Bitcoin Halving 2025: Bitcoin Halving 2025 What To Expect

Bitcoin halving is a significant event in the cryptocurrency world, occurring approximately every four years. It’s a programmed reduction in the rate at which new Bitcoins are created, impacting the supply and potentially influencing the market price. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for navigating the cryptocurrency landscape.
Bitcoin Halving Mechanics and Historical Price Impact
The Bitcoin halving event is a core component of Bitcoin’s design, intended to control inflation. Every 210,000 blocks mined, the reward given to miners for successfully adding a block to the blockchain is cut in half. This programmed scarcity is a key differentiator from traditional fiat currencies. Historically, halving events have been followed by periods of increased price volatility, often leading to significant price increases in the months and years following the event. However, it’s crucial to remember that correlation does not equal causation; other market factors also play a substantial role.
Expected Block Reward Reduction in 2025
In 2025, the Bitcoin halving will reduce the block reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC per block. This represents a 50% decrease in the newly minted Bitcoin entering circulation with each block added to the blockchain. This reduction in supply is anticipated to have a significant impact on the market dynamics, potentially affecting price and overall market sentiment. The precise effect, however, remains uncertain and subject to various economic and market forces.
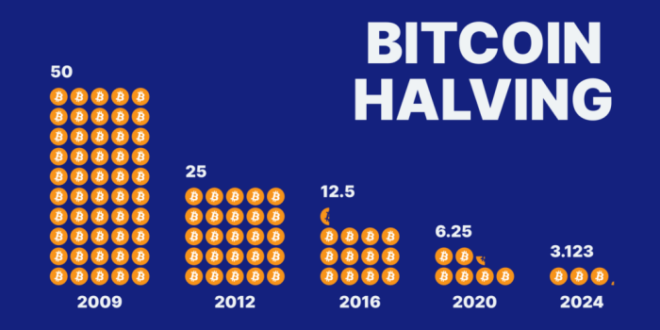
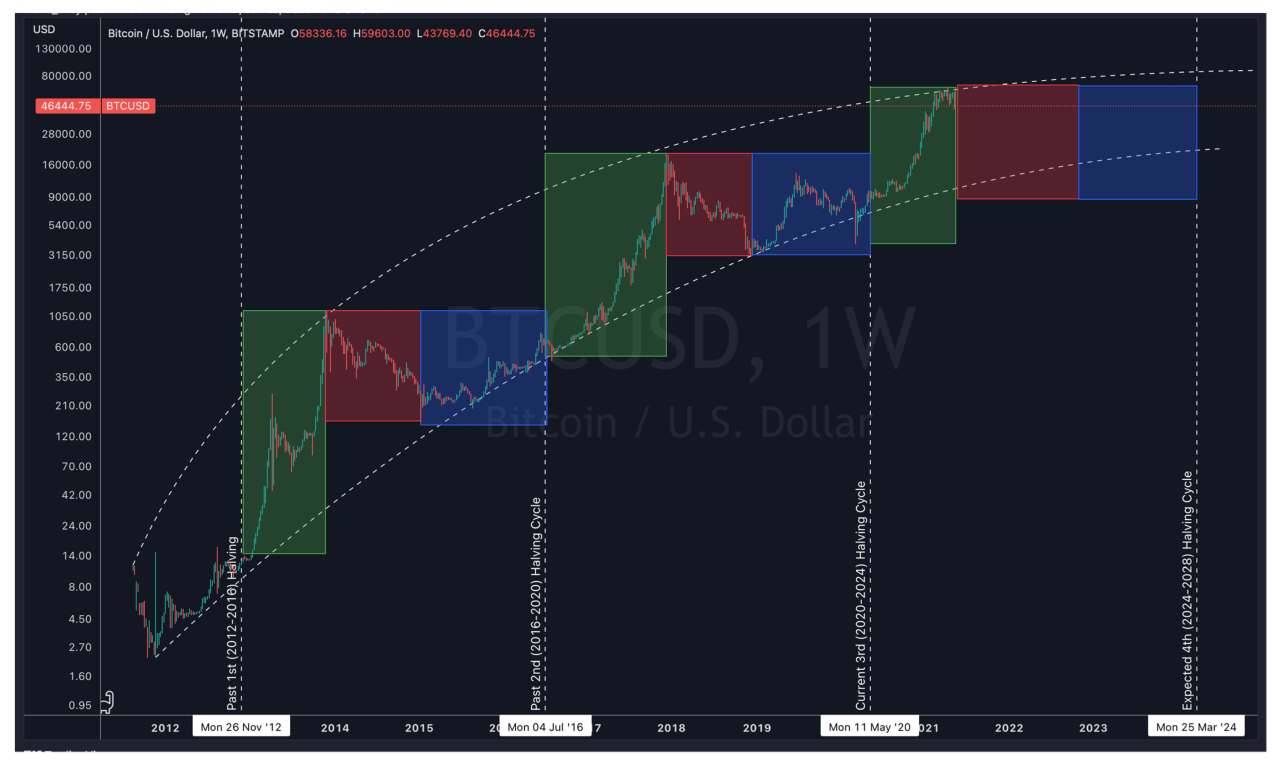
Timeline of Past Bitcoin Halvings and Subsequent Price Movements
Bitcoin has experienced three previous halving events. Analyzing these past events offers insights into potential future price behavior, though past performance is not indicative of future results.
| Halving Date | Block Reward Before | Block Reward After | Approximate Price Movement (Post-Halving) |
|---|---|---|---|
| November 28, 2012 | 50 BTC | 25 BTC | Significant price increase over the following year |
| July 9, 2016 | 25 BTC | 12.5 BTC | Substantial price appreciation within two years |
| May 11, 2020 | 12.5 BTC | 6.25 BTC | Significant price increase followed by a correction |
Comparison of Key Metrics Across Previous Halvings
The following table summarizes key metrics across the previous halving events, offering a comparative perspective. Note that price movements are complex and influenced by numerous factors beyond the halving itself.
| Halving Date | Block Reward (BTC) | Mining Difficulty (Approximate) | Price (USD) – 1 year Post Halving (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| November 28, 2012 | 25 | Relatively Low | > $1000 |
| July 9, 2016 | 12.5 | Substantially Higher | >$10000 |
| May 11, 2020 | 6.25 | Significantly Higher |
Predicting the Price Impact of the 2025 Halving
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation, is widely anticipated to impact its price. However, predicting the precise extent of this impact remains challenging due to the complex interplay of various market forces. While historical halvings have shown a correlation with subsequent price increases, extrapolating this trend directly to 2025 requires careful consideration of several factors.
Short-Term and Long-Term Price Effects
The short-term effects of the 2025 halving are likely to be characterized by increased volatility. As the halving approaches, anticipation may drive price increases, potentially leading to a “buy the rumor, sell the news” pattern. Following the event, the reduced supply could exert upward pressure on price, but this effect might be gradual, unfolding over months or even years. Long-term price effects are more uncertain and depend heavily on macroeconomic conditions, regulatory developments, and overall market sentiment. The historical precedent of previous halvings suggests a bullish long-term trend, but significant deviations are possible. For example, the 2012 halving was followed by a period of consolidation before a substantial price surge, while the 2016 halving saw a more gradual price increase leading up to the 2017 bull market.
Comparison of Price Prediction Models
Several models attempt to forecast Bitcoin’s price post-halving. Simple models might extrapolate historical price movements after previous halvings, assuming similar patterns will repeat. More sophisticated models incorporate additional variables, such as on-chain metrics (e.g., network hash rate, transaction volume), macroeconomic indicators (e.g., inflation rates, interest rates), and sentiment analysis from social media and news sources. However, all models are inherently limited by their underlying assumptions and the inherent unpredictability of the market. No model can perfectly capture the nuances of Bitcoin’s price dynamics. For instance, a model relying solely on past halving data might underestimate the impact of increased institutional adoption or stricter regulatory frameworks.
Factors Influencing Price Beyond the Halving
Beyond the halving itself, several external factors could significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. Regulatory clarity or uncertainty in major jurisdictions will play a crucial role. Positive regulatory developments could boost investor confidence, while stricter regulations could dampen enthusiasm. Macroeconomic conditions, including inflation and interest rates, will also impact Bitcoin’s attractiveness as an investment asset. A period of high inflation might drive demand for Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation, while rising interest rates could divert investment towards more traditional assets. Market sentiment, driven by news events, technological advancements, and broader market trends, will be a key determinant of price fluctuations. A negative news cycle, for instance, could trigger a sell-off regardless of the halving’s impact.
Illustrative Price Scenarios
| Scenario | Market Conditions | Price Range (USD) in 2026 |
|---|---|---|
| Bullish | Strong institutional adoption, positive regulatory environment, continued macroeconomic uncertainty | $100,000 – $200,000 |
| Neutral | Moderate institutional adoption, mixed regulatory signals, stable macroeconomic environment | $50,000 – $100,000 |
| Bearish | Slow institutional adoption, negative regulatory developments, strong macroeconomic headwinds | $25,000 – $50,000 |
The Impact on Bitcoin Mining
The Bitcoin halving, occurring approximately every four years, significantly impacts the profitability and operational dynamics of the Bitcoin mining industry. This event reduces the block reward miners receive for successfully adding new transactions to the blockchain, directly affecting their revenue streams and potentially triggering a cascade of consequences throughout the ecosystem. Understanding these impacts is crucial for assessing the future health and stability of the Bitcoin network.
The reduced block reward following the 2025 halving will undoubtedly affect miners’ profitability. With less Bitcoin earned per block, miners will need to adapt to maintain their operations. This could involve increasing mining efficiency, consolidating operations, or potentially exiting the market altogether. The extent of the impact will depend on several factors, including the prevailing Bitcoin price, electricity costs, and the overall competitiveness of the mining landscape. For example, a high Bitcoin price could offset the reduced block reward, while high energy costs could exacerbate the challenges faced by miners. Conversely, a drop in the Bitcoin price coupled with high energy costs could lead to widespread miner capitulation.
Miner Profitability and Operational Adjustments
The halving’s immediate effect is a 50% reduction in the block reward. Miners will need to either drastically reduce their operational costs or see their profit margins shrink significantly. This will necessitate strategic adjustments, such as upgrading to more energy-efficient hardware, optimizing their mining operations, or seeking out cheaper electricity sources. Some miners may choose to consolidate their operations, merging with larger entities to achieve economies of scale and improve their chances of survival in a more competitive market. Others, unable to adapt, may be forced to shut down their operations entirely. This scenario has played out in previous halvings, leading to a period of market consolidation and increased efficiency within the mining sector.
Changes in Mining Hash Rate and Difficulty, Bitcoin Halving 2025 What To Expect
The halving’s impact on the mining hash rate (the total computational power dedicated to mining Bitcoin) is complex and often unpredictable. Initially, the hash rate might experience a temporary dip as less profitable miners are forced to exit the market. However, historically, the hash rate tends to recover and even increase over time as more efficient miners remain and new, more advanced hardware is deployed. The Bitcoin network automatically adjusts the mining difficulty to maintain a consistent block time of approximately 10 minutes. Therefore, a drop in hash rate will lead to a decrease in difficulty, making it easier for the remaining miners to find blocks and maintain profitability. Conversely, a rise in hash rate after the initial adjustment will lead to an increase in difficulty. This adjustment mechanism is crucial for the network’s security and stability.
Consolidation within the Bitcoin Mining Industry
The 2025 halving is likely to accelerate the ongoing trend of consolidation within the Bitcoin mining industry. Smaller, less efficient mining operations will struggle to compete with larger, more established players who can benefit from economies of scale and access to cheaper resources. This could lead to a smaller number of larger mining pools dominating the network, potentially raising concerns about centralization, although this concern is partially mitigated by the decentralized nature of the Bitcoin network itself. Past halvings have shown clear evidence of this consolidation, with many smaller miners exiting the market or being absorbed by larger entities.
Comparison of Mining Hardware and Energy Efficiency
Understanding the energy efficiency of different mining hardware is critical for assessing miner profitability. The following table provides a simplified comparison, keeping in mind that specific performance varies depending on the model and manufacturer. This is a snapshot and doesn’t include all available hardware.
| Hardware Type | Approximate Hash Rate (TH/s) | Approximate Power Consumption (Watts) | Approximate Energy Efficiency (J/TH) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antminer S19 XP | 140 | 3010 | 21.5 |
| Whatsminer M50S++ | 130 | 3470 | 26.7 |
| Antminer S9 (Older Generation) | 13.5 | 1380 | 102.2 |
Note: These figures are estimates and can vary. Energy efficiency (J/TH) represents the joules of energy consumed per terahash of computing power. Lower values indicate greater efficiency. The significant difference in energy efficiency between newer and older hardware highlights the importance of technological advancements in maintaining profitability in the face of reduced block rewards.
Bitcoin Supply and Demand Dynamics
The Bitcoin halving, occurring approximately every four years, significantly impacts the cryptocurrency’s supply and demand dynamics. This event reduces the rate at which new Bitcoin enters circulation, influencing its price and overall market behavior. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the post-halving landscape.
The halving directly affects the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation by cutting the reward miners receive for verifying transactions on the blockchain in half. Before the halving, miners receive a certain number of Bitcoin for each block they successfully mine. After the halving, this reward is reduced, meaning fewer new Bitcoin are added to the existing supply. This controlled inflation mechanism is a core feature of Bitcoin’s design, intended to create scarcity over time.
Bitcoin Scarcity and Price Appreciation
Bitcoin’s inherent scarcity is a key driver of its potential price appreciation. The fixed supply of 21 million Bitcoin, coupled with the halving mechanism, ensures that the supply will never exceed this limit. As demand increases while supply remains constrained, the price is expected to rise, reflecting the increased value placed on each individual Bitcoin. This dynamic is similar to other scarce assets like gold, where limited supply and growing demand contribute to price increases. For example, the previous halvings in 2012 and 2016 were followed by significant price increases, although the timing and magnitude of these increases varied due to other market factors. Predicting the exact price impact of the 2025 halving remains challenging, but the underlying scarcity principle suggests a potential upward pressure on price.
Institutional Investment and Retail Adoption
The demand for Bitcoin is shaped by a complex interplay of institutional and retail investors. Institutional investors, such as large corporations and investment funds, often view Bitcoin as a potential hedge against inflation or a diversification tool within their portfolios. Their significant investments can drive substantial price increases. Simultaneously, retail adoption, driven by individual investors and users, plays a crucial role in creating sustained demand. Increased awareness and understanding of Bitcoin’s underlying technology and potential benefits can lead to higher adoption rates and thus increased demand. The 2021 bull run, for example, saw significant participation from both institutional and retail investors, leading to a rapid price surge. However, the market is susceptible to shifts in sentiment, so sustained demand relies on ongoing adoption and a positive outlook on Bitcoin’s long-term prospects.
Comparison with Other Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin’s supply and demand dynamics differ significantly from many other cryptocurrencies. While some cryptocurrencies also have a fixed supply, many others have an unlimited or much larger supply than Bitcoin. This difference impacts their potential for price appreciation.
| Metric | Bitcoin | Ethereum | Other Altcoins (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Supply | 21 million | Unlimited (but deflationary mechanisms are being implemented) | Varies greatly; some have unlimited supply |
| Inflation Rate | Decreasing, approaching zero | Decreasing, but still inflationary | Varies greatly; some are highly inflationary |
| Market Capitalization | Dominant in the crypto market | Second largest | Significantly smaller than Bitcoin and Ethereum |
| Institutional Adoption | High, growing steadily | High, growing steadily | Generally lower than Bitcoin and Ethereum |