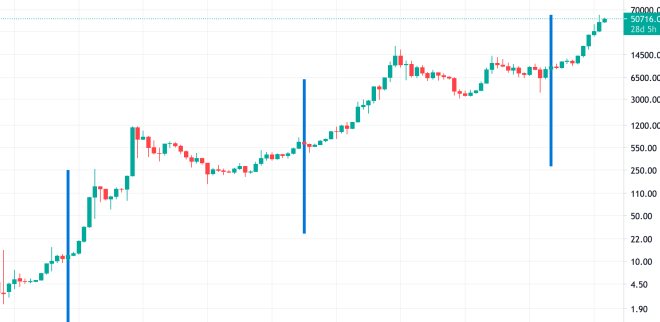
Bitcoin Halving 2025
The Bitcoin halving, a pre-programmed event reducing the rate of newly mined Bitcoin by half, is anticipated to occur in 2025. This event has historically had a significant impact on Bitcoin’s price and market sentiment, creating both excitement and uncertainty within the cryptocurrency community. Understanding the historical context and potential economic factors influencing the 2025 halving is crucial for navigating the market’s complexities.
Historical Impact of Bitcoin Halvings, Date Halving Bitcoin 2025
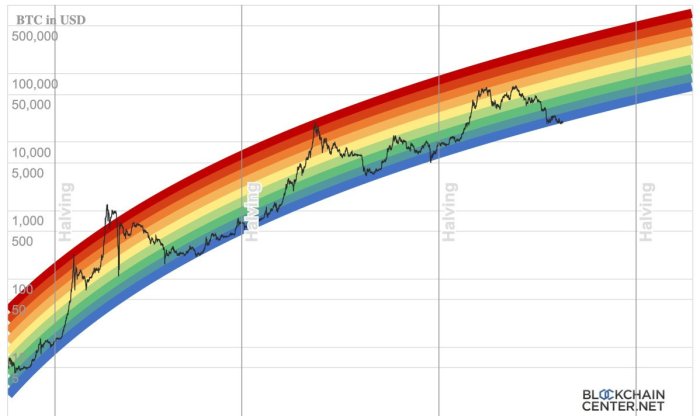
Previous Bitcoin halvings have demonstrated a correlation, though not a guaranteed causation, between the event and subsequent price increases. The first halving in 2012 saw a gradual price rise following the event. The second halving in 2016 preceded a significant bull market. The third halving in 2020 also showed a price surge, although the market experienced volatility before and after the event. It’s important to note that while these events are often associated with price appreciation, other macroeconomic factors and market sentiment play a significant role in shaping Bitcoin’s price trajectory. The timing and magnitude of price movements post-halving have varied considerably, highlighting the complexity of predicting market behavior.
Economic Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price
Several economic factors could significantly influence Bitcoin’s price in the lead-up to and aftermath of the 2025 halving. These include the overall state of the global economy, regulatory developments concerning cryptocurrencies, the adoption rate of Bitcoin by institutions and individuals, and the level of competition from alternative cryptocurrencies. Macroeconomic conditions such as inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical events will also play a crucial role. For example, a period of high inflation might increase demand for Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation, potentially driving up its price. Conversely, a period of economic uncertainty could lead to investors liquidating their Bitcoin holdings, causing price drops.
Comparison of the 2025 Halving with Previous Events
While historical trends suggest a potential price increase following the 2025 halving, it’s crucial to acknowledge significant differences from previous events. The cryptocurrency market is considerably more mature and regulated than in 2012, 2016, or even 2020. The increased institutional involvement and regulatory scrutiny might dampen the magnitude of any price surge. Furthermore, the overall macroeconomic climate in 2025 could differ significantly from the conditions prevailing during previous halving events, further complicating price predictions. The increased market sophistication and regulatory landscape make a direct comparison challenging, requiring a nuanced analysis considering the unique context of 2025.
Potential Price Scenarios
Predicting Bitcoin’s price is inherently speculative, but we can illustrate potential scenarios based on different assumptions.
Date Halving Bitcoin 2025 – Scenario 1: Bullish Scenario
This scenario assumes sustained institutional adoption, positive regulatory developments, and continued global macroeconomic uncertainty driving demand for Bitcoin as a safe haven asset. The chart below would show a gradual price increase leading up to the halving, followed by a significant price surge post-halving, possibly exceeding previous bull market highs. The chart would include a timeline from early 2024 to late 2026, with a clear upward trend, potentially reaching price targets significantly higher than current levels. Key chart elements would include a price axis (USD), a time axis (date), a line graph illustrating the price trajectory, and annotations highlighting the halving event and key price levels.
Scenario 2: Bearish Scenario
This scenario assumes a negative macroeconomic climate, increased regulatory pressure leading to decreased adoption, and significant competition from alternative cryptocurrencies. The chart would depict a relatively flat or even slightly downward trend in the lead-up to the halving, with a limited price increase or even a price decline following the event. The chart’s elements would be similar to Scenario 1, but the line graph would illustrate a flat or downward trend, with annotations highlighting potential support and resistance levels.
Scenario 3: Neutral Scenario
This scenario assumes a moderate level of institutional adoption, neutral regulatory developments, and a stable global macroeconomic environment. The chart would show a relatively stable price leading up to the halving, followed by a moderate price increase post-halving, potentially less significant than previous bull markets. The chart would illustrate a less dramatic price movement compared to the bullish and bearish scenarios, highlighting the potential for a more subdued market reaction.
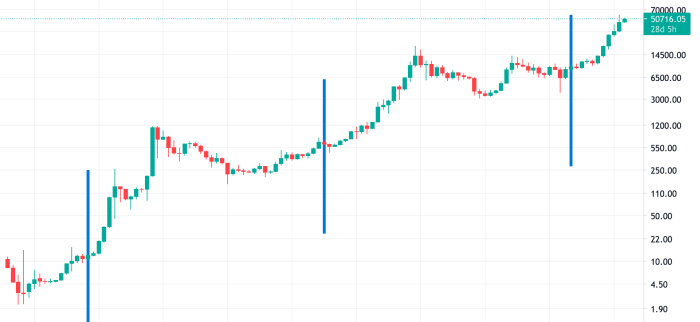
The Mechanics of Bitcoin Halving: Date Halving Bitcoin 2025
Bitcoin halving is a crucial programmed event in the Bitcoin network that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. This process, built into Bitcoin’s core code, is designed to control inflation and maintain the scarcity of Bitcoin over time. Understanding its mechanics is key to grasping Bitcoin’s long-term value proposition.
The Bitcoin halving process directly impacts the reward miners receive for verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain. Every 210,000 blocks mined, approximately every four years, the block reward is cut in half. This halving reduces the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation, thereby influencing its price and overall market dynamics. The initial block reward was 50 BTC, and each subsequent halving has reduced this reward.
The Halving Algorithm and Scarcity
The halving schedule is determined by a pre-programmed algorithm embedded within Bitcoin’s code. This algorithm dictates that the block reward is halved at a fixed interval of 210,000 blocks. This consistent, predictable schedule contributes significantly to Bitcoin’s scarcity. Unlike fiat currencies, which central banks can print at will, Bitcoin’s supply is inherently limited to a maximum of 21 million coins. The halving mechanism ensures that this limit is approached gradually, reinforcing its value proposition as a deflationary asset. The long-term implication is a progressively decreasing rate of new Bitcoin entering the market, potentially driving up its value as demand remains constant or increases.
Comparison with Other Cryptocurrency Mining Reward Systems
Many other cryptocurrencies also employ mining reward systems, but their mechanisms often differ significantly from Bitcoin’s halving. Some cryptocurrencies have no fixed halving schedule, while others use different algorithms to adjust block rewards. For instance, some cryptocurrencies may adjust the block reward based on network hash rate or inflation targets. This contrasts with Bitcoin’s fixed, predictable halving, which contributes to its unique characteristics. The lack of a similar, predictable scarcity mechanism in other cryptocurrencies highlights Bitcoin’s distinct approach to controlling inflation and maintaining its long-term value.
Timeline of Key Events Surrounding the 2025 Halving
The following timeline illustrates key events surrounding the 2025 Bitcoin halving, showing the anticipation and potential market impact leading up to and following the event. Predicting precise market reactions is impossible, but historical data from previous halvings provides valuable insights.
| Date | Event | Potential Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 – 2024 | Increased anticipation and speculation surrounding the 2025 halving | Potential price increase due to increased demand and investor interest |
| Mid-2024 | Approaching the halving event | Increased volatility and potential price fluctuations as the halving date nears |
| Early 2025 | Bitcoin Halving Event | Historically, halvings have been followed by significant price increases, though the timing and magnitude vary |
| 2025 – 2026 | Post-halving period | Potential price stabilization or further increase, depending on various market factors including adoption rate and macroeconomic conditions |
Impact on Mining and Miners
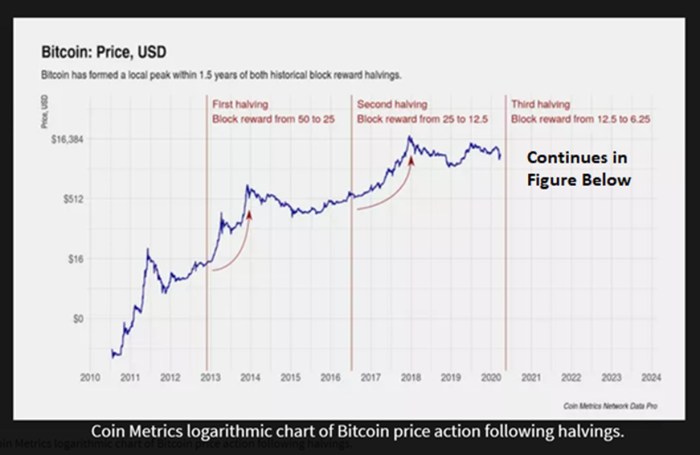
The Bitcoin halving event, scheduled for 2025, will significantly impact the profitability of Bitcoin mining and the overall energy consumption of the network. This reduction in block rewards, a core element of the Bitcoin protocol, forces miners to adapt their strategies to remain profitable and competitive within the ecosystem. The consequences will be felt across different geographical regions, highlighting variations in resilience and operational costs.
The halving directly reduces the Bitcoin reward miners receive for successfully adding a block to the blockchain. This translates to a decrease in revenue, forcing miners to evaluate their operational efficiency and explore alternative strategies to maintain profitability. Increased competition, coupled with fluctuating Bitcoin prices, will determine which mining operations survive and thrive. The impact on energy consumption is also substantial, as miners will need to carefully consider their energy costs in light of reduced income.
Mining Profitability and Energy Consumption
The halving’s impact on mining profitability is directly proportional to the decrease in block rewards. Before the halving, miners receive a certain amount of Bitcoin for each block they successfully mine. After the halving, this reward is cut in half. To maintain profitability, miners must either reduce their operational costs (e.g., energy consumption, hardware maintenance) or see a rise in the Bitcoin price. The latter is not guaranteed and depends on market forces. The energy consumption of the Bitcoin network is closely tied to mining profitability. If profitability declines, less efficient miners might be forced to shut down, potentially reducing the network’s overall energy consumption. Conversely, a rise in Bitcoin’s price could offset the reduced block reward, encouraging more miners to join the network and potentially increasing energy consumption.
Miner Adaptation Strategies
Miners will employ various strategies to adapt to the reduced block rewards. These include: optimizing mining hardware and software for greater efficiency, negotiating lower energy costs with providers, diversifying revenue streams (e.g., through transaction fees or mining other cryptocurrencies), and consolidating operations to achieve economies of scale. Some miners might choose to relocate to regions with lower electricity costs or more favorable regulatory environments. The success of these strategies will depend on individual miner capabilities and the prevailing market conditions. Historically, miners have demonstrated adaptability, showcasing resilience in navigating previous halving events.
Resilience of Mining Operations Across Regions
The resilience of Bitcoin mining operations varies significantly across geographical regions due to differences in electricity costs, regulatory frameworks, and access to infrastructure. Regions with abundant renewable energy sources and low electricity prices (e.g., parts of China, Kazakhstan, and North America) tend to have more resilient mining operations. Conversely, regions with high electricity costs or strict regulations might see a decline in mining activity following the halving. Political stability and government policies also play a crucial role, as regulatory uncertainty can negatively impact mining investment and profitability. The geographic distribution of mining power is dynamic and constantly shifts based on these factors.
Comparison of Hashrate, Mining Difficulty, and Profitability Across Halvings
| Halving Event | Hashrate Before (EH/s) | Hashrate After (EH/s) | Mining Difficulty Adjustment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 0.01 – 0.1 | 0.1 – 1 | Increased significantly |
| 2016 | 1 – 2 | 2 – 5 | Increased significantly |
| 2020 | 100 – 150 | 150 – 200 | Increased significantly |