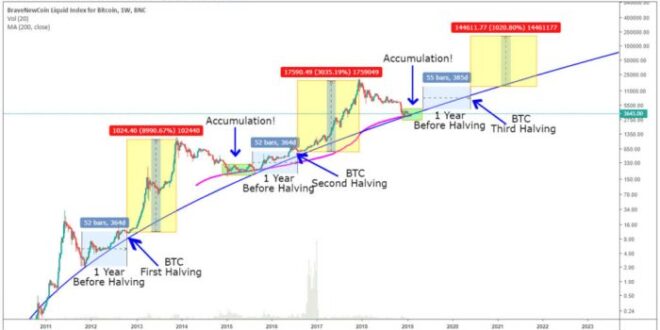
2025 Bitcoin Halving
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, anticipated to occur in April, marks a significant event in the cryptocurrency’s lifecycle. This periodic reduction in the rate of newly mined Bitcoin is a core feature of its design, intended to control inflation and maintain scarcity. Understanding its mechanics and potential impact is crucial for anyone involved in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Bitcoin Halving Mechanics and Historical Impact
The Bitcoin halving mechanism is programmed into the Bitcoin protocol. Every 210,000 blocks mined (approximately every four years), the reward given to Bitcoin miners for verifying transactions is cut in half. This halving directly impacts the rate at which new Bitcoin enters circulation. Historically, halvings have been followed by periods of increased Bitcoin price, although the extent and duration of these price increases have varied. The first halving in 2012 saw a relatively modest price increase, while the second in 2016 and the third in 2020 preceded significant bull runs, albeit with periods of volatility and correction. The correlation between halvings and price appreciation is not definitively causal, but the reduced supply is a contributing factor to a potentially tighter market.
Anticipated Effects on Supply and Demand
The 2025 halving will reduce the block reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC. This reduction in supply, coupled with anticipated continued demand, is expected to create upward pressure on the price. However, the actual impact depends on several factors including macroeconomic conditions, regulatory developments, and overall market sentiment. A decrease in the rate of new Bitcoin entering the market creates a scenario where demand potentially outstrips supply, leading to a price increase. This dynamic is a key driver of the bullish predictions surrounding the 2025 halving.
Potential Price Scenarios
Following the 2025 halving, several price scenarios are possible. A bullish scenario might see a significant price surge, potentially exceeding previous all-time highs, driven by the reduced supply and increased investor interest. This could be similar to the bull runs observed after the 2016 and 2020 halvings, though the magnitude is difficult to predict. A more conservative bullish scenario anticipates a gradual price increase over a longer period. Conversely, a bearish scenario might see the price remain relatively stagnant or even decline, due to factors like a broader economic downturn, regulatory uncertainty, or a decrease in overall investor confidence. This scenario highlights the importance of considering macroeconomic factors that can influence Bitcoin’s price independently of the halving.
Comparison to Previous Halvings
While the halving mechanism remains consistent, each event occurs within a unique macroeconomic and market context. The 2012 halving took place in a relatively nascent market with lower overall adoption and less regulatory scrutiny. The 2016 and 2020 halvings occurred in more mature markets with increased institutional involvement and greater regulatory attention. The 2025 halving will likely occur in a market further shaped by these trends, making direct comparisons challenging but providing valuable historical context for informed speculation.
Timeline of Key Events
The following timeline illustrates key events leading up to and following the 2025 Bitcoin halving. This is a simplified representation and specific dates are subject to change.
| Date | Event | Impact | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q4 2024 | Increased Market Speculation | Price Volatility | Anticipation of the halving |
| April 2025 (approx.) | Bitcoin Halving | Reduced Block Reward | Core event, impacting supply |
| Q2-Q3 2025 | Potential Price Surge | Increased Market Capitalization | Bullish scenario response |
| Q4 2025 – 2026 | Market Consolidation/Correction | Price Volatility | Natural market adjustment |
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price After the Halving
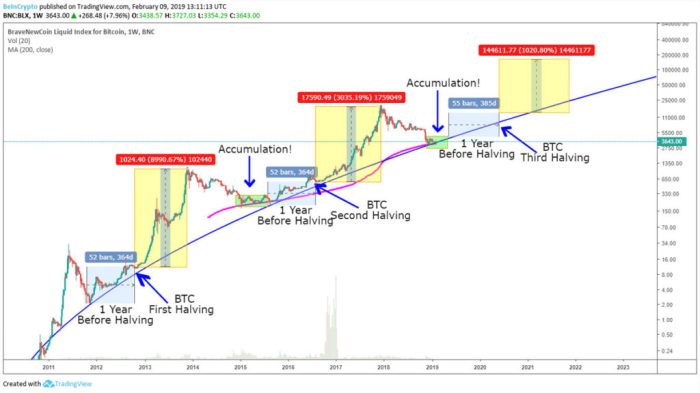
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, reducing the block reward for miners by half, is a significant event expected to impact Bitcoin’s price. However, the price movement is not solely determined by the halving itself; numerous interconnected factors will play crucial roles in shaping the market in the period surrounding and following this event. Understanding these influences is vital for navigating the potential volatility.
Macroeconomic Factors
Broad economic conditions significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. High inflation, for example, can drive investors towards Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation, potentially increasing demand and price. Conversely, rising interest rates, making traditional investments more attractive, could divert capital away from Bitcoin, leading to price decreases. The overall global economic outlook – recessionary fears versus robust growth – also plays a critical role. A pessimistic outlook might lead investors to seek safe haven assets, potentially benefiting Bitcoin, while positive economic growth could lead investors to prioritize higher-yield investments. The strength of the US dollar, a common benchmark against which Bitcoin is valued, also influences its price. A strengthening dollar typically puts downward pressure on Bitcoin’s price, while a weakening dollar can have the opposite effect.
Regulatory Developments and Governmental Policies
Governmental regulations and policies surrounding cryptocurrencies are potent forces impacting Bitcoin’s price. Favorable regulatory frameworks, such as clear guidelines for cryptocurrency trading and taxation, can boost investor confidence and increase institutional adoption. Conversely, stringent regulations, bans, or uncertain regulatory environments can create volatility and negatively impact price. Examples include China’s previous ban on cryptocurrency mining and trading, which significantly impacted the market, or the ongoing debates in various countries regarding cryptocurrency taxation and classification. These regulatory shifts directly influence investor sentiment and market liquidity.
Institutional Adoption and Large-Scale Investments
The involvement of institutional investors, such as large corporations, hedge funds, and pension funds, is increasingly significant in the cryptocurrency market. Increased institutional adoption leads to greater liquidity, reduced volatility (to a certain extent), and a higher market capitalization. Large-scale investments by these entities can drive substantial price increases due to the sheer volume of capital involved. The opposite is also true; if institutional investors decide to divest from Bitcoin, it could trigger a significant price correction. Examples of this include the investments made by MicroStrategy and Tesla, which significantly impacted Bitcoin’s price at the time.
Technological Advancements and Bitcoin Network Upgrades
Technological advancements within the Bitcoin network itself can also influence its price. Successful upgrades improving scalability, transaction speed, or security can increase investor confidence and attract new users. Conversely, setbacks or delays in upgrades could negatively affect market sentiment. The development of the Lightning Network, for instance, aims to improve Bitcoin’s scalability, potentially making it more attractive for everyday transactions and driving price appreciation if successful. Conversely, a significant security breach or a major network failure could severely impact investor confidence and lead to price drops.
Miner Behavior and Mining Profitability
After the halving, miners’ profitability decreases as the block reward is reduced. This can lead to several outcomes. Some miners might choose to shut down operations if the cost of mining exceeds the revenue generated, reducing the network’s hashrate. This could theoretically increase the security risk of the network. Conversely, miners may become more efficient to maintain profitability, potentially driving innovation in mining hardware and techniques. The overall impact on price depends on the balance between reduced mining profitability, potential network security concerns, and the market’s reaction to these factors. The price of Bitcoin would need to increase to compensate for the reduced mining rewards to ensure miners remain profitable.
Bitcoin’s Long-Term Prospects Beyond 2025: 2025 Bitcoin Halving Date
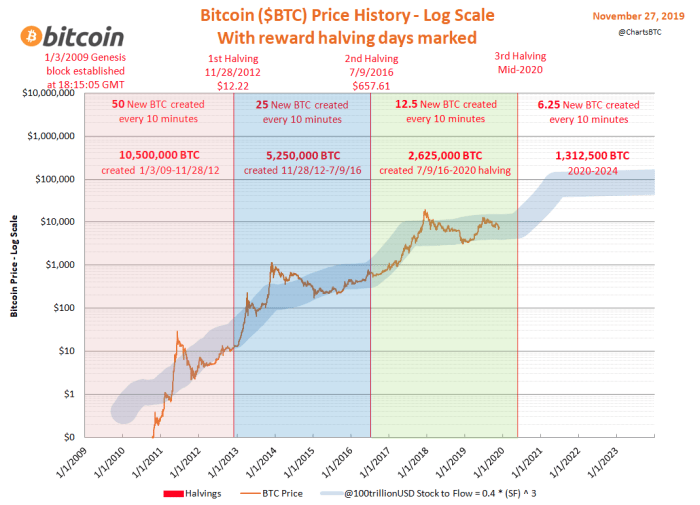
The 2025 Bitcoin halving is a significant event, but it’s only one piece of a much larger puzzle concerning Bitcoin’s long-term trajectory. Predicting the future of any asset, especially one as volatile as Bitcoin, is inherently challenging. However, by considering various factors alongside the halving’s impact on supply, we can construct a plausible outlook for Bitcoin’s future.
Bitcoin’s price, beyond the immediate post-halving effects, will likely be driven by a complex interplay of factors. These include macroeconomic conditions (inflation, recessionary pressures, etc.), regulatory developments globally, technological advancements within the Bitcoin ecosystem, and the overall adoption rate by individuals and institutions. The halving’s impact, while significant in reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation, will be felt alongside these broader market forces.
Bitcoin as a Store of Value and Medium of Exchange
The potential for Bitcoin to become a mainstream store of value is arguably its strongest long-term prospect. Its fixed supply, decentralized nature, and growing recognition as a hedge against inflation are key drivers. However, its volatility remains a significant hurdle to widespread adoption as a medium of exchange. For Bitcoin to become a commonly used currency for everyday transactions, its price needs to stabilize and transaction fees must become significantly lower. Real-world examples, such as El Salvador’s adoption of Bitcoin as legal tender, highlight both the potential and the challenges involved in widespread adoption. While El Salvador’s experiment provides a case study, its success remains debatable, illustrating the complexities involved in transitioning to a Bitcoin-based economy.
Bitcoin’s Performance Compared to Other Assets
Understanding Bitcoin’s potential requires comparing its performance and risk profile to other alternative investments.
| Asset | Average Annual Return (Past 10 Years) | Volatility (Past 10 Years) | Correlation with Bitcoin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | 200% (approx.) | High | N/A |
| Gold | 5% (approx.) | Low to Moderate | Weak Positive |
| S&P 500 | 10% (approx.) | Moderate | Weak Positive |
| Real Estate | Variable, depends on location and market conditions | Moderate to Low | Weak to no correlation |
*Note: These figures are approximate and based on past performance, which is not indicative of future results. The correlation values represent general trends and can fluctuate.*
Challenges and Opportunities for Bitcoin
Bitcoin faces several challenges beyond 2025, including regulatory uncertainty, scalability issues, and the ongoing threat of competing cryptocurrencies. However, opportunities abound. Increased institutional adoption, technological advancements (like the Lightning Network), and growing awareness of its underlying technology could significantly boost its value and utility. The development of more user-friendly interfaces and improved security measures will also be crucial for wider adoption. For example, the increasing use of custodial services by institutional investors indicates a growing level of comfort and trust in Bitcoin’s security and potential.
Risks and Uncertainties Associated with Bitcoin
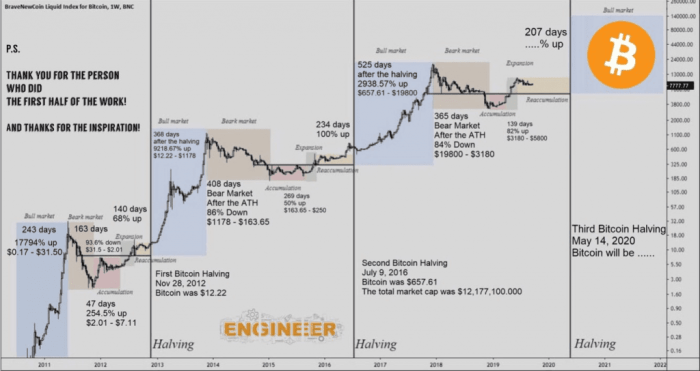
Investing in Bitcoin, while potentially lucrative, carries significant risks. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed investment decisions and mitigating potential losses. This section details the key risks associated with Bitcoin, encompassing volatility, regulatory uncertainty, security concerns, and environmental impact.
Volatility and Market Manipulation
Bitcoin’s price is notoriously volatile, experiencing substantial fluctuations in short periods. These swings can be driven by various factors, including news events, market sentiment, and regulatory changes. For example, the price of Bitcoin plummeted significantly in 2022 due to a combination of macroeconomic factors and the collapse of several major cryptocurrency exchanges. The potential for market manipulation also contributes to volatility. Large holders, or “whales,” can influence the price through coordinated buying or selling, creating artificial price increases or crashes. This manipulation can significantly impact smaller investors who may lack the resources to withstand such price swings. The decentralized nature of Bitcoin makes it challenging to completely prevent such manipulation, although regulatory efforts are underway to address this issue.
Regulatory Uncertainty, 2025 Bitcoin Halving Date
The regulatory landscape surrounding Bitcoin varies considerably across jurisdictions. Some countries have embraced Bitcoin and established clear regulatory frameworks, while others maintain a more cautious or even hostile stance. This regulatory uncertainty creates risks for investors, as changes in regulations can significantly impact the value and usability of Bitcoin. For instance, a government ban on Bitcoin transactions could dramatically reduce its value. The lack of consistent global regulation also presents challenges for cross-border transactions and investment.
Security Risks
Bitcoin’s security relies on robust cryptographic techniques and a decentralized network. However, security risks remain. These include the potential for hacking of exchanges, theft of private keys, and vulnerabilities in Bitcoin wallets. The loss of private keys renders the associated Bitcoin inaccessible, resulting in permanent loss of funds. Furthermore, exchanges, while generally secure, have been targets of successful hacking attempts in the past, leading to significant losses for users. Sophisticated phishing scams also pose a considerable risk, targeting unsuspecting users to steal their Bitcoin.
Environmental Concerns
Bitcoin mining, the process of validating transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain, consumes significant amounts of energy, primarily due to the computational power required. This energy consumption raises environmental concerns, particularly regarding carbon emissions. While the energy source used for mining varies geographically, a large portion still relies on fossil fuels. However, initiatives promoting the use of renewable energy sources in Bitcoin mining are gaining traction, aiming to reduce the environmental footprint of this technology. This shift towards sustainable energy sources is crucial for the long-term viability and acceptance of Bitcoin.
Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
The following list summarizes key risks and potential mitigation strategies:
- Risk: High Volatility. Mitigation: Dollar-cost averaging, setting stop-loss orders, only investing what you can afford to lose.
- Risk: Regulatory Uncertainty. Mitigation: Staying informed about regulatory developments, diversifying geographically, considering jurisdictions with clear regulatory frameworks.
- Risk: Security Breaches. Mitigation: Using reputable exchanges and wallets, enabling two-factor authentication, regularly backing up private keys, avoiding phishing scams.
- Risk: Market Manipulation. Mitigation: Diversifying investments, avoiding emotional trading, relying on fundamental analysis rather than short-term price movements.
- Risk: Environmental Impact. Mitigation: Supporting miners who utilize renewable energy sources, advocating for environmentally friendly mining practices.
The Importance of Diversification
Diversification is a fundamental principle of risk management in investing. Including Bitcoin in an investment portfolio should be done strategically, acknowledging its high volatility. Diversification across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and other cryptocurrencies, can help mitigate the overall risk and reduce the impact of potential losses in any single asset. A well-diversified portfolio aims to balance risk and return, minimizing the impact of adverse events on the overall portfolio value. This approach is particularly important for Bitcoin, given its inherent volatility and uncertainty.