Understanding Bitcoin Halving Mechanics
Bitcoin halving is a crucial programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. This mechanism is fundamental to Bitcoin’s design, impacting its inflation rate and long-term scarcity. Understanding its mechanics is key to grasping Bitcoin’s economic model.
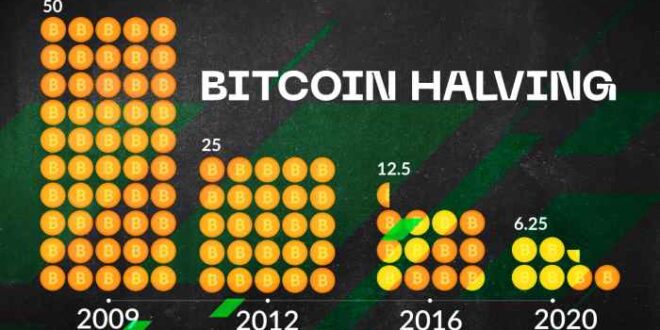
The Bitcoin halving process is a pre-programmed reduction in the block reward, the amount of Bitcoin awarded to miners for successfully adding a block of transactions to the blockchain. This reward is halved approximately every four years, or every 210,000 blocks mined. This predictable schedule ensures a controlled and gradually decreasing supply of new Bitcoins entering circulation.
The Halving Mechanism
The halving mechanism is embedded within the Bitcoin code. It’s a simple yet powerful algorithm that automatically adjusts the block reward. Initially, the block reward was 50 BTC. After the first halving, it became 25 BTC, then 12.5 BTC, and so on. Each halving event precisely cuts the reward in half. This process continues until the maximum supply of 21 million Bitcoin is reached, at which point the block reward will become zero. Miners will then rely solely on transaction fees to incentivize their participation in securing the network.
Mathematical Principles of Bitcoin’s Halving Schedule
The halving schedule is based on a geometric progression. The formula for calculating the total number of Bitcoin created after n halvings is:
Total Bitcoin = 50 * (1 – (1/2)^n) * 2^n
where ‘n’ represents the number of halvings that have occurred. This formula shows how the total number of Bitcoins approaches but never exceeds 21 million. The constant halving ensures a predictable decrease in inflation, gradually transitioning Bitcoin from an inflationary asset to a deflationary one.
Visual Representation of Halving’s Impact on New Bitcoin Issuance
Imagine a graph with the x-axis representing time (in years) and the y-axis representing the number of new Bitcoins issued per year. Initially, the line would be relatively high, representing the large number of Bitcoins added during early years. After each halving, the line would drop sharply, representing the reduced issuance rate. The line would continue to approach zero, never quite reaching it, mirroring the asymptotic approach to the 21 million Bitcoin limit. This visual demonstrates the decreasing rate of inflation over time.
Long-Term Implications of Halving on Bitcoin’s Scarcity
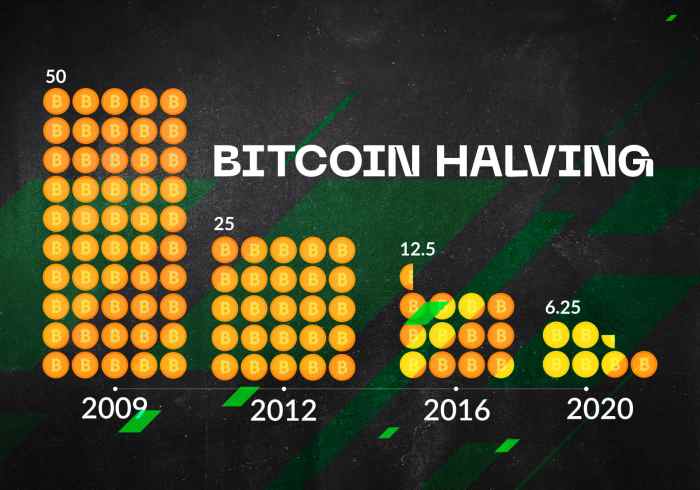
The halving mechanism is a cornerstone of Bitcoin’s scarcity. As the supply of new Bitcoins decreases, each Bitcoin becomes relatively more scarce. This increased scarcity, coupled with potential increases in demand, is anticipated to drive up the value of Bitcoin over the long term. Historical data from previous halvings has shown a correlation between halving events and subsequent price increases, although the precise extent of the impact is subject to market forces and other economic factors. For example, the halving in 2012 and 2016 were followed by significant bull markets, though other market forces also contributed. The upcoming 2024 halving is expected to follow a similar pattern, though this is not guaranteed.
Market Predictions and Price Analysis for 2025
The 2025 Bitcoin halving is a significant event anticipated to impact the cryptocurrency’s price. Predicting the exact market reaction is impossible, but analyzing historical trends, considering influencing factors, and reviewing expert opinions provides a framework for understanding potential price movements. This analysis will explore various predictions and models, highlighting the inherent volatility surrounding such a pivotal event.
Potential Market Reactions to the 2025 Halving
Historically, Bitcoin’s price has shown a tendency to increase in the period following a halving event. This is primarily attributed to the reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin, potentially increasing scarcity and driving up demand. However, this is not a guaranteed outcome, and other market forces can significantly influence the price. The 2012 and 2016 halvings saw price increases in the subsequent months and years, but the timing and magnitude of these increases varied. For example, the price surge after the 2016 halving was less immediate than after the 2012 halving. This highlights the complexity of predicting the precise market reaction.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price After the Halving
Several factors beyond the halving itself can significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. These include macroeconomic conditions (like inflation rates and interest rate hikes), regulatory changes (both favorable and unfavorable), technological advancements within the Bitcoin network, and overall market sentiment and adoption rates. For instance, a global economic downturn could negatively affect Bitcoin’s price regardless of the halving, while widespread institutional adoption could drive prices significantly higher. Similarly, regulatory clarity in major markets could boost investor confidence, whereas increased regulatory scrutiny could lead to price drops.
Comparison of Expert Predictions
Expert opinions on Bitcoin’s price post-halving vary considerably. Some analysts predict substantial price increases, pointing to the halving’s deflationary effect and increasing institutional adoption. Others are more cautious, highlighting the potential for market corrections and the impact of macroeconomic factors. For example, some analysts have projected prices reaching $100,000 or more by the end of 2025, while others predict a more modest increase or even a temporary price decline before a later surge. The divergence in predictions underscores the inherent uncertainty in forecasting cryptocurrency prices.
Comparative Table of Price Prediction Models
The following table compares different price prediction models, highlighting the range of potential outcomes. Note that these are illustrative examples and not exhaustive of all models or predictions.
| Model Name | Prediction Methodology | Price Prediction (USD) by end of 2025 | Underlying Assumptions |
|———————-|———————————————|—————————————|—————————————————————–|
| Stock-to-Flow Model | Based on Bitcoin’s scarcity and historical data | $150,000 – $200,000 | Continued institutional adoption, stable macroeconomic conditions |
| On-Chain Analysis | Analyzing network activity and transaction data | $75,000 – $125,000 | Moderate adoption growth, potential for market corrections |
| Technical Analysis | Studying price charts and technical indicators | $50,000 – $100,000 | Varies depending on specific indicators and interpretations |
Potential for Volatility, Halving Bitcoin 2025 Countdown
The period surrounding the 2025 halving is likely to be characterized by increased market volatility. As investors anticipate the halving’s impact, price fluctuations are expected to be more pronounced. This volatility stems from the uncertainty surrounding the market’s response to the reduced supply, combined with the influence of external factors. Historically, Bitcoin has experienced significant price swings in the lead-up to and following previous halving events, suggesting that similar volatility should be anticipated in 2025. This heightened volatility presents both risks and opportunities for investors.
Impact on Mining and Bitcoin Miners: Halving Bitcoin 2025 Countdown
The Bitcoin halving, scheduled for 2025, significantly impacts the profitability of Bitcoin mining operations by reducing the block reward miners receive for verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain. This reduction, by half, necessitates adjustments within the industry to maintain profitability and operational sustainability.
The halving directly affects the revenue stream of Bitcoin miners. With fewer newly minted bitcoins awarded per block, miners must adapt to compensate for the decreased income. This situation forces a reevaluation of operational costs, including energy consumption, hardware maintenance, and personnel expenses.
Miner Profitability Adjustments
Miners will likely implement several strategies to offset the reduced block rewards. These include optimizing mining efficiency through improved hardware, software updates, and more efficient energy management. Many will focus on securing cheaper energy sources, perhaps by relocating operations to regions with lower electricity costs or investing in renewable energy solutions. Additionally, some miners may choose to increase their hashrate by acquiring more mining equipment, although this involves significant upfront capital investment. The overall success of these adjustments will depend on various factors including the price of Bitcoin and the overall mining difficulty. For example, a significant increase in the Bitcoin price could mitigate the impact of the halving on profitability, while a decrease could exacerbate the situation.
Industry Consolidation
The halving is expected to accelerate consolidation within the Bitcoin mining industry. Less efficient and less capitalized mining operations might find it challenging to remain profitable after the block reward reduction. This could lead to smaller miners being forced to shut down or merge with larger, more established entities. This consolidation could result in a more centralized mining landscape, with a smaller number of larger players controlling a greater share of the network’s hashrate. This is analogous to the consolidation seen in other industries following periods of economic downturn, where only the most efficient and well-capitalized companies survive.
Challenges and Opportunities for Miners
The halving presents both challenges and opportunities for Bitcoin miners. The primary challenge is maintaining profitability in the face of reduced rewards. This necessitates stringent cost management, technological innovation, and strategic decision-making. However, the halving also presents opportunities. Miners who successfully navigate the challenges will be better positioned to capitalize on the long-term growth potential of Bitcoin. Those who can optimize their operations and secure cheaper energy will gain a competitive advantage. Furthermore, the increased demand for more efficient mining hardware and software could create new market opportunities for technology providers. The 2012 and 2016 halvings, for instance, served as catalysts for technological advancements in mining hardware and software.
Long-Term Sustainability of Bitcoin Mining
The long-term sustainability of Bitcoin mining post-halving depends on several factors, including the price of Bitcoin, the efficiency of mining operations, and the development of new mining technologies. Historically, Bitcoin’s price has tended to increase following halving events, which would offset the reduced block rewards. However, this is not guaranteed. Continued innovation in mining hardware and software is crucial for maintaining profitability in the long term. The adoption of renewable energy sources can also contribute to the long-term sustainability of Bitcoin mining by reducing its environmental impact and lowering operational costs. The success of these factors will ultimately determine the long-term health and viability of the Bitcoin mining industry.
Investor Sentiment and Strategies
The 2025 Bitcoin halving is generating considerable buzz within the investment community, with sentiment ranging from cautious optimism to outright bullishness. Many anticipate a price increase following the halving, mirroring historical trends, while others remain skeptical, citing macroeconomic uncertainties and the potential for market manipulation. The overall sentiment is heavily influenced by the interplay of historical data, current market conditions, and individual investor risk tolerance.
Investor strategies surrounding the halving are diverse and reflect varying levels of risk appetite and investment horizons. Some investors may adopt a “buy-and-hold” strategy, accumulating Bitcoin before the halving and holding it for the long term, expecting significant price appreciation. Others might employ more active trading strategies, attempting to profit from price volatility before and after the event. A third approach could involve diversifying investments across various asset classes to mitigate risk, potentially allocating a portion of their portfolio to Bitcoin.
Pre-Halving Investment Strategies
Investors considering Bitcoin before the halving have several options. A common strategy is dollar-cost averaging (DCA), where investors regularly invest a fixed amount of money regardless of price fluctuations, reducing the impact of market volatility. Alternatively, some might choose to lump-sum invest, committing a significant amount of capital at once, aiming to capitalize on potential price increases. However, this carries a higher risk, as a sudden price drop could lead to substantial losses. Finally, some investors might utilize leverage through derivatives trading, aiming to amplify potential gains but simultaneously increasing their exposure to risk.
Post-Halving Investment Strategies
After the halving, investors may adopt different approaches. Some might continue to hold their Bitcoin, expecting continued price appreciation driven by reduced supply. Others might consider taking profits, selling a portion or all of their holdings to secure gains. The choice often depends on individual risk tolerance and investment goals. Active traders might attempt to capitalize on post-halving price fluctuations, but this requires careful timing and risk management. For instance, an investor might employ trailing stop-loss orders to protect profits while allowing for further upside potential.
Risk and Reward Analysis
The risk-reward profile varies considerably across different investment strategies. A buy-and-hold strategy generally carries lower transaction costs but exposes investors to potential long-term price declines. Active trading strategies offer higher potential returns but also significantly increase the risk of losses due to market volatility. Leveraged trading amplifies both potential gains and losses, making it suitable only for sophisticated investors with a high risk tolerance. Diversification mitigates risk by spreading investments across multiple assets but might result in lower overall returns compared to concentrated Bitcoin holdings.
Risk Management Considerations
Effective risk management is crucial for navigating the volatility surrounding the Bitcoin halving. Investors should only invest amounts they can afford to lose, avoiding excessive leverage or over-extending their financial capacity. Diversification across various asset classes can help reduce portfolio risk. Setting stop-loss orders can limit potential losses in case of unexpected price drops. Thorough research and understanding of market dynamics are essential to making informed investment decisions.
Macroeconomic Influences on Investor Decisions
Macroeconomic factors play a significant role in shaping investor sentiment and decisions regarding Bitcoin. Inflationary pressures, interest rate hikes by central banks, and geopolitical instability can all influence the demand for Bitcoin as a store of value or hedge against inflation. For example, during periods of high inflation, investors might seek refuge in Bitcoin, driving up demand and potentially increasing its price. Conversely, rising interest rates might make alternative investments more attractive, potentially reducing Bitcoin’s appeal. Economic downturns can also significantly affect investor confidence and risk appetite, impacting Bitcoin’s price.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Bitcoin Halving 2025
The Bitcoin halving is a significant event in the cryptocurrency world, occurring approximately every four years. Understanding its mechanics and potential impact is crucial for both investors and those interested in the future of Bitcoin. This section addresses some common questions surrounding the 2025 halving.
Bitcoin Halving Explained
The Bitcoin halving is a programmed reduction in the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. This event, hardcoded into the Bitcoin protocol, cuts the reward given to Bitcoin miners in half for successfully verifying and adding transactions to the blockchain. This mechanism is designed to control Bitcoin’s inflation rate, making it a deflationary asset in the long term. The initial block reward was 50 BTC, and it has been halved three times already, currently standing at 6.25 BTC per block.
Timing of the Next Bitcoin Halving
The next Bitcoin halving is expected to occur in the spring of 2025, around April or May. The precise date depends on the block generation time, which can fluctuate slightly. However, based on historical data and the current block generation rate, a timeframe around this period is highly probable. Predicting the exact date with complete certainty is impossible due to the inherent variability in block times.
Bitcoin Halving’s Effect on Price
Historically, Bitcoin halvings have been followed by periods of significant price appreciation. This is largely attributed to the reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoins, potentially increasing scarcity and driving demand. The 2012 and 2016 halvings both saw substantial price increases in the months and years following the event. However, it’s important to note that other factors also influence Bitcoin’s price, and past performance is not indicative of future results. External economic conditions, regulatory changes, and overall market sentiment all play a role. For example, the 2020 halving was followed by a significant price surge, but that was also influenced by broader adoption and institutional investment.
Potential Risks Associated with the Halving
While often viewed positively, the halving also presents potential risks. A significant price increase after the halving could lead to a subsequent correction or “bubble burst,” resulting in losses for investors who bought at inflated prices. Furthermore, the halving could exacerbate the existing volatility of Bitcoin, leading to sharp price swings. Additionally, the reduced block reward might negatively impact smaller miners who struggle to remain profitable with lower revenue. This could lead to centralization of mining power, potentially impacting the network’s decentralization.
Investor Preparation for the Bitcoin Halving
Investors should approach the halving with a balanced perspective, acknowledging both the potential opportunities and risks. Thorough research and a well-defined investment strategy are essential. Diversification across different asset classes is crucial to mitigate risk. Investors should only invest what they can afford to lose and avoid making impulsive decisions based solely on price predictions. Considering long-term investment horizons and avoiding emotional reactions to short-term market fluctuations is crucial for successful navigation of this significant event. Understanding the underlying technology and the long-term vision of Bitcoin is also key to making informed investment choices.
Illustrative Examples
Analyzing past Bitcoin halvings provides valuable insights into potential market reactions surrounding the 2025 event. While past performance is not indicative of future results, understanding historical trends offers a framework for informed speculation. The following examples highlight the price movements and market sentiment surrounding each halving, offering a comparative analysis to aid in understanding the potential impact of the upcoming event.
Bitcoin Halving Events: A Historical Overview
Three Bitcoin halvings have occurred to date: November 28, 2012; July 9, 2016; and May 11, 2020. Each event saw a reduction in the Bitcoin block reward, impacting the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation. This change in supply dynamics has historically been followed by periods of price appreciation, although the timing and magnitude of these price increases have varied significantly.
Market Conditions Before, During, and After Each Halving
Prior to the 2012 halving, Bitcoin’s price was relatively low, hovering around $12. The halving itself didn’t immediately trigger a dramatic price surge. However, the subsequent months witnessed a gradual increase, culminating in a significant price rally in late 2013. Before the 2016 halving, Bitcoin traded around $650. The price saw a gradual increase in the months following the halving, eventually peaking at nearly $20,000 in late 2017. Leading up to the 2020 halving, Bitcoin’s price was approximately $9,000. A notable price increase followed, reaching highs above $60,000 in 2021. These examples show that while a halving doesn’t immediately cause a price jump, it often precedes a period of price appreciation.
Comparative Analysis of Bitcoin Halvings
| Halving Date | Price Before Halving (USD) | Price After Halving (Peak, USD) | Time to Peak (Months) | Block Reward Reduction (BTC) |
|—————–|—————————-|——————————-|———————–|—————————–|
| November 28, 2012 | ~$12 | ~$1,100 | ~12 | 50% |
| July 9, 2016 | ~$650 | ~$20,000 | ~18 | 50% |
| May 11, 2020 | ~$9,000 | ~$64,000 | ~12 | 50% |
Investor Reactions to Past Halvings
Following the 2012 halving, many investors remained skeptical, with some even selling their holdings. However, those who held onto their Bitcoin benefited significantly from the subsequent price increase. The 2016 halving saw increased anticipation amongst investors, with many viewing it as a bullish signal. This led to increased investment and trading activity. The 2020 halving generated substantial excitement and anticipation, attracting a wave of new investors to the cryptocurrency market. Investor behavior across these events highlights the importance of long-term investment strategies and the potential risks and rewards associated with market volatility.
Lessons Learned from Past Halvings
Past halvings demonstrate the impact of reduced supply on Bitcoin’s price. However, it’s crucial to remember that other factors, such as regulatory changes, macroeconomic conditions, and overall market sentiment, also significantly influence price movements. The timing and magnitude of price increases after each halving have varied considerably. Therefore, while halvings can be considered a bullish catalyst, it is unwise to rely solely on this event for investment decisions. A comprehensive understanding of the broader market context is essential for informed investment strategies.