Effects on Bitcoin Price and Volatility: Bitcoin Mining Halving 2025
The Bitcoin halving, scheduled for 2025, is a significant event expected to impact the cryptocurrency’s price and volatility. This reduction in the rate of new Bitcoin creation traditionally influences the market dynamics, although the extent of the impact remains a subject of ongoing debate and analysis. Historical data provides some clues, but predicting the future price action with certainty is impossible due to the numerous intertwined factors at play.
The 2025 halving will likely trigger increased price volatility in the lead-up to and immediate aftermath of the event. This volatility is a result of heightened anticipation and speculation amongst market participants. The reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin creates a scarcity effect, potentially driving up demand and price. However, the market’s reaction is never guaranteed and can be significantly influenced by macroeconomic conditions and other unrelated events.
Bitcoin Price Volatility Predictions
Predicting the exact price movement is inherently speculative. However, considering the historical impact of previous halvings, a period of increased volatility is anticipated around the 2025 event. The 2012 and 2016 halvings were followed by periods of significant price appreciation, though these were also interwoven with substantial market corrections. Extrapolating directly from these past events is risky, as market conditions and the overall crypto landscape have significantly evolved. A reasonable prediction would be heightened volatility, potentially leading to both substantial price increases and considerable price drops in the months surrounding the halving. The magnitude of these swings, however, remains uncertain.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin Price Beyond the Halving
Several factors beyond the halving itself can influence Bitcoin’s price. Macroeconomic conditions, such as inflation rates, interest rate adjustments by central banks, and overall economic growth, play a crucial role. Regulatory developments in various jurisdictions also significantly affect investor sentiment and market participation. Furthermore, the adoption rate of Bitcoin by institutions and individuals, the development of new Bitcoin-related technologies and applications, and the emergence of competing cryptocurrencies all contribute to the complex price dynamics. The interplay of these elements will ultimately determine whether the halving’s scarcity effect will dominate or be overshadowed by other market forces.
Bullish Market Response Scenario
A bullish scenario would involve a gradual increase in Bitcoin’s price in the months leading up to the halving, fueled by anticipation and accumulation by investors expecting a post-halving price surge. The halving itself would act as a catalyst, triggering a significant price rally driven by reduced supply and increased demand. This rally could be further amplified by positive macroeconomic news, increased institutional adoption, and positive regulatory developments. In this scenario, the price could potentially reach new all-time highs, surpassing previous peaks by a considerable margin, mirroring (though not necessarily replicating) the post-halving price increases observed in 2013 and 2017. This would be a period of sustained positive momentum, characterized by low sell-offs and strong investor confidence.
Bearish Market Response Scenario
Conversely, a bearish scenario could see a subdued or even negative price reaction to the halving. This could be due to several factors. A prolonged period of macroeconomic uncertainty, stringent regulatory crackdowns, or a significant negative event within the cryptocurrency space could overshadow the halving’s impact. In this case, the reduced supply might not be sufficient to counteract bearish sentiment, leading to a period of price stagnation or even a decline. This scenario might also involve a sell-off by miners who might be forced to liquidate their holdings due to lower profitability from reduced block rewards. The overall market sentiment would be negative, with investors hesitant to invest, leading to a prolonged period of bearish price action.
The Role of Mining Difficulty Adjustment
The Bitcoin network’s mining difficulty adjustment is a crucial mechanism that maintains a consistent block generation time, approximately 10 minutes, despite fluctuations in the overall computational power (hash rate) dedicated to mining. This self-regulating system is essential for the network’s stability and security, particularly in the context of halving events.
The mining difficulty is a measure of how computationally challenging it is to solve the cryptographic puzzle required to add a new block to the blockchain. It’s dynamically adjusted every 2016 blocks (approximately two weeks) based on the time it took to mine the previous 2016 blocks. If the previous blocks were mined faster than the target (10 minutes per block), the difficulty increases; conversely, if they were mined slower, the difficulty decreases. This ensures the network maintains its intended block generation rate, even with changes in miner participation and computing power.
Mining Difficulty’s Impact on Post-Halving Profitability
A Bitcoin halving reduces the block reward miners receive for successfully adding a block to the blockchain. This directly impacts the profitability of mining. The difficulty adjustment mechanism plays a vital role in mitigating the immediate effects of this reduced reward. Immediately after a halving, the profitability of mining Bitcoin drops significantly. However, if the hash rate remains constant or increases, the mining difficulty will eventually adjust upwards, making mining less profitable for less efficient miners. This process of difficulty adjustment acts as a natural market correction, weeding out less profitable operations and stabilizing the network’s security. Conversely, if the hash rate decreases significantly post-halving, the difficulty will adjust downwards, making mining more profitable and potentially attracting new miners.
A Model Illustrating Halving, Difficulty, and Hash Rate Interplay
Let’s consider a simplified model. Assume before a halving, the block reward is 6.25 BTC, and the average mining difficulty is represented by a value ‘D’. The total hash rate dedicated to Bitcoin mining is ‘H’. After the halving, the block reward is reduced to 3.125 BTC.
Initially, profitability plummets because the reward is halved. If the hash rate (H) remains relatively constant, the increased competition for the reduced reward leads to a longer time to mine 2016 blocks. The difficulty adjustment mechanism then increases the difficulty (to a new value, let’s say ‘D1’, where D1 > D), making it harder to mine blocks. This reduces the overall profitability of mining, potentially causing less efficient miners to leave the network.
However, if, due to factors like anticipation of future price appreciation or the availability of cheaper energy, the hash rate increases to a new level ‘H1’ (H1 > H) after the halving, the time to mine 2016 blocks could remain relatively stable or even decrease slightly. In this scenario, the difficulty adjustment might increase moderately (to ‘D2’), or even stay relatively constant, maintaining a degree of profitability for existing miners and potentially attracting new ones. The interplay between these three factors – halving, difficulty, and hash rate – determines the overall health and stability of the Bitcoin network after each halving event. The market adjusts dynamically, influenced by various factors including energy costs, technological advancements, and investor sentiment. A detailed, accurate prediction of these factors is challenging, but historical data and market analysis can provide insights into likely scenarios.
Long-Term Implications for Bitcoin’s Decentralization
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, while primarily affecting the rate of new Bitcoin issuance, possesses significant long-term implications for the network’s decentralization. This stems from its impact on miner profitability and, consequently, the distribution of mining power across different entities and geographic locations. Understanding these implications is crucial for assessing Bitcoin’s resilience and future sustainability.
The halving reduces the block reward miners receive for validating transactions. This directly impacts the profitability of mining, potentially leading to a shakeout within the industry. Less profitable miners, often those with older, less efficient equipment or higher operational costs, might be forced to exit the market. This could concentrate mining power in the hands of larger, more established operations with access to cheaper energy and advanced hardware.
Mining Power Concentration Before and After the Halving
Prior to the halving, a significant portion of Bitcoin’s hash rate (a measure of mining power) was already concentrated among a relatively small number of large mining pools. These pools, often located in countries with favorable energy policies and low electricity costs like China (before the 2021 crackdown) and Kazakhstan, wield considerable influence over the network. The halving could exacerbate this trend, potentially leading to a further consolidation of mining power within a smaller number of entities. For example, if smaller miners are forced to shut down due to reduced profitability, their hash rate would be absorbed by larger players, increasing the concentration. The exact degree of this concentration will depend on various factors, including the price of Bitcoin and the efficiency of new mining hardware. Analysis of on-chain data and mining pool statistics before and after previous halvings can provide valuable insights into the likely impact of the 2025 event.
Centralization Risks Associated with Mining Hardware and Geographic Locations
The use of specialized ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miners contributes to centralization risks. The high cost and specialized nature of ASICs create a barrier to entry for smaller miners, favoring larger operations with the capital to invest in these machines. Furthermore, the geographic concentration of mining operations, often driven by access to cheap energy sources, presents further risks. A significant portion of mining activity concentrated in a single region or under the control of a few powerful entities raises concerns about potential censorship or manipulation of the network. For instance, a government crackdown on mining in a specific region could significantly impact the network’s hash rate and its overall decentralization.
Arguments for and Against the Long-Term Sustainability of Bitcoin’s Mining Model
Arguments for the long-term sustainability often center on the inherent economic incentives within the system. The proof-of-work mechanism, while energy-intensive, provides a robust security model that incentivizes miners to act honestly. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of the network makes it resilient to single points of failure. The open-source nature of Bitcoin’s software also fosters innovation and competition in mining hardware and techniques, potentially mitigating centralization risks over time.
Conversely, arguments against the sustainability focus on the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining and the growing centralization of mining power. The energy consumption associated with proof-of-work is a major concern, raising questions about its long-term viability in a world increasingly focused on environmental sustainability. Moreover, the concentration of mining power among a few large entities raises concerns about the network’s resilience to attacks and potential manipulation. The long-term success of Bitcoin’s mining model hinges on a balance between its security and its environmental and economic impacts. The ongoing development of more energy-efficient mining hardware and exploration of alternative consensus mechanisms could play a critical role in shaping the future of Bitcoin’s decentralized architecture.
Alternative Mining Strategies and Technologies
The Bitcoin mining landscape is constantly evolving, driven by the relentless pursuit of profitability and efficiency. The 2025 halving will undoubtedly accelerate this evolution, pushing miners to explore and adopt alternative strategies and technologies to maintain their operations’ viability. This exploration includes shifting mining locations, employing more energy-efficient hardware, and investigating alternative consensus mechanisms.
The impact of these changes will be multifaceted, influencing not only individual miners’ profitability but also the broader Bitcoin network’s security, decentralization, and environmental footprint. The following sections delve into some of the key developments and their potential consequences.
Alternative Mining Locations
Miners are increasingly seeking out regions with lower energy costs and more favorable regulatory environments. Historically, regions with abundant hydropower, such as parts of China and the Scandinavian countries, have been popular choices. However, regulatory changes and increased scrutiny of energy consumption have led miners to explore other locations, including those with access to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. This geographical shift influences the network’s decentralization, as mining power becomes concentrated in specific regions depending on their energy and regulatory landscape. For example, the migration from China to North America and Central Asia post-2021 demonstrates this dynamic. The availability of cheap, sustainable energy sources will play a critical role in shaping the future distribution of mining operations.
Energy-Efficient Mining Hardware
The development of Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) has been central to Bitcoin mining’s evolution. However, continuous innovation is pushing the boundaries of energy efficiency. New generations of ASICs are designed to deliver higher hash rates with lower power consumption. This translates to increased profitability for miners and a reduced environmental impact per unit of hash rate. For instance, the shift from older generation ASICs consuming hundreds of watts to newer models consuming significantly less power, showcases this trend. This ongoing improvement in hardware efficiency is vital for the long-term sustainability of Bitcoin mining.
Alternative Consensus Mechanisms
While Bitcoin currently relies on Proof-of-Work (PoW), alternative consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are gaining traction in other cryptocurrencies. PoS networks typically require significantly less energy than PoW networks. While unlikely to directly impact Bitcoin itself, the success and adoption of PoS systems could influence future discussions around energy consumption and the environmental impact of blockchain technologies. The ongoing debate about the energy efficiency of different consensus mechanisms underscores the broader implications of technological advancements within the cryptocurrency space. The long-term dominance of PoW or the eventual adoption of a hybrid system remains a key point of discussion within the industry.
Environmental Implications of Different Mining Strategies
The environmental impact of Bitcoin mining is a complex issue. The energy consumption of PoW mining is undeniably significant, but the source of that energy plays a crucial role. Mining operations powered by renewable energy sources have a considerably smaller carbon footprint compared to those reliant on fossil fuels. The shift towards renewable energy sources for Bitcoin mining is crucial for mitigating its environmental impact. For example, a mining operation using hydroelectric power will have a drastically lower carbon footprint than one relying on coal-fired power plants. The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources by mining operations demonstrates a conscious effort to reduce the environmental footprint of the Bitcoin network.
Investor Sentiment and Market Speculation
The Bitcoin halving, a predictable event reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation, significantly influences investor sentiment and market speculation. This influence stems from the interplay of supply and demand dynamics, amplified by the inherent volatility of the cryptocurrency market and the psychological biases of investors. Understanding past reactions and the psychology surrounding these events is crucial for navigating the market around the 2025 halving.
The anticipation surrounding a halving often leads to a period of price appreciation in the months leading up to the event. This is driven by the expectation of decreased supply, theoretically increasing scarcity and value. However, the post-halving price trajectory is less predictable, influenced by a multitude of factors beyond just the reduced issuance rate.
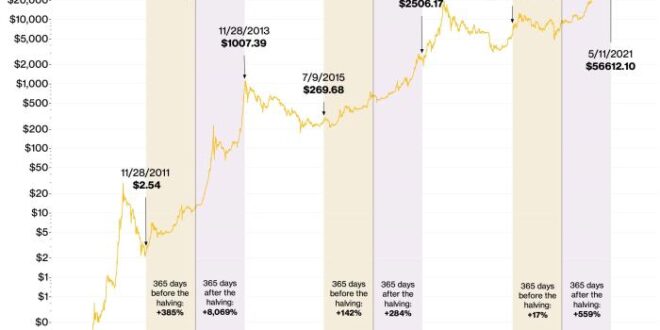
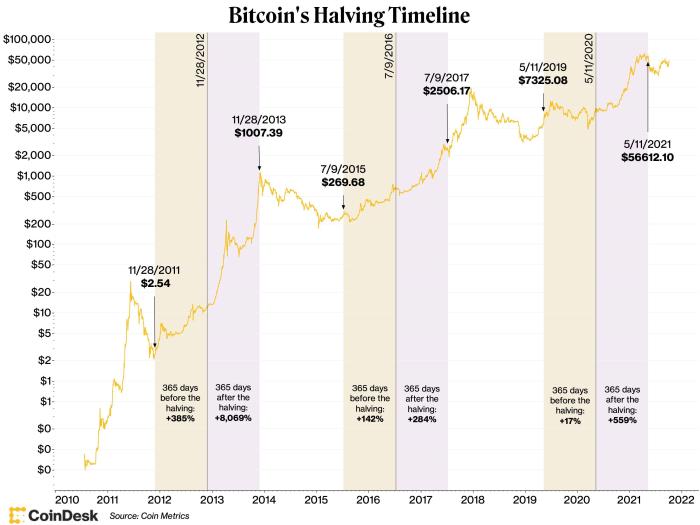
Past Market Reactions to Halving Events
The previous Bitcoin halvings have shown varied market reactions. The 2012 halving saw a gradual price increase following the event, while the 2016 halving was followed by a significant bull run. The 2020 halving, however, resulted in a more complex pattern, with a period of consolidation before a substantial price surge. These differing outcomes highlight the multifaceted nature of market dynamics and the influence of external factors beyond the halving itself, such as macroeconomic conditions, regulatory changes, and overall market sentiment. It is important to note that while a halving event can act as a catalyst, it is not the sole determinant of price movements.
Investor Psychology Leading Up To and Following a Halving
Investor psychology plays a significant role in shaping market reactions to halving events. Leading up to a halving, FOMO (fear of missing out) can drive up prices as investors rush to accumulate Bitcoin before the reduced supply takes effect. Conversely, following a halving, some investors might take profits, leading to temporary price corrections. This behavior reflects the inherent risk and reward associated with Bitcoin investment, further amplified by the speculative nature of the cryptocurrency market. Furthermore, the perception of risk and reward can shift dramatically depending on the overall economic climate and prevailing investor sentiment. For example, during periods of economic uncertainty, Bitcoin might be seen as a safe haven asset, leading to increased demand, regardless of the halving event.
Historical Correlation Between Halving Events and Price Movements
Analyzing historical data reveals a complex relationship between Bitcoin halvings and subsequent price movements. While the halvings have often been followed by periods of price appreciation, the magnitude and timing of these increases have varied considerably. A simple correlation analysis might show a positive relationship between halvings and subsequent price increases, but this relationship is not deterministic. Numerous other factors, such as technological advancements, regulatory developments, and broader market trends, significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. Therefore, attributing price changes solely to the halving event would be an oversimplification. A more nuanced approach requires considering the interplay of multiple factors to gain a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics. For instance, a detailed time-series analysis incorporating macroeconomic indicators and other relevant variables could provide a more accurate picture of the relationship.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
This section addresses common queries surrounding the Bitcoin mining halving event, a significant occurrence in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Understanding these aspects is crucial for navigating the potential market shifts and long-term implications.
Bitcoin Mining Halving Explained
A Bitcoin mining halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the reward given to Bitcoin miners for successfully adding a block of transactions to the blockchain by half. This occurs approximately every four years, or every 210,000 blocks mined. The halving is designed to control the inflation rate of Bitcoin, ensuring its scarcity over time. The initial reward was 50 BTC per block; after each halving, this reward is cut in half.
Timing of the Next Bitcoin Halving
The next Bitcoin halving is expected around April 2025. The exact date depends on the rate at which miners add blocks to the blockchain, which can fluctuate slightly. However, given the predictable nature of block generation, a timeframe around April 2025 is highly likely. This event will reduce the block reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC.
Impact of a Halving on Bitcoin’s Price
Historically, Bitcoin halvings have been followed by periods of increased price appreciation. This is primarily attributed to the reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin entering the market. However, it’s crucial to remember that price movements are influenced by numerous factors beyond the halving, including overall market sentiment, regulatory developments, and macroeconomic conditions. The 2012 and 2016 halvings were followed by significant price increases, but this is not a guaranteed outcome for the 2025 event. Other factors such as the prevailing economic climate will undoubtedly play a role.
Risks and Opportunities for Bitcoin Miners After a Halving, Bitcoin Mining Halving 2025
The halving presents both risks and opportunities for Bitcoin miners. The reduced block reward directly impacts miners’ profitability. Miners may need to adjust their operational costs, potentially leading to consolidation within the mining industry, with less efficient miners being forced to shut down. However, the expectation of a price increase following a halving can offset the reduced reward, making it potentially more profitable in the long run for those who can withstand the short-term challenges. The opportunity lies in successfully navigating the transition and maintaining profitability through operational efficiency and technological advancements.
Halving’s Impact on Bitcoin’s Long-Term Sustainability
The halving mechanism is integral to Bitcoin’s long-term sustainability. By controlling inflation and ensuring scarcity, it helps maintain Bitcoin’s value proposition as a store of value and a hedge against inflation. The gradual reduction in new Bitcoin supply mirrors the characteristics of precious metals like gold, contributing to its perceived long-term value. This controlled inflation is a key element of Bitcoin’s design and contributes to its resilience as a decentralized digital currency.
Illustrative Data Representation
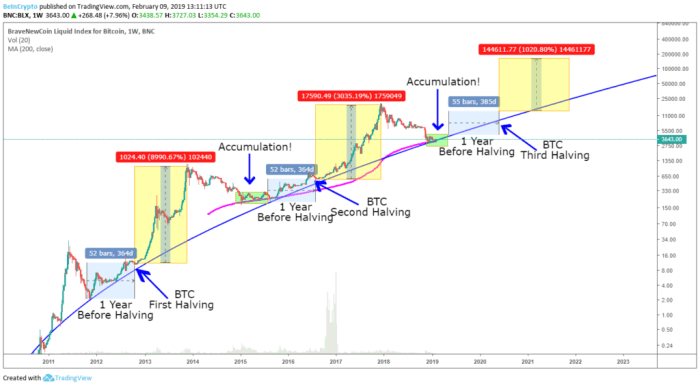
Analyzing historical halving events provides valuable insights into potential market reactions. While past performance is not indicative of future results, examining trends can help contextualize expectations surrounding the 2025 halving. Below, we present a table summarizing key metrics from previous halvings, followed by a description of a visual representation highlighting the price relationship.
Bitcoin Halving Metrics Comparison
The following table compares key metrics for the previous Bitcoin halvings. Note that the “Price After” column reflects a price point sometime after the halving, not an immediate post-halving price, due to the dynamic nature of the market. Precise timing for price analysis after a halving is difficult to standardize.
| Date | Block Reward (BTC) | Price Before (USD) | Price After (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| November 28, 2012 | 50 BTC | ~13 USD | ~100 USD (approx. 1 year later) |
| July 9, 2016 | 25 BTC | ~650 USD | ~20,000 USD (approx. 3 years later) |
| May 11, 2020 | 12.5 BTC | ~8,700 USD | ~64,000 USD (approx. 1 year later) |
Visual Representation: Halving Events and Bitcoin Price
A line graph would effectively illustrate the historical relationship between Bitcoin halving events and subsequent price movements. The x-axis would represent time, showing the dates of each halving clearly marked. The y-axis would represent the price of Bitcoin in USD. Each halving event would be marked with a distinct vertical line or symbol. The line graph itself would plot the Bitcoin price over time. This visual would clearly show the price trajectory before, during, and after each halving, allowing for observation of trends and potential correlations. While not a predictive tool, it serves as a valuable historical overview. For example, the graph would demonstrate the significant price appreciation following the 2016 and 2020 halvings, though the timing and magnitude of these increases varied. The graph’s purpose is to showcase the historical relationship, not to predict future price movements.
Bitcoin Mining Halving 2025 is a significant event impacting the cryptocurrency’s supply and mining profitability. Determining the precise date is crucial for miners to adjust their strategies. To find out exactly when this halving will occur, you can check this resource: When Is The Bitcoin Halving 2025. Knowing this date allows miners to prepare for the reduced block rewards and the potential consequences on the network’s security and transaction fees.
The Bitcoin Mining Halving 2025 will undoubtedly shape the market in the following years.
The Bitcoin Mining Halving 2025 event is a significant milestone in the cryptocurrency’s history, impacting the reward miners receive for verifying transactions. Precisely determining the impact requires knowing the exact date of this halving, which you can find by checking this helpful resource: Date Of Bitcoin Halving 2025. Understanding this date is crucial for predicting potential market shifts following the Bitcoin Mining Halving 2025.
The Bitcoin Mining Halving in 2025 is a significant event, impacting the supply of new Bitcoins entering circulation. Understanding the potential consequences on price is crucial, and for insightful analysis on this, check out this resource on Bitcoin Price Next Halving 2025. Ultimately, the halving’s effect on Bitcoin mining profitability and network security remains a key factor in the cryptocurrency’s long-term prospects.
The Bitcoin Mining Halving 2025 event is a significant moment for the cryptocurrency’s future, impacting miner profitability and potentially influencing the price. Understanding the precise timing is crucial, and you can find a detailed analysis of this at When Halving Bitcoin 2025. This knowledge is essential for anyone interested in the long-term implications of the Bitcoin Mining Halving 2025 and its effects on the network’s security and overall health.
The Bitcoin Mining Halving 2025 event is a significant occurrence in the cryptocurrency world, impacting the rate of new Bitcoin creation and potentially influencing its price. Pinpointing the exact date is crucial for miners and investors alike, and you can find a reliable prediction by checking this resource for the Date For Bitcoin Halving 2025. Understanding this date allows for better preparation regarding the subsequent changes in Bitcoin mining profitability and network security.
The Bitcoin Mining Halving in 2025 is a significant event impacting the cryptocurrency’s reward structure. Understanding the precise date of this halving is crucial for miners and investors alike. To find the exact date, you can check this resource: Bitcoin 2025 Halving Date. This information is essential for accurately predicting the potential effects on Bitcoin’s mining profitability and overall market dynamics after the 2025 Bitcoin Mining Halving.