 and 2016 halvings saw a period of price consolidation after the event, followed by a significant bull run months later. The 2020 halving also exhibited similar trends, although the subsequent bull run was preceded by a significant period of price consolidation.
Long-Term Price Effects
The long-term effects of the halving are predicted to be more significant. The reduction in Bitcoin’s inflation rate, caused by the halving, is a deflationary pressure that could theoretically drive up its value over the longer term. This effect is based on the fundamental principle of supply and demand: a decrease in supply, assuming constant or increasing demand, will typically lead to price appreciation. However, this is not guaranteed, and other market forces can significantly influence the long-term price trajectory. The narrative surrounding scarcity and the perceived value of Bitcoin also play a considerable role. The adoption rate of Bitcoin, regulatory changes, and macroeconomic conditions will also heavily influence its price in the long run.
Comparison to Previous Halvings
Analyzing the previous three halvings provides valuable context for predicting the 2025 event. The 2012 halving was followed by a significant price increase, though the market was still relatively nascent. The 2016 halving also resulted in a substantial price surge, albeit with a time lag. The 2020 halving led to a period of price consolidation, followed by a significant bull market that peaked in late 2021. While all three halvings were followed by periods of price appreciation, the timing and magnitude varied considerably. This underscores the complexity of predicting market behavior and the influence of factors beyond the halving itself.
Hypothetical Market Scenario for 2025
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario. In the months leading up to the 2025 halving (anticipated to be in late March or early April), we could see a gradual increase in Bitcoin’s price driven by anticipation. This could be accompanied by increased trading volume and overall market excitement. Immediately after the halving, there might be a period of short-term price volatility as the market adjusts to the new reality of reduced block rewards. This could involve both upward and downward price movements. However, if the overall market sentiment remains positive, driven by continued adoption and positive macroeconomic conditions, a significant bull run could ensue, potentially over several months or even years. Conversely, a negative macroeconomic environment or regulatory crackdown could dampen the positive impact of the halving, resulting in a less pronounced price increase or even a price decline. This scenario emphasizes the interplay between the halving’s impact and other external factors.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price Post-Halving: When Is The Bitcoin Halving In 2025
While the Bitcoin halving significantly reduces the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation, impacting supply, it’s not the sole determinant of price. Numerous other factors, interacting in complex ways, will shape Bitcoin’s price trajectory in 2025 and beyond. Understanding these interwoven influences is crucial for a comprehensive perspective.
Regulatory Changes
Government regulations globally play a pivotal role in shaping cryptocurrency markets. Stringent regulations can stifle adoption and potentially suppress price, while supportive or clear regulatory frameworks can foster growth and increase investor confidence, driving prices upward. For example, the increasing clarity around Bitcoin’s regulatory status in certain jurisdictions has historically correlated with price increases. Conversely, sudden crackdowns or unclear regulatory landscapes can lead to significant price drops. The evolving regulatory landscape remains a major source of uncertainty and volatility.
Technological Advancements
Innovations within the Bitcoin ecosystem and broader blockchain technology significantly impact Bitcoin’s value proposition and, consequently, its price. Improvements in scalability, transaction speed, and energy efficiency can increase Bitcoin’s usability and appeal, potentially boosting demand and price. Conversely, significant technological setbacks or the emergence of superior competing technologies could negatively impact Bitcoin’s market share and price. The development of the Lightning Network, for instance, is a positive technological advancement aiming to improve Bitcoin’s scalability.
Macroeconomic Conditions
Global macroeconomic factors exert a powerful influence on Bitcoin’s price. Periods of economic uncertainty, inflation, or geopolitical instability can drive investors towards Bitcoin as a safe haven asset, increasing demand and pushing prices higher. Conversely, periods of economic stability or a shift in investor sentiment away from riskier assets could lead to price declines. The correlation between Bitcoin’s price and the performance of traditional financial markets, particularly during times of inflation, has been observed repeatedly.
Comparative Influence of Factors
| Factor | Short-Term Influence | Long-Term Influence | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Changes | High | High | A sudden ban in a major market can cause immediate price drops; clear regulatory frameworks can attract institutional investment over time. |
| Technological Advancements | Moderate | High | A major upgrade improving transaction speed might see a short-term price bump, but long-term adoption will drive sustained growth. |
| Macroeconomic Conditions | High | Moderate | Global recessionary fears can drive a short-term surge in Bitcoin’s price as investors seek safe haven assets, but long-term impact depends on the overall economic recovery. |
Investment Strategies Around the Halving
The Bitcoin halving, a significant event in the cryptocurrency’s lifecycle, often triggers considerable market volatility. Understanding this volatility and employing appropriate investment strategies is crucial for navigating the potential opportunities and risks. Different approaches exist, each with its own risk-reward profile, and past halvings offer valuable lessons for investors.
Buy-and-Hold Strategy
This strategy involves purchasing Bitcoin and holding it for the long term, regardless of short-term price fluctuations. The core belief is that Bitcoin’s value will appreciate over time due to its scarcity and increasing adoption. The primary risk is the potential for significant price drops before the halving and in the period immediately following it. However, historically, buy-and-hold investors have often profited significantly in the long run following past halving events. For example, investors who held Bitcoin through the 2012 and 2016 halvings experienced substantial gains over the subsequent years. The reward is the potential for substantial long-term returns, but requires significant patience and risk tolerance.
Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA) Strategy
DCA involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the price. This strategy mitigates the risk of investing a large sum at a market peak. While it may not yield the highest returns if the price consistently rises, it reduces the impact of volatility and prevents impulsive decisions based on short-term price movements. The risk is lower than a lump-sum investment, but the potential rewards might also be lower compared to a perfectly timed market entry. During previous halvings, DCA has proven to be a relatively stable and less emotionally charged approach, particularly beneficial for investors with a long-term horizon.
Trading Strategy
Trading involves actively buying and selling Bitcoin based on short-term price movements and market analysis. This strategy aims to capitalize on price volatility around the halving, potentially generating quick profits. However, it requires significant market knowledge, technical analysis skills, and risk management expertise. The high risk stems from the potential for significant losses if market predictions are inaccurate. Successful trading around past halvings has been achieved by those with a deep understanding of technical indicators and market sentiment. However, many traders have also experienced substantial losses due to unpredictable market swings. The reward is the potential for high returns, but only if executed skillfully and with a strong risk management plan.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Strategies
Successful strategies during past halvings often involved a combination of long-term holding and strategic trading. Investors who bought Bitcoin before the halving and held through the subsequent price increase experienced substantial gains. Conversely, those who attempted to time the market perfectly often missed out on significant gains or incurred losses due to inaccurate predictions. For example, those who sold their Bitcoin immediately after a halving, expecting a rapid price drop, often missed out on the subsequent price appreciation. Conversely, those who held through periods of price stagnation or even decline eventually saw their investments significantly appreciate.
The Halving and Bitcoin Mining
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event reducing the block reward paid to miners, significantly impacts the profitability and sustainability of Bitcoin mining operations. This reduction in reward directly affects miners’ revenue streams, triggering a cascade of consequences throughout the Bitcoin ecosystem, influencing everything from network security to the evolution of mining hardware.
The halving cuts the block reward in half, meaning miners receive fewer bitcoins for verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain. This immediately reduces the profitability of mining, as the income generated from block rewards is halved. This decreased profitability necessitates adjustments across the mining industry.
Miner Profitability and Network Security
The halving’s impact on miner profitability is directly tied to the security of the Bitcoin network. Miners secure the network by investing significant computational power in solving complex cryptographic puzzles. Their participation is incentivized by the block reward and transaction fees. A reduction in profitability could lead some miners to become unprofitable and cease operations, potentially weakening the network’s security if the overall hash rate (a measure of the computational power dedicated to mining) drops significantly. However, historically, the network has adapted, demonstrating resilience. For example, following previous halvings, some less efficient miners have exited the market, while more efficient operations have continued, maintaining a strong network hash rate. The overall effect has been a consolidation of the mining industry, favoring larger, more efficient operations.
Consequences for Miners: Increased Competition and Consolidation, When Is The Bitcoin Halving In 2025
Reduced profitability post-halving intensifies competition among miners. Miners must either improve their efficiency (through better hardware, more efficient energy sources, or improved operational strategies) or risk becoming unprofitable. This competitive pressure drives consolidation within the mining industry. Smaller, less efficient mining operations may be forced to merge with larger entities or cease operations altogether. This leads to a more concentrated mining landscape, dominated by larger, more resource-rich players. This concentration can have both positive and negative implications. While it can enhance network security through the concentration of hashing power in more reliable hands, it also raises concerns about centralization and potential vulnerabilities.
Changes in Mining Hardware and Energy Consumption
The halving incentivizes innovation in mining hardware and energy efficiency. To maintain profitability in a lower-reward environment, miners are driven to adopt more energy-efficient and powerful mining hardware. This constant drive for efficiency results in a technological arms race, leading to the development of more advanced ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) designed specifically for Bitcoin mining. The shift towards more efficient hardware reduces the overall energy consumption per bitcoin mined, but the overall energy consumption of the network might still increase if the total hash rate increases due to the entry of new, efficient miners. This is a complex dynamic, dependent on the interplay of reduced reward per bitcoin mined and the adoption of more efficient hardware and mining practices. For example, the transition from older, less efficient ASICs to newer, more efficient models after previous halvings has demonstrably improved the network’s energy efficiency per bitcoin.
Beyond the Price
The Bitcoin halving, while significantly impacting price, is far more than just a market event. Its consequences ripple across the entire Bitcoin ecosystem and even influence the broader cryptocurrency landscape. Understanding these broader implications is crucial for a complete perspective on the halving’s significance.
The halving’s impact extends beyond simple price fluctuations to influence the fundamental aspects of Bitcoin’s functionality and long-term viability. These effects are intertwined and contribute to a complex picture of how this event shapes the future of Bitcoin and digital currencies.
Network Decentralization
The Bitcoin halving directly affects the profitability of Bitcoin mining. Reduced block rewards mean miners need to rely more on transaction fees to remain profitable. This incentivizes miners to focus on optimizing transaction processing efficiency and security rather than solely pursuing block rewards. This, in turn, strengthens network decentralization by potentially reducing the dominance of large mining pools and encouraging a more distributed network of miners. The increased reliance on transaction fees also incentivizes higher transaction volume, which benefits the overall health and resilience of the network. Historically, halvings have been followed by periods of increased hashrate (the computational power securing the network), suggesting that miners adapt and consolidate, rather than simply exiting the market.
Adoption and Technological Developments
A halving can trigger renewed interest in Bitcoin, leading to increased adoption. The anticipation surrounding the event often generates significant media coverage, educating a wider audience about Bitcoin and prompting new users to explore the technology. This heightened awareness can drive demand, further impacting the price, but also potentially broadening the user base and strengthening the network’s overall utility. Furthermore, the halving might incentivize development within the Bitcoin ecosystem. As miners seek new ways to optimize profitability, technological innovation in mining hardware and software is often stimulated. This can lead to advancements in areas such as energy efficiency and mining pool management, further enhancing the network’s robustness and sustainability.
Impact on the Broader Cryptocurrency Market and Financial Landscape
The Bitcoin halving’s influence extends beyond the Bitcoin network itself. It can significantly affect the broader cryptocurrency market, creating ripple effects across other digital assets. For example, the anticipation and subsequent price movements in Bitcoin often lead to correlated price changes in altcoins (alternative cryptocurrencies). Investors may shift their portfolios based on perceived opportunities or risks associated with the halving. The event also highlights the evolving nature of the digital asset space and the potential for significant market shifts, attracting attention from both traditional and decentralized finance players. This increased interest can lead to greater regulatory scrutiny and potentially shape future financial policies related to cryptocurrencies. The increased focus on Bitcoin’s scarcity post-halving can also impact how other cryptocurrencies are perceived and valued, potentially driving innovation in areas such as tokenomics and consensus mechanisms.