Bitcoin Halving After 2025
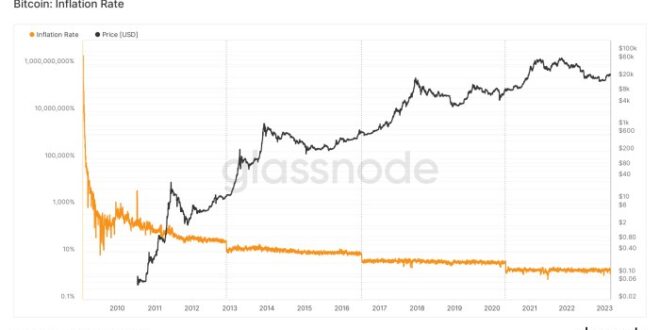
The Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. This occurs approximately every four years, and it’s a key element influencing Bitcoin’s scarcity and, consequently, its price. Understanding the mechanics and historical impact of these halvings is crucial for anticipating potential future market trends.
Bitcoin Halving Mechanics, Bitcoin Halving After 2025
The Bitcoin halving mechanism is built into the Bitcoin code. Every 210,000 blocks mined, the reward given to miners for verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain is cut in half. Initially, the reward was 50 BTC per block. After the first halving, it became 25 BTC, then 12.5 BTC, and currently stands at 6.25 BTC. This reduction in block reward directly impacts the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation. The total supply of Bitcoin is capped at 21 million, meaning the halving events eventually lead to a complete cessation of new Bitcoin creation.
Historical Impact of Bitcoin Halvings
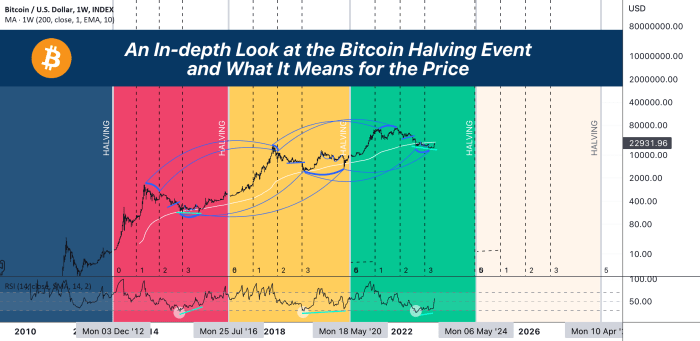
Previous halving events have shown a strong correlation with subsequent price increases. While not a guaranteed predictor, the halving typically creates a period of decreased supply, potentially leading to increased demand and price appreciation. The first halving in 2012 saw a relatively modest price increase. However, the subsequent halvings in 2016 and 2020 were followed by significant bull runs, although other market factors also played a role. It is important to note that the price increase after a halving is not immediate; it usually takes several months, even years, for the effects to fully manifest. The timing and magnitude of price movements are influenced by a multitude of factors beyond the halving itself, including regulatory changes, macroeconomic conditions, and overall market sentiment.
Projected Timeline for Future Halvings
Based on the current block generation rate, the next halving is projected to occur around 2028, followed by another approximately four years later in 2032. These projections are subject to slight variations depending on the actual block mining time. It is important to understand that these are estimations based on current trends and are not guaranteed to be perfectly accurate. Changes in mining difficulty or hashing power could slightly alter the timing.
Anticipated Effects of Future Halvings Compared to Past Events
While past halvings provide valuable insights, predicting the future impact with certainty is impossible. The crypto market has matured significantly since the first halving, with increased institutional investment and regulatory scrutiny. Therefore, the effects of future halvings might differ from past experiences. Factors like increased adoption, improved infrastructure, and changes in global economic conditions could significantly influence the market’s reaction. Comparing the 2020 halving to previous events reveals a more pronounced price surge after a longer period, suggesting that market maturity and anticipation could alter the timeline and intensity of price responses. Future halvings might see a more gradual price appreciation rather than a sudden, sharp increase, although this is speculative.
Supply and Demand Dynamics Post-2025 Halving
The Bitcoin halving events, occurring approximately every four years, significantly impact the cryptocurrency’s supply and, consequently, its price. The halving reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created, effectively decreasing the inflation rate of the Bitcoin network. Analyzing the post-2025 halving requires considering both the reduced supply and the anticipated demand dynamics. This analysis will explore the potential consequences of this interplay on Bitcoin’s market value.
The expected changes in Bitcoin’s supply after the 2025 halving, and subsequent halvings, are straightforward: a 50% reduction in the rate of new Bitcoin creation. Before the halving, approximately 900 new Bitcoins are added to circulation daily. Post-halving, this number will decrease to approximately 450. This gradual reduction in supply creates scarcity, a fundamental economic principle that often drives price increases. The impact of this reduced supply is expected to be felt over time, as the market adjusts to the new issuance schedule. However, the magnitude of the price impact is subject to numerous other factors, including overall market sentiment, regulatory changes, and adoption rates.
Bitcoin Price Impact Due to Decreased Supply
A decreased supply of Bitcoin, all else being equal, typically exerts upward pressure on its price. This is because the same (or potentially increased) demand now competes for a smaller quantity of available Bitcoin. The scarcity created by the halving makes each Bitcoin inherently more valuable. Historical data suggests a correlation between Bitcoin halvings and subsequent price increases, though the timing and magnitude of these increases have varied. For example, the 2012 and 2016 halvings were followed by significant bull markets, but the market conditions and overall economic climate play a crucial role in determining the precise outcome. The extent to which the price rises depends heavily on whether demand can keep pace or even outstrip the reduced supply.
Increased Demand and Reduced Supply Interaction
The interaction between increased demand and reduced supply is crucial in determining the post-halving price trajectory. If demand remains stable or even increases, the reduced supply will likely lead to a significant price appreciation. This is because the limited supply will struggle to meet the existing demand, pushing prices upwards to balance the market. Several factors could contribute to increased demand, including growing institutional adoption, increased mainstream awareness, and further development of Bitcoin’s underlying technology and infrastructure. A scenario where institutional investors, for example, see Bitcoin as a safe haven asset during times of economic uncertainty could trigger a substantial surge in demand, amplifying the impact of the halving.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating Supply and Demand Interplay
Let’s imagine a hypothetical scenario. Assume that the post-2025 halving leads to a 50% reduction in Bitcoin’s daily issuance, as expected. Simultaneously, let’s assume a surge in institutional investment, driven by concerns about inflation and geopolitical instability. This increased demand, coupled with the reduced supply, could create a significant price increase. For example, if the price before the halving was $50,000, the combined effect of reduced supply and increased demand could potentially push the price to $100,000 or even higher within a year or two, depending on the pace of adoption and overall market sentiment. However, it is crucial to remember that this is just a hypothetical example; the actual price movement will depend on a complex interplay of various market forces. This scenario highlights the potential for substantial price appreciation, but also underscores the inherent uncertainty associated with predicting cryptocurrency prices.
Mining and Hashrate Implications
The Bitcoin halving, occurring approximately every four years, significantly impacts the profitability of Bitcoin mining and, consequently, the network’s hashrate. This event reduces the block reward miners receive for verifying transactions, altering the economic landscape of the Bitcoin mining industry. Understanding these implications is crucial for assessing the long-term health and security of the Bitcoin network.
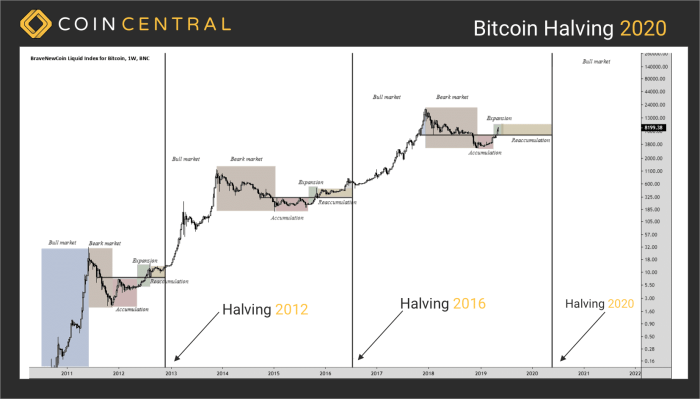
The profitability of Bitcoin mining after a halving is directly tied to the price of Bitcoin and the cost of mining. Following a halving, the revenue generated per block is cut in half. Miners must then either reduce their operational costs or see their profits diminish. This can lead to a period of adjustment where less profitable mining operations shut down, leading to a decrease in the network’s hashrate. However, if the price of Bitcoin rises sufficiently after the halving, it can offset the reduced block reward, maintaining or even increasing profitability for efficient miners. The 2012 and 2016 halvings provide historical examples of this dynamic; while there were initial drops in hashrate, the price increases ultimately led to a resurgence in mining activity.
Bitcoin Mining Profitability After Halving
The profitability of Bitcoin mining is calculated by comparing the revenue generated from block rewards and transaction fees against the operational costs. These costs include electricity consumption, hardware maintenance, cooling systems, and facility rent. After a halving, the revenue stream is halved, putting pressure on miners with higher operational costs. Miners with access to cheaper electricity, more efficient hardware, and optimized operations will likely be more resilient to this reduction. For example, miners located in regions with low electricity prices, such as some parts of Kazakhstan or North America, will have a competitive advantage compared to those in areas with higher energy costs. Those miners who cannot maintain profitability may be forced to shut down, sell their equipment, or relocate to more favorable regions.
Impact on Bitcoin Hashrate
The Bitcoin hashrate, a measure of the computational power dedicated to securing the network, is directly influenced by mining profitability. A decrease in profitability often leads to a decline in hashrate as less profitable miners cease operations. This reduction in hashrate can temporarily increase the risk of successful 51% attacks, though the network’s overall security is generally considered robust even with fluctuations. However, historical data suggests that the hashrate typically recovers and even surpasses previous levels as the price of Bitcoin adjusts and more efficient mining operations emerge. The 2020 halving, for instance, saw an initial dip followed by a significant increase in hashrate as the price of Bitcoin rose.
Consequences of Decreased Mining Profitability
A decrease in mining profitability can have several consequences. Beyond the immediate impact on hashrate, it can lead to consolidation within the mining industry. Larger, more established mining operations with economies of scale are better positioned to weather periods of reduced profitability, potentially leading to market dominance by fewer players. This could raise concerns about centralization, although the decentralized nature of Bitcoin is generally considered robust against such risks. Furthermore, a prolonged period of low profitability could discourage new entrants into the mining industry, potentially slowing the growth of the network’s computational power. Finally, a significant decrease in hashrate could, in theory, make the network more vulnerable to attacks, although the likelihood of this remains low due to the overall resilience of the network and the high barrier to entry for successful attacks.
Mining Landscape Before and After Halving
Before a halving, the mining landscape is typically characterized by a higher level of competition and potentially less efficient operations. The higher block reward incentivizes more miners to join the network, leading to increased competition for block rewards. After a halving, the landscape shifts towards a more consolidated market. Only the most efficient and cost-effective miners are likely to remain profitable, leading to a more concentrated distribution of mining power. This shift can lead to a more sustainable, though potentially less diverse, mining ecosystem. The increased efficiency, however, can also contribute to the overall resilience of the Bitcoin network.
Bitcoin’s Role in the Global Economy Post-2025
Bitcoin’s future role in the global economy after the 2025 halving is a subject of considerable debate and speculation. While its ultimate impact remains uncertain, several factors suggest a significant, albeit evolving, influence on global finance and investment strategies. The halving event, along with broader macroeconomic trends, will play a crucial role in shaping Bitcoin’s trajectory.
Bitcoin’s potential as a long-term store of value hinges on its inherent scarcity, limited supply, and growing adoption as a hedge against inflation. Its decentralized nature and resistance to censorship are also key factors influencing its appeal to investors seeking alternatives to traditional financial systems. The scarcity of Bitcoin, capped at 21 million coins, is a compelling argument for its long-term value proposition. Historically, assets with limited supply have tended to appreciate in value over time, particularly during periods of economic uncertainty. However, this is not a guarantee, and its value is susceptible to market volatility and regulatory changes.
Bitcoin’s Store of Value Potential
The halving event directly impacts Bitcoin’s inflation rate, making it potentially more attractive as a store of value. Reduced supply coupled with sustained or increased demand can lead to price appreciation. However, this effect is not guaranteed, as market sentiment and external economic factors can heavily influence Bitcoin’s price. For example, the 2021 bull run saw a significant price increase, but subsequent market corrections demonstrate the volatility inherent in cryptocurrency markets. A comparison to gold, a traditional store of value, is relevant here. Gold’s price has historically been influenced by factors like inflation, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment. Similarly, Bitcoin’s price is susceptible to these same factors, alongside its unique characteristics as a digital asset. Long-term price prediction is difficult, but the combination of scarcity and growing institutional adoption provides a compelling case for Bitcoin’s continued relevance as a store of value.
Halving’s Impact on Bitcoin Adoption
The halving’s impact on Bitcoin’s adoption rate is complex. While the reduced supply could increase scarcity and drive up prices, potentially attracting new investors, it might also create a barrier to entry for those less willing to pay higher prices. The adoption rate will likely depend on various factors, including macroeconomic conditions, regulatory developments, and the development of user-friendly applications and infrastructure. For example, the increasing integration of Bitcoin into payment platforms and financial services could boost adoption. Conversely, stringent regulatory measures could hinder its widespread use. Ultimately, the halving’s effect on adoption will be determined by the interplay of these diverse influences.
Bitcoin’s Position within the Cryptocurrency Market
Bitcoin maintains a dominant position within the broader cryptocurrency market, often referred to as the “king of crypto.” Its first-mover advantage, established network effect, and brand recognition contribute significantly to its market capitalization and influence. However, the rise of alternative cryptocurrencies (altcoins) presents both a challenge and an opportunity. Altcoins offer potentially higher returns but often come with greater risk. Bitcoin’s dominance could be challenged by technological advancements in other cryptocurrencies or by the emergence of new, compelling projects. The evolution of the cryptocurrency landscape will be crucial in shaping Bitcoin’s relative position within the market.
Potential Scenarios for Bitcoin in Future Financial Systems
Several scenarios exist regarding Bitcoin’s role in future financial systems. One possibility is its increasing integration into existing financial infrastructures, potentially acting as a digital gold or a store of value within institutional portfolios. Another scenario involves Bitcoin becoming a more widely used medium of exchange, facilitating cross-border payments and reducing reliance on traditional banking systems. A more radical scenario could see Bitcoin playing a pivotal role in a decentralized financial system, challenging the dominance of central banks and traditional financial institutions. The actual outcome will depend on technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and the adoption rate among individuals and institutions. The example of El Salvador’s adoption of Bitcoin as legal tender, although controversial, highlights the potential for Bitcoin to play a more significant role in national economies. However, it also showcases the challenges and risks associated with such a significant shift.
Regulatory Landscape and Future Outlook: Bitcoin Halving After 2025
The future of Bitcoin is inextricably linked to the evolving regulatory landscape. Governments worldwide are grappling with how to classify and regulate this decentralized digital asset, leading to a complex and often unpredictable environment for investors and businesses. The actions taken by various jurisdictions will significantly influence Bitcoin’s price, adoption rate, and overall impact on the global financial system.
The impact of future regulations on Bitcoin will be multifaceted. Different regulatory approaches, ranging from outright bans to comprehensive frameworks, will create varied market conditions and influence investor sentiment. For example, clear and consistent regulatory frameworks could foster greater institutional investment and mainstream adoption, while inconsistent or overly restrictive regulations could stifle innovation and drive activity to less regulated jurisdictions. This dynamic interplay between regulatory action and market response will shape Bitcoin’s trajectory in the years to come.
Government Policies and Bitcoin’s Price and Adoption
Government policies play a pivotal role in shaping Bitcoin’s price and adoption. Favorable regulations, such as clear tax guidelines and licensing frameworks for cryptocurrency exchanges, can increase investor confidence and attract institutional capital, potentially driving up the price. Conversely, restrictive regulations, such as outright bans or excessive transaction taxes, can suppress price and limit adoption. The regulatory approach taken by major economies, particularly the United States, China, and the European Union, will have a disproportionate impact on the global Bitcoin market. For instance, China’s 2021 crackdown on cryptocurrency mining significantly impacted Bitcoin’s price and hash rate, demonstrating the potent influence of government policy.
Challenges and Opportunities in a Regulated Environment
A regulated environment presents both challenges and opportunities for Bitcoin. Challenges include navigating complex compliance requirements, dealing with potential regulatory uncertainty, and managing the risk of increased scrutiny from financial authorities. Opportunities include increased legitimacy, greater access to traditional financial markets, and potentially lower volatility as regulatory clarity reduces uncertainty. The successful navigation of these challenges and the exploitation of these opportunities will depend on the adaptability of the Bitcoin ecosystem and the collaborative efforts of industry stakeholders and regulators. For example, the development of self-regulatory organizations (SROs) within the cryptocurrency industry could help bridge the gap between industry best practices and government oversight.
Hypothetical Regulatory Framework for Bitcoin Post-2025
A hypothetical regulatory framework for Bitcoin post-2025 could involve a tiered approach, classifying Bitcoin differently depending on its use case. For instance, Bitcoin used for speculative trading could be subject to stricter Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, similar to traditional securities. Meanwhile, Bitcoin used for peer-to-peer transactions or as a store of value could face less stringent regulations, focusing more on consumer protection and preventing market manipulation. This framework would aim to balance the need for financial stability and investor protection with the promotion of innovation and the inherent decentralization of Bitcoin. Such a framework would need to be internationally coordinated to avoid regulatory arbitrage and ensure a level playing field for global participants. The implementation of such a framework would require significant international cooperation and a willingness to adapt to the unique characteristics of Bitcoin and the broader cryptocurrency landscape.
Technological Advancements and Their Influence
Technological advancements will significantly shape Bitcoin’s future, particularly in the post-2025 halving era. Increased mining efficiency, improved scaling solutions, and potential disruptive technologies will all play crucial roles in determining Bitcoin’s trajectory. The interplay between these factors and the reduced block reward will be a key determinant of Bitcoin’s long-term viability and adoption.
Bitcoin’s technological landscape is constantly evolving, and the impact of these advancements will be felt across various aspects of the network, from mining profitability to user experience. Understanding these changes is crucial for assessing Bitcoin’s future prospects.
Impact of Technological Advancements on Bitcoin Mining Efficiency
Advances in semiconductor technology, specifically the development of more energy-efficient Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), are constantly improving Bitcoin mining efficiency. This leads to lower operational costs for miners, potentially offsetting the impact of reduced block rewards after halvings. For example, the transition from older ASIC generations to newer, more powerful models has demonstrably increased hash rate while decreasing energy consumption per unit of hash power. This efficiency improvement allows miners to remain profitable even with a lower Bitcoin reward per block. Furthermore, innovations in cooling techniques and renewable energy sources are also contributing to increased mining efficiency and a reduced environmental footprint.
Influence of Scaling Solutions on Bitcoin’s Transaction Speed and Fees
Scaling solutions, such as the Lightning Network and the Taproot upgrade, aim to address Bitcoin’s scalability challenges. The Lightning Network, a layer-2 solution, enables faster and cheaper transactions off-chain, significantly reducing the load on the main Bitcoin blockchain. Taproot, a layer-1 upgrade, improves transaction efficiency and privacy. Successful implementation and adoption of these scaling solutions could alleviate the potential for increased transaction fees and slower confirmation times that might otherwise arise from increased demand after a halving event. The success of these solutions will depend on factors such as user adoption and the development of user-friendly interfaces.
Potential Technological Disruptions to Bitcoin’s Future
While Bitcoin’s underlying technology is robust, potential technological disruptions could impact its future. The emergence of quantum computing, for example, poses a theoretical threat to Bitcoin’s cryptographic security. However, significant advancements are needed before quantum computers pose a realistic threat, and the Bitcoin community is actively researching countermeasures. Other potential disruptions include the development of superior alternative cryptocurrencies or significant changes in the global regulatory environment. These scenarios, however, are speculative and their likelihood is subject to considerable uncertainty.
Technological Landscape Comparison: Pre- and Post-Halving
Before halvings, the technological focus often centered on increasing mining hardware efficiency to maintain profitability despite a constant block reward. Post-halving, the emphasis shifts towards optimizing network efficiency and scalability through layer-2 solutions and protocol upgrades. The pre-halving period might see a higher focus on pure hash rate competition, while the post-halving era emphasizes more sophisticated approaches to managing transaction throughput and reducing costs. This transition reflects a broader shift in the Bitcoin ecosystem’s priorities, from a purely quantitative focus on mining to a more qualitative focus on network performance and user experience.