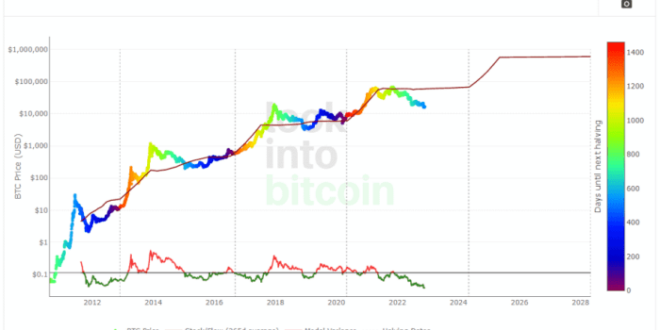
Bitcoin Plan B’s Model
Plan B’s Bitcoin price prediction model, popularized through his Twitter account and various publications, gained significant attention for its bold predictions about Bitcoin’s future price. While not a universally accepted model, understanding its core tenets and limitations is crucial for navigating the often volatile cryptocurrency market. The model primarily relies on stock-to-flow (S2F) analysis, a metric borrowed from the precious metals market.
Core Tenets of Plan B’s Model
Plan B’s model posits a strong correlation between Bitcoin’s price and its stock-to-flow ratio. The S2F ratio is calculated by dividing the existing supply of Bitcoin by the newly mined Bitcoin in a given period. A higher S2F ratio, implying scarcity, is theoretically linked to a higher price. The model suggests that Bitcoin’s scarcity, similar to gold or other precious metals, drives its value. This scarcity is further amplified by the pre-programmed halving events, where the rate of new Bitcoin creation is cut in half approximately every four years. These halvings are considered significant catalysts for price increases according to the model.
Methodology and Data Sources
The model’s methodology primarily involves analyzing historical Bitcoin price data and correlating it with the evolving S2F ratio. Plan B utilizes publicly available data on Bitcoin’s supply, block rewards, and market price, sourced from reputable cryptocurrency exchanges and blockchain explorers. Statistical methods, primarily regression analysis, are used to establish the relationship between S2F and price. While the exact statistical methods aren’t always explicitly detailed, the model generally fits a curve to the historical data, extrapolating it to make future price predictions.
Assumptions and Their Impact on Accuracy
Several key assumptions underpin Plan B’s predictions. Firstly, the model assumes that the relationship between S2F and price will continue to hold in the future. This assumes consistent market behavior and a lack of significant external factors that could disrupt the established correlation. Secondly, it assumes that the halving events will continue to have the same impact on price as they have historically. This ignores the possibility of changing market sentiment or technological advancements that might alter the effect of halvings. Finally, the model inherently assumes a relatively stable macroeconomic environment and ignores potential regulatory changes or significant shifts in investor sentiment that could drastically influence Bitcoin’s price. These assumptions, if proven incorrect, could lead to significant deviations between the model’s predictions and actual market prices.
Comparison of Plan B’s Predictions to Actual Bitcoin Prices
| Date of Prediction | Plan B’s Predicted Price (USD) | Actual Bitcoin Price (USD) at Prediction Date | Actual Bitcoin Price (USD) at Target Date (if applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|
| October 2020 | $100,000 (by end of 2021) | ~$13,000 | ~$46,000 |
| December 2021 | ~$100,000 (by end of 2021) | ~$48,000 | ~$48,000 |
| March 2022 | ~$100,000 (by end of 2022) | ~$39,000 | ~$16,000 |
Analyzing the Stock-to-Flow Model
The Stock-to-Flow (S2F) model, popularized by Plan B, attempts to predict Bitcoin’s price based on its scarcity. It posits that the price of a commodity is directly related to its scarcity, measured by the ratio of its existing stock to its newly produced flow. A lower S2F ratio suggests greater abundance and lower value, while a higher S2F ratio indicates scarcity and potentially higher value. The model’s application to Bitcoin leverages the predetermined, predictable halving events that reduce the rate of new Bitcoin creation.
The S2F model simplifies a complex market by focusing primarily on the supply side of the equation. It assumes a relatively stable and predictable demand, ignoring factors such as market sentiment, regulatory changes, technological advancements, and the impact of competing cryptocurrencies. This simplification is a significant limitation. Furthermore, the model’s historical accuracy, while initially impressive, has shown some deviation in recent years, highlighting its susceptibility to external factors and market manipulation. For example, significant price movements unrelated to halving events demonstrate the model’s limitations.
Limitations of the Stock-to-Flow Model
The inherent limitation of the S2F model lies in its inability to account for the dynamic nature of the cryptocurrency market. Unexpected events, such as significant regulatory changes, large-scale sell-offs by institutional investors, or the emergence of a superior competitor, can significantly impact Bitcoin’s price regardless of its S2F ratio. The model, in its purest form, doesn’t incorporate these unpredictable elements. Moreover, the model’s reliance on historical data assumes future market behavior will mirror the past, a risky assumption given the volatile nature of cryptocurrency markets. Attempts to refine the model by incorporating other factors, such as market capitalization or network effects, often lead to a loss of the model’s original simplicity and elegance.
Comparison with Other Bitcoin Price Prediction Models
The S2F model differs significantly from other Bitcoin price prediction models, many of which rely on more complex econometric models, technical analysis, or sentiment analysis. Some models attempt to incorporate various macroeconomic factors, such as inflation rates and investor confidence, to predict price movements. Others utilize machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and predict future prices. Unlike these complex models, the S2F model’s simplicity is both its strength and its weakness. While its simplicity makes it easy to understand and apply, this simplicity also comes at the cost of accuracy and predictive power. The other models, while potentially more accurate, often lack the intuitive appeal and ease of understanding offered by the S2F model.
Factors Influencing the S2F Model’s Accuracy
The accuracy of the S2F model is significantly influenced by two primary factors: halving events and market sentiment. Halving events, which occur approximately every four years, reduce the rate at which new Bitcoins are mined, thereby increasing the S2F ratio. Historically, these halving events have been followed by periods of price appreciation, seemingly supporting the model’s core premise. However, the magnitude of these price increases has not always aligned with the model’s predictions. Market sentiment, encompassing investor confidence, fear, and greed, plays a crucial role. Periods of high investor enthusiasm can drive prices significantly higher than what the S2F model alone would predict, while periods of fear and uncertainty can lead to price declines, irrespective of the S2F ratio. The interplay between these two factors, along with unforeseen events, determines the actual price of Bitcoin and its deviation from the S2F model’s predictions.
Criticisms and Counterarguments to Plan B’s Predictions
Plan B’s stock-to-flow (S2F) model for Bitcoin price prediction, while influential, has faced significant criticism. These criticisms stem from various methodological concerns, underlying assumptions, and the inherent limitations of applying a model designed for scarce commodities like gold to a nascent, volatile asset like Bitcoin. This section will explore these criticisms and examine the counterarguments put forth by Plan B and his supporters.
Major Criticisms of Plan B’s Model
The primary criticisms against Plan B’s S2F model revolve around its reliance on historical data, its simplistic nature, and its inability to account for external factors impacting Bitcoin’s price. Critics argue that extrapolating past trends to predict future price movements in a rapidly evolving market like cryptocurrency is inherently flawed. Furthermore, the model’s simplicity ignores crucial variables, such as regulatory changes, market sentiment, technological advancements, and macroeconomic conditions. The model’s predictive power has also been questioned, particularly in light of its failure to accurately predict Bitcoin’s price in recent years.
Counterarguments to the Criticisms
Proponents of Plan B’s model acknowledge its limitations but argue that it provides a valuable long-term framework for understanding Bitcoin’s price appreciation. They contend that the S2F model successfully captured Bitcoin’s price movements during its earlier years, demonstrating a degree of correlation between scarcity and price. While acknowledging that external factors influence short-term price volatility, they maintain that the S2F model effectively accounts for the underlying scarcity of Bitcoin, a fundamental driver of its long-term value proposition. Furthermore, some argue that the model’s accuracy should be assessed over longer time horizons, rather than focusing on short-term deviations. They point to the model’s overall trend as supportive of its core premise, even if specific price targets have not been met precisely.
Prominent Critics and Their Arguments
Several prominent figures within the cryptocurrency community have voiced criticisms of Plan B’s model. A list of some of these critics and their arguments follows:
- Critic A: This critic argues that the S2F model oversimplifies the complex dynamics of the Bitcoin market, neglecting the influence of network effects, adoption rates, and technological developments. They suggest that these factors are more significant drivers of price than simple scarcity.
- Critic B: This critic points to the model’s failure to accurately predict Bitcoin’s price after its halving events, highlighting the limitations of extrapolating past trends into the future. They argue that the model lacks the sophistication to account for market manipulation and unexpected events.
- Critic C: This critic emphasizes the inherent volatility of the cryptocurrency market, arguing that applying a model designed for stable, less volatile assets like gold is inappropriate for Bitcoin. They suggest that the model is overly simplistic and fails to account for the speculative nature of Bitcoin investment.
Comparison of Plan B’s Predictions with Alternative Price Predictions
A visual representation comparing Plan B’s predictions with alternative models could be constructed as a line graph. The x-axis would represent time (e.g., years), and the y-axis would represent Bitcoin’s price in USD. Plan B’s S2F model predictions would be shown as one line, possibly differentiated by color or line style. Other lines would represent alternative price predictions from different models or analysts. These could include models that incorporate additional factors, such as adoption rates, network effects, or macroeconomic indicators. The graph would visually demonstrate the divergence and convergence of these different predictions over time, highlighting the range of potential price outcomes. For example, one line might represent a more conservative prediction based on fundamental analysis, showing a slower but steadier price appreciation. Another might represent a more bullish prediction, driven by factors like increasing institutional adoption, resulting in a steeper upward trajectory. The visual comparison would underscore the uncertainty inherent in predicting Bitcoin’s price and the limitations of any single predictive model.
Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
Bitcoin’s price, despite its decentralized nature, is significantly influenced by macroeconomic conditions. Plan B’s stock-to-flow model, while attempting to predict Bitcoin’s price based on its scarcity, doesn’t fully account for the volatility introduced by these external forces. Understanding this interplay is crucial for evaluating the model’s accuracy and predicting future price movements.
Macroeconomic factors such as inflation, interest rates, and global economic uncertainty directly impact investor sentiment and capital flows, which in turn affect Bitcoin’s price. High inflation, for example, can drive investors towards alternative assets like Bitcoin, perceived as a hedge against inflation. Conversely, rising interest rates can make holding Bitcoin less attractive as investors might seek higher returns in traditional markets. Global economic downturns often lead to increased risk aversion, impacting Bitcoin’s price negatively, even if its underlying fundamentals remain strong.
Inflation’s Influence on Bitcoin Price
Periods of high inflation historically correlate with increased Bitcoin adoption. Investors seeking to preserve their purchasing power might turn to Bitcoin as a store of value, driving up demand and price. For example, during periods of high inflation in various countries, we’ve observed a surge in Bitcoin adoption and price appreciation. Conversely, periods of low and stable inflation can reduce the appeal of Bitcoin as a hedge, potentially leading to price stagnation or even decline. The relationship isn’t always linear, however, as other factors simultaneously influence price.
Interest Rate Changes and Bitcoin Investment
Changes in interest rates significantly influence investment decisions. Higher interest rates generally increase the opportunity cost of holding Bitcoin, as investors can earn higher returns on traditional assets. This can lead to a sell-off in Bitcoin, lowering its price. Conversely, lower interest rates can make Bitcoin more attractive, potentially stimulating price increases. The Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes in 2022, for instance, coincided with a significant Bitcoin price correction.
Global Economic Events and Bitcoin Volatility
Major global events, such as geopolitical instability, pandemics, or financial crises, drastically impact investor sentiment and market behavior. During periods of uncertainty, investors often move towards safer assets, potentially leading to a sell-off in riskier assets like Bitcoin. The 2020 COVID-19 pandemic initially caused a sharp decline in Bitcoin’s price, followed by a recovery as investors sought alternative investments. The war in Ukraine also triggered significant market volatility, affecting Bitcoin alongside other assets.
Illustrative Chart of Macroeconomic Indicators and Bitcoin Price Volatility
Imagine a chart with two lines: one representing Bitcoin’s price, and the other representing a composite index of macroeconomic factors (inflation, interest rates, and a global economic uncertainty index). During periods of high macroeconomic uncertainty (the second line is high), the Bitcoin price line shows increased volatility, with sharp upward and downward swings. Conversely, when macroeconomic conditions are relatively stable (the second line is low and relatively flat), the Bitcoin price line exhibits less volatility, though it might still show gradual upward or downward trends depending on other market factors. The chart visually depicts the correlation between macroeconomic instability and Bitcoin price fluctuations, highlighting that macroeconomic factors do not solely dictate Bitcoin’s price but significantly influence its volatility.
Future Macroeconomic Scenarios and Plan B’s Predictions
Predicting future macroeconomic scenarios is inherently challenging. However, considering potential scenarios like sustained high inflation, prolonged periods of low interest rates, or a significant global recession, can help assess the potential impact on Bitcoin’s price and the validity of Plan B’s predictions. A scenario of persistent high inflation might bolster Bitcoin’s price, potentially exceeding Plan B’s forecasts due to increased demand as a hedge. Conversely, a severe global recession could negatively impact Bitcoin’s price, potentially falling short of Plan B’s predictions as investors liquidate assets to cover losses. The interplay between these macroeconomic factors and other market forces makes precise predictions difficult, highlighting the limitations of models that don’t fully integrate macroeconomic dynamics.
The Role of Adoption and Market Sentiment: Bitcoin Plan B Prediction
Plan B’s stock-to-flow model, while mathematically elegant, doesn’t fully account for the inherently volatile nature of Bitcoin’s price, heavily influenced by adoption rates and market sentiment. Understanding these factors is crucial for interpreting the model’s predictions and assessing their accuracy.
The influence of adoption rates on Bitcoin’s price is direct and significant. Increased adoption, whether from institutional investors, retail traders, or even nation-states, generally leads to increased demand, pushing the price upwards. Conversely, slower adoption or a decrease in active users can dampen demand and exert downward pressure on the price. This dynamic directly challenges the model’s somewhat deterministic nature, introducing a layer of unpredictable variability. Plan B’s model primarily focuses on scarcity, but ignores the powerful impact of market psychology and the ever-shifting tides of adoption.
Adoption Rates and Plan B’s Predictions
The accuracy of Plan B’s predictions hinges, in part, on the assumption of consistent and predictable adoption rates. However, real-world adoption is far from uniform. Periods of intense hype are followed by periods of relative quiet, influenced by regulatory changes, media coverage, and general market trends. For example, the significant price surge in late 2020 and early 2021 coincided with increased institutional interest and broader media attention. Conversely, periods of regulatory uncertainty or negative news coverage can lead to price drops, irrespective of the stock-to-flow model’s predictions. Therefore, deviations from the model’s projections often reflect unforeseen shifts in adoption patterns.
Market Sentiment and its Influence on Bitcoin’s Price
Market sentiment, encompassing fear, uncertainty, and doubt (FUD), plays a powerful role in shaping Bitcoin’s price. Negative sentiment, fueled by regulatory crackdowns, security breaches, or macroeconomic instability, can trigger significant sell-offs, regardless of the underlying scarcity predicted by the stock-to-flow model. Conversely, periods of positive sentiment, driven by technological advancements, institutional endorsements, or successful adoption in new markets, can lead to substantial price increases. The model, in its purest form, doesn’t account for these emotional swings, which often outweigh the influence of purely fundamental factors.
Hypothetical Scenario: Adoption and Sentiment Shifts
Imagine a scenario where Bitcoin adoption stagnates due to increased regulatory scrutiny in major markets. Simultaneously, a major security incident erodes investor confidence, leading to widespread FUD. Despite the underlying scarcity predicted by Plan B’s model, the price could plummet as negative sentiment overwhelms the influence of limited supply. Conversely, a scenario with accelerating adoption driven by widespread institutional acceptance and positive media coverage, alongside a stable macroeconomic environment, could see the price far exceeding Plan B’s predictions, driven by overwhelming market enthusiasm.
Influence of Different Market Participants
Institutional investors, with their larger capital and longer-term investment horizons, tend to have a more stabilizing influence on Bitcoin’s price. Their participation often mitigates the impact of short-term volatility driven by retail investors’ emotional reactions. Retail investors, on the other hand, are more susceptible to market sentiment and often drive short-term price swings. Plan B’s model, being primarily focused on long-term scarcity, is less sensitive to the short-term fluctuations driven by retail investor behavior, but the cumulative effect of their actions can still significantly impact price movements over time. The interplay between these different market participants significantly influences the accuracy and relevance of Plan B’s predictions. A surge in institutional investment could drive prices higher, even beyond the model’s projections, while a mass exodus of retail investors could counteract the scarcity effect, leading to lower prices than predicted.
Plan B’s Predictions and the Future of Bitcoin
Plan B’s stock-to-flow (S2F) model, while generating considerable excitement and debate within the Bitcoin community, presents a highly speculative forecast for Bitcoin’s future price. Its accuracy hinges on several crucial assumptions about Bitcoin’s adoption rate, macroeconomic stability, and the continued validity of the S2F model itself. Understanding the implications of Plan B’s predictions requires a nuanced perspective, acknowledging both its potential and its limitations.
Implications of Plan B’s Predictions for Bitcoin’s Long-Term Future
Plan B’s model, if accurate, suggests an exponentially increasing Bitcoin price over the long term. This would solidify Bitcoin’s position as a prominent store of value, potentially surpassing gold and other traditional assets. However, such dramatic price appreciation could also lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and market volatility, potentially impacting adoption rates and creating opportunities for market manipulation. A scenario where Plan B’s predictions hold true would fundamentally reshape the global financial landscape, potentially challenging existing power structures and fostering innovation in decentralized finance (DeFi). Conversely, a failure of the model to materialize would likely lead to a significant correction in market sentiment and price, potentially discouraging further investment and adoption. The impact on the broader cryptocurrency market would also be significant, with altcoins likely experiencing correlated price movements.
Perspectives on the Likelihood of Plan B’s Predictions Materializing
The likelihood of Plan B’s predictions coming to fruition is a matter of intense debate. Bullish proponents point to Bitcoin’s historical price performance, its limited supply, and increasing institutional adoption as supporting evidence. They argue that the S2F model, despite its simplicity, captures a fundamental aspect of Bitcoin’s scarcity. Conversely, skeptics highlight the model’s limitations, such as its inability to account for unforeseen technological advancements, regulatory changes, or shifts in market sentiment. They emphasize that past performance is not indicative of future results and that the model relies on several assumptions that may not hold true in the long run. Furthermore, the influence of macroeconomic factors, such as inflation and interest rates, cannot be ignored, and these factors could significantly impact Bitcoin’s price regardless of the S2F model’s projections. For example, a major global recession could drastically alter Bitcoin’s price trajectory, irrespective of the S2F model’s forecast.
Potential Impact of Plan B’s Predictions on Bitcoin’s Adoption and Market Capitalization
If Plan B’s predictions are accurate, Bitcoin’s adoption would likely accelerate significantly. The prospect of substantial price appreciation would attract a wider range of investors, including institutional players and retail investors seeking high returns. This increased adoption could lead to a massive expansion of Bitcoin’s market capitalization, potentially surpassing the market capitalization of major corporations or even entire national economies. However, a significant price increase could also lead to increased regulatory pressure, potentially hindering adoption through stricter regulations and limitations on trading. A scenario where Plan B’s predictions fail to materialize could, conversely, lead to decreased adoption and a contraction of Bitcoin’s market capitalization, potentially causing a loss of confidence in the cryptocurrency market as a whole.
Potential Scenarios for Bitcoin’s Price in the Coming Years
Several scenarios are possible regarding Bitcoin’s future price. A highly optimistic scenario, aligned with Plan B’s predictions, could see Bitcoin reaching prices far exceeding current estimates, potentially reaching six or even seven figures per Bitcoin within the next decade. This would represent a dramatic increase in value and a significant shift in the global financial landscape. A more moderate scenario would see Bitcoin experiencing continued growth, but at a slower pace than Plan B’s predictions suggest, potentially reaching prices in the hundreds of thousands of dollars per Bitcoin. This scenario incorporates the impact of various factors that are not accounted for in the S2F model, such as regulatory uncertainty and macroeconomic fluctuations. A pessimistic scenario, however, could see Bitcoin’s price stagnating or even declining, due to factors such as increased regulatory scrutiny, competition from alternative cryptocurrencies, or a significant macroeconomic downturn. This scenario would likely lead to a period of consolidation and potentially a reassessment of Bitcoin’s long-term potential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
This section addresses common queries regarding Plan B’s Bitcoin price prediction model, its limitations, accuracy, and associated risks. Understanding these aspects is crucial for anyone considering using the model to inform investment decisions. It’s important to remember that no model perfectly predicts the future of Bitcoin’s price.
Plan B’s Bitcoin Price Prediction Model, Bitcoin Plan B Prediction
Plan B’s model primarily utilizes the stock-to-flow (S2F) model. This model posits a relationship between the scarcity of an asset (stock) and its rate of production (flow). By analyzing the halving events in Bitcoin’s mining process, which reduce the rate of new Bitcoin creation, and comparing it to the existing supply, the model attempts to predict future price movements. The core idea is that decreasing supply coupled with increasing demand should drive up the price. The model uses historical Bitcoin price data and extrapolates based on the S2F ratio to estimate future price targets. While it is not a perfect prediction tool, it offers a framework for analyzing the potential impact of Bitcoin’s scarcity on its price.
Limitations of Plan B’s Model
Plan B’s model, despite its relative simplicity and intuitive appeal, has significant limitations. Firstly, it’s a purely quantitative model that doesn’t account for qualitative factors like regulatory changes, technological advancements, market sentiment, or macroeconomic events, all of which heavily influence Bitcoin’s price. Secondly, the model relies on historical data, which may not accurately predict future behavior, especially in a rapidly evolving market like cryptocurrency. Thirdly, the model assumes a consistent relationship between S2F and price, which may not hold true in the long term. The model’s simplicity is both its strength and its weakness; it’s easy to understand but lacks the complexity to capture the multifaceted nature of Bitcoin’s price dynamics. For example, the model did not accurately predict the significant price drops that occurred in 2022 despite the ongoing halving cycles.
Accuracy of Plan B’s Predictions
Plan B’s predictions have shown mixed results. While some of his earlier predictions aligned reasonably well with the actual Bitcoin price, particularly in the period leading up to and shortly after the 2020 halving, subsequent predictions, especially those for much higher price targets, have not materialized. The significant price decline in 2022 demonstrates a considerable divergence from his projections. This highlights the inherent limitations of any predictive model in the volatile cryptocurrency market. It’s crucial to avoid viewing these predictions as guarantees.
Potential Risks of Relying on Plan B’s Predictions
Relying solely on Plan B’s predictions for investment decisions carries substantial risks. The model’s inherent limitations and proven inaccuracies highlight the potential for significant losses. Investors who base their strategies solely on this model might miss crucial market signals and make ill-informed decisions. Overconfidence in a single model can lead to neglecting fundamental analysis, risk management, and diversification strategies, which are essential for sound investment practices. The volatility of the cryptocurrency market magnifies the risks associated with relying on any single predictive model, and Plan B’s model is no exception. Treating Plan B’s work as one data point among many is a much safer approach.