Bitcoin Halving 2025
The Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. This occurs approximately every four years, and significantly impacts the inflation rate of the cryptocurrency. Understanding its mechanics and historical impact is crucial for assessing its potential influence on the market in 2025.
Bitcoin Halving Mechanics and Historical Impact
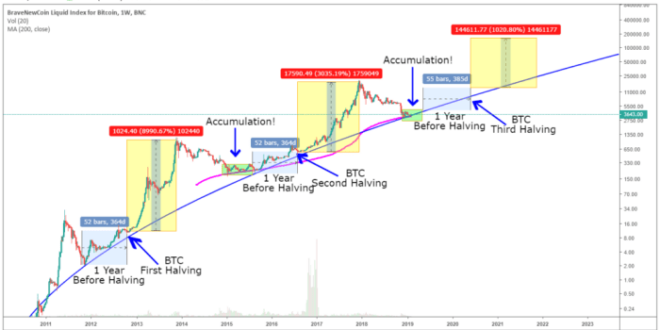
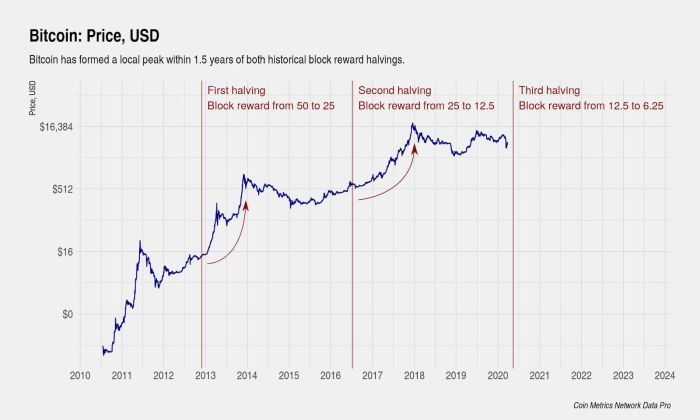
The Bitcoin halving mechanism is built into the Bitcoin code. Every 210,000 blocks mined, the reward given to miners for successfully adding a block to the blockchain is halved. Initially, the reward was 50 BTC per block. After the first halving, it became 25 BTC, then 12.5 BTC, and currently stands at 6.25 BTC. Historically, halving events have been followed by periods of significant price appreciation, though the timing and magnitude of these increases have varied. The first halving in November 2012 saw a gradual price increase over the following year. The second halving in July 2016 preceded a substantial bull run starting in late 2016 and peaking in late 2017. The third halving in May 2020 was followed by a bull run that culminated in late 2021. While correlation doesn’t equal causation, the historical data suggests a strong link between halvings and subsequent price increases.
Expected Date and Implications of the 2025 Bitcoin Halving
The 2025 Bitcoin halving is expected to occur in the spring or early summer of 2025, though the precise date depends on the block mining rate. This event will reduce the miner reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC per block. The primary implication is a further decrease in Bitcoin’s inflation rate, making it even scarcer. This reduced supply, coupled with potentially sustained or increased demand, could exert upward pressure on the price. However, it’s important to note that macroeconomic factors, regulatory changes, and overall market sentiment will also play significant roles in shaping the price trajectory. The 2025 halving’s impact will likely depend on the prevailing market conditions at the time. For example, a period of economic uncertainty might lead to increased demand for Bitcoin as a safe haven asset, amplifying the halving’s effect. Conversely, a strong economic climate might reduce the impact.
Comparison of Previous Halving Cycles and Projections for 2025
Comparing previous halving cycles reveals varying post-halving price behaviors. While all three previous halvings were followed by bull markets, the timing and intensity differed significantly. The time lag between the halving and the peak price varied, and the magnitude of the price increase also differed substantially. Predicting the exact outcome of the 2025 halving is impossible. However, by analyzing past cycles, considering current market conditions, and factoring in potential future influences, analysts can formulate educated projections. Many anticipate a similar, though not necessarily identical, pattern to previous cycles, with a potential price increase following the 2025 halving. However, the extent of this increase remains uncertain and subject to various market dynamics.
Halving Events and Bitcoin’s Scarcity
A chart depicting the relationship between Bitcoin halvings and its scarcity could be constructed as follows: The x-axis would represent time, marking the dates of each halving event (2012, 2016, 2020, and the projected 2025). The y-axis would represent the Bitcoin inflation rate (the percentage increase in the Bitcoin supply per year). Each data point would represent the inflation rate after each halving. A line graph would connect these points, illustrating the decreasing inflation rate over time. A legend could be included, clearly defining the axes and the data represented. The chart would visually demonstrate how each halving event reduces Bitcoin’s inflation rate, contributing to its scarcity. The projected 2025 data point would show a further decrease in the inflation rate, highlighting the increasing scarcity of Bitcoin after this event. The chart would clearly illustrate the decreasing inflation rate over time, visually demonstrating the impact of halving events on Bitcoin’s scarcity. This visual representation would emphasize the inherent deflationary nature of Bitcoin’s design, a key factor often cited as a driver of its value proposition.
Analyzing the Bitcoin Halving Chart
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed reduction in the rate of new Bitcoin creation, is a significant event anticipated to influence the cryptocurrency’s price. Analyzing historical data alongside various predictive models allows us to explore potential price trajectories leading up to and following the 2025 halving. While precise prediction is impossible, understanding the interplay of influencing factors provides a valuable framework for informed speculation.
Hypothetical Bitcoin Price Chart Scenarios
The following scenarios illustrate potential price movements around the 2025 halving. These are purely hypothetical and should not be considered financial advice. We’ll consider three scenarios: bullish, neutral, and bearish.
A bullish scenario might show a gradual price increase in the year leading up to the halving, driven by anticipation. The halving itself could act as a catalyst, leading to a more significant price surge. This surge could be followed by a period of consolidation before further upward movement. Conversely, a neutral scenario would depict a less dramatic price change. The halving might cause a temporary price bump, but overall price movement would remain relatively flat, reflecting a market that is neither strongly bullish nor bearish. Finally, a bearish scenario could show a downward trend leading up to the halving, perhaps driven by macroeconomic factors or regulatory uncertainty. The halving, in this case, might offer only temporary support, with the price continuing a downward trajectory afterward. Visualizing these scenarios requires a chart (which cannot be included here due to limitations of this text-based format), but one could imagine a line graph showing the Bitcoin price on the y-axis and time on the x-axis, with distinct lines representing each of these three scenarios.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price Post-Halving
Several factors beyond the halving itself can significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. Regulatory clarity or uncertainty in major markets, such as the United States or the European Union, can dramatically influence investor confidence and thus price. Increased adoption by institutional investors or widespread consumer use would likely drive price upward. Conversely, decreased adoption or negative regulatory actions could exert downward pressure. Macroeconomic conditions, including inflation rates, interest rates, and overall economic growth, also play a substantial role. A global recession, for instance, might negatively affect risk assets like Bitcoin, while periods of high inflation might drive investors towards Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation.
Comparison of Price Prediction Models
Various models attempt to predict Bitcoin’s future price. These range from simple technical analysis based on historical price patterns to more complex models incorporating macroeconomic indicators and network fundamentals. Some models use on-chain metrics, such as transaction volume and network hash rate, to gauge network health and user activity, suggesting a correlation between these metrics and price. Others rely on quantitative analysis of supply and demand, focusing on the decreasing supply of Bitcoin after each halving. These models often make different assumptions and yield different price ranges.
Price Prediction Model Comparison Table
| Model Type | Methodology | Assumptions | Predicted Price Range (USD) | Example/Real-Life Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stock-to-Flow Model | Analyzes the relationship between Bitcoin’s supply and its price. | Assumes scarcity drives price appreciation. | $100,000 – $1,000,000+ (highly variable depending on the version of the model) | The original Stock-to-Flow model, popularized by PlanB, has been used extensively to predict Bitcoin’s price, though its accuracy has been debated in recent times. |
| On-Chain Analysis | Examines data from the Bitcoin blockchain (transaction volume, hash rate, etc.). | Assumes on-chain activity correlates with price. | Variable, dependent on specific metrics and interpretation. | Analyzing the increase in the number of active addresses can be used as a proxy for adoption, which in turn may suggest future price movement. |
| Technical Analysis | Studies price charts and technical indicators (moving averages, RSI, etc.). | Assumes historical price patterns repeat. | Highly variable, depending on chosen indicators and interpretation. | Identifying support and resistance levels on a price chart can help predict potential price reversals. |
Mining and Hash Rate Impacts
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, reducing the block reward by half, will significantly impact Bitcoin mining profitability and the network’s overall hash rate. Understanding these impacts is crucial for assessing the future health and security of the Bitcoin network. The interplay between miner profitability, difficulty adjustments, and the resulting hash rate changes will shape the post-halving landscape.
The halving directly affects miner revenue. With fewer newly minted Bitcoins awarded per block, miners’ profitability will decrease unless the price of Bitcoin rises proportionally or operating costs fall significantly. This reduction in profitability could lead to some miners becoming unprofitable and shutting down their operations, potentially impacting the network’s security. However, history suggests that this effect is not always immediately drastic, and the price often increases over time after the halving event. The impact of the 2025 halving on profitability will depend largely on the prevailing Bitcoin price and the efficiency of mining operations.
Bitcoin Mining Difficulty Adjustment, Bitcoin Halving Chart 2025
Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment mechanism is designed to maintain a consistent block time of approximately 10 minutes. After a halving, the reduced block reward initially lowers the overall profitability of mining. This may lead to a decrease in the hash rate (the total computational power dedicated to mining) as less-efficient miners become unprofitable and leave the network. The network’s difficulty automatically adjusts downwards in response to the lower hash rate, restoring the target block time. This adjustment helps ensure the network’s stability and prevents excessively long block times. The magnitude of this difficulty adjustment will depend on the extent to which the hash rate drops after the halving.
Hash Rate Changes After Previous Halvings
A visual representation comparing historical halving events and subsequent hash rate changes would show a general trend. Imagine a line graph with the x-axis representing time, encompassing periods before and after each halving event (2012, 2016, 2020). The y-axis would represent the Bitcoin hash rate. The graph would depict a relatively stable hash rate before each halving, followed by a temporary dip immediately after, reflecting the initial impact on miner profitability. However, over time, the hash rate generally recovers and often surpasses previous levels, driven by factors like increased Bitcoin price and the adoption of more efficient mining hardware. This recovery highlights the resilience of the Bitcoin network and the adaptation of miners to changing economic conditions.
Mining Landscape Before and After Previous Halvings
The mining landscape has evolved considerably since Bitcoin’s inception. Before the first halving, mining was relatively decentralized, with numerous small-scale miners participating. However, over time, larger, more sophisticated mining operations emerged, leading to increased centralization within larger mining pools. After each halving, there’s often a period of consolidation, where less efficient miners exit the market, resulting in fewer, larger mining entities dominating the hash rate. The 2012, 2016, and 2020 halvings all demonstrated this trend, with a reduction in the number of active miners and an increase in the dominance of major mining pools. This consolidation, while potentially raising concerns about centralization, also often leads to increased efficiency and resilience of the network overall, as larger operations can better weather economic fluctuations.
Bitcoin Halving and Market Sentiment
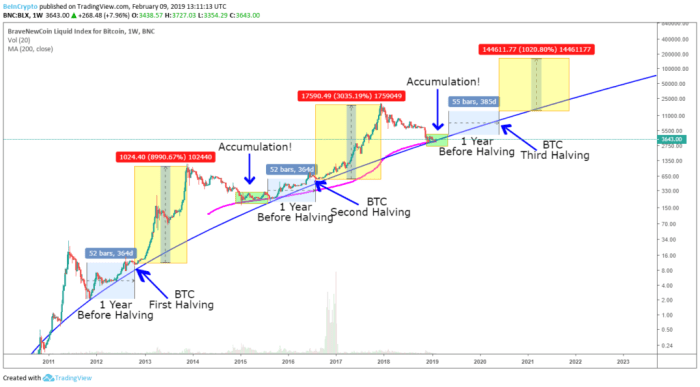
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation, significantly impacts market sentiment. Historically, these events have been followed by periods of increased price volatility and often, though not always, price appreciation. Understanding how investor sentiment shifts around halvings is crucial for navigating the market’s potential reactions.
Investor sentiment leading up to and following a Bitcoin halving typically exhibits a cyclical pattern. Anticipation often builds months before the event, leading to price increases fueled by speculation and the expectation of future scarcity. After the halving, the market may experience a period of consolidation or even a price correction before a potential upswing. This pattern is not guaranteed, however, and various factors influence the market’s ultimate response.
Market Reactions to the 2025 Halving
Predicting the precise market reaction to the 2025 halving is inherently speculative, but we can draw insights from past halvings and current market conditions. The 2012 and 2016 halvings were followed by significant price increases, although the timeframes varied. The 2020 halving also saw a price increase, but the timing and magnitude were different from previous cycles. Currently, the market is grappling with macroeconomic uncertainty and regulatory concerns, which could influence the 2025 halving’s impact. A conservative prediction might suggest a period of increased volatility followed by a gradual price appreciation, but significant external factors could alter this trajectory. For example, if global economic conditions improve significantly, Bitcoin’s price could experience a more dramatic rise. Conversely, a major regulatory crackdown could dampen the positive effects of the halving.
The Role of Social Media and News Coverage
Social media and news coverage play a significant role in shaping market sentiment around Bitcoin halvings. The amplification of narratives, both positive and negative, through these channels can heavily influence investor decisions. Positive news coverage focusing on scarcity and the potential for price increases can fuel bullish sentiment, while negative coverage highlighting regulatory risks or market corrections can trigger sell-offs. The spread of misinformation and hype on social media platforms adds another layer of complexity to the equation, making it crucial for investors to critically evaluate information sources. For instance, a viral tweet from a prominent figure in the crypto space could significantly influence short-term price movements, even if the underlying information lacks substance.
Differing Investor Reactions
Different investor groups react to Bitcoin halvings in distinct ways. Long-term holders (HODLers) are generally less affected by short-term price fluctuations and tend to remain invested regardless of immediate market reactions. They view the halving as a positive long-term event that increases Bitcoin’s scarcity and potential value. Short-term traders, on the other hand, are more sensitive to price movements and may engage in speculative trading around the halving, attempting to profit from short-term price volatility. Their reactions are often driven by market sentiment and news coverage, making them more susceptible to emotional decision-making. Institutional investors might take a more measured approach, considering the halving alongside broader macroeconomic factors and regulatory landscapes before making significant investment decisions. The interplay between these different investor groups shapes the overall market dynamics surrounding the halving.
Long-Term Implications of the 2025 Halving
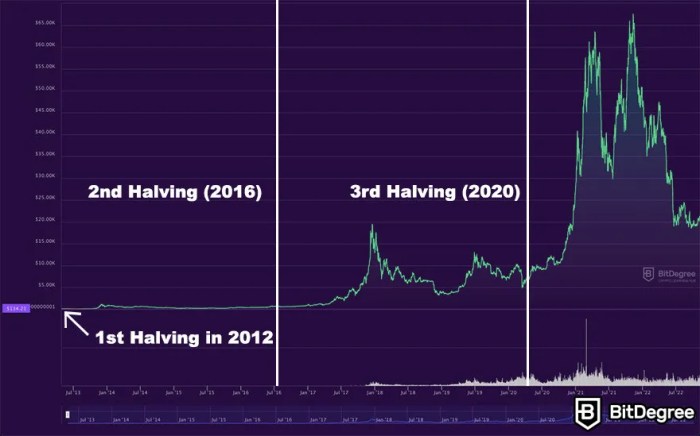
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation by half, is anticipated to have profound and long-lasting effects on the cryptocurrency market. While short-term price volatility is expected, the long-term consequences will shape the future of Bitcoin and the broader crypto landscape, impacting adoption, market dominance, and the overall investment narrative.
The reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin, coupled with persistent demand, is predicted to create upward pressure on the price. This, however, is not a guaranteed outcome and depends on various factors including macroeconomic conditions, regulatory developments, and overall market sentiment. The halving’s impact is a complex interplay of economic forces and market psychology.
Bitcoin’s Role as a Store of Value and Medium of Exchange
The 2025 halving could significantly bolster Bitcoin’s position as a store of value. The decreased inflation rate inherent in the halving mechanism makes Bitcoin more attractive to investors seeking a hedge against inflation in traditional markets. Increased scarcity, driven by the reduced supply, could further cement its appeal as a long-term investment asset. However, its adoption as a medium of exchange faces significant hurdles. Transaction fees, network speed, and volatility continue to hinder widespread everyday use. While some merchants accept Bitcoin, its adoption as a primary means of payment remains limited, particularly in comparison to established fiat currencies. The halving’s effect on transaction volume and merchant adoption will depend heavily on improvements in scalability and user experience.
Bitcoin’s Long-Term Growth Compared to Other Cryptocurrencies
The 2025 halving is likely to influence the competitive landscape within the cryptocurrency market. While Bitcoin’s first-mover advantage and established network effect provide a strong foundation, other cryptocurrencies with different functionalities and technological advancements could potentially gain market share. Altcoins focusing on scalability, smart contracts, or decentralized finance (DeFi) might attract investors seeking solutions that Bitcoin currently lacks. The relative growth trajectories of Bitcoin and altcoins post-halving will depend on technological innovation, regulatory changes, and the evolution of investor preferences. For example, the rise of Ethereum and its DeFi ecosystem demonstrates how alternative cryptocurrencies can carve out significant market niches, even with Bitcoin’s established dominance.
Potential Long-Term Effects Timeline
The following timeline illustrates potential long-term effects, acknowledging the inherent uncertainty in predicting cryptocurrency market behavior. These are potential scenarios, not guaranteed outcomes.
| Year | Potential Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | Bitcoin Halving | The halving event occurs, reducing the block reward. Initial price volatility is expected. |
| 2026-2027 | Gradual Price Increase | Increased scarcity and anticipation of further price appreciation lead to a gradual, potentially sustained, price rise. |
| 2028-2030 | Increased Institutional Adoption | Larger financial institutions may increase their Bitcoin holdings, further driving demand and price appreciation. This is contingent on regulatory clarity and continued market stability. |
| 2030+ | Maturation of the Bitcoin Ecosystem | The Bitcoin network matures, potentially integrating improved scalability solutions and enhanced user experience. This could lead to broader adoption as both a store of value and a medium of exchange. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Bitcoin Halving Chart 2025
This section addresses some common questions regarding the Bitcoin halving, focusing on the upcoming event in 2025 and its potential implications. Understanding these key aspects can help investors and enthusiasts navigate the complexities surrounding this significant event in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Bitcoin Halving Explained
The Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created (mined) by half. This occurs approximately every four years, or every 210,000 blocks mined. The halving mechanism is designed to control Bitcoin’s inflation rate, mimicking the scarcity of precious metals like gold. Essentially, it makes Bitcoin progressively harder to mine over time.
Timing of the Next Bitcoin Halving
The next Bitcoin halving is expected to occur in the Spring of 2025. The precise date depends on the time it takes to mine the 210,000 blocks, but estimations place it around April or May of 2025. Block times can fluctuate slightly due to variations in the computational power dedicated to mining. However, the general timeframe remains consistent with the historical pattern.
Bitcoin Halving’s Impact on Price
Historically, Bitcoin halving events have been followed by periods of significant price appreciation. The halvings in 2012, 2016, and 2020 all preceded notable bull markets. The reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin, coupled with increasing demand, can exert upward pressure on the price. However, it’s crucial to remember that this is not a guaranteed outcome. Other market factors, including macroeconomic conditions, regulatory changes, and overall investor sentiment, play significant roles in determining Bitcoin’s price. For instance, the 2020 halving was followed by a significant bull run, reaching an all-time high in late 2021. However, the subsequent market correction demonstrates the complex interplay of factors influencing price. Predicting the precise impact of the 2025 halving on price is impossible; various scenarios are possible, ranging from modest price increases to another significant bull market.
Risks of Investing Around a Halving Event
Investing in Bitcoin around a halving event carries several risks. The heightened anticipation can lead to speculative bubbles, potentially resulting in sharp price corrections after the event. Market volatility is inherently higher during periods of significant market events. Furthermore, the cryptocurrency market is highly susceptible to regulatory changes and unforeseen technological disruptions. It’s essential to conduct thorough research, diversify investments, and only invest what one can afford to lose. The potential for significant price swings, both upward and downward, necessitates a cautious approach and a long-term investment strategy. The 2012 halving, for example, saw a period of price consolidation before the subsequent bull run, highlighting the unpredictable nature of market reactions.