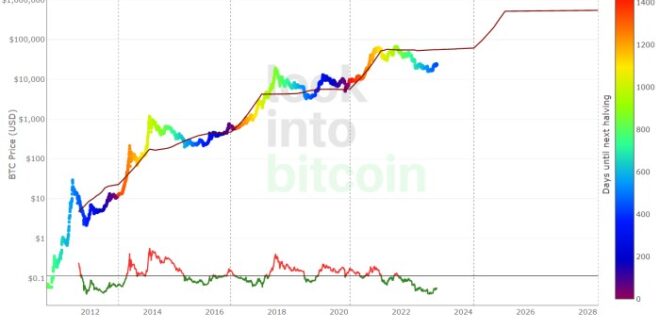
Predicting the 2025 Halving’s Impact
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation by half, is anticipated to occur in 2025. Predicting its impact on price is complex, requiring consideration of various interacting factors. While historically halvings have preceded significant price increases, the current market environment presents unique challenges and opportunities.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price After the 2025 Halving
Several factors will likely influence Bitcoin’s price trajectory following the 2025 halving. These include the inherent scarcity of Bitcoin, amplified by the reduced supply, alongside macroeconomic conditions, regulatory developments, and overall market sentiment. The interplay of these elements will determine the extent and duration of any price appreciation. For example, strong institutional adoption and positive regulatory changes could significantly amplify the impact of the halving, while negative macroeconomic news could dampen the effect.
Comparison of Market Conditions Leading Up to Previous Halvings
The market conditions leading up to the 2025 halving differ significantly from those preceding previous halvings. The 2012 and 2016 halvings occurred during periods of relatively nascent Bitcoin adoption and less pronounced macroeconomic uncertainty. In contrast, the 2025 halving approaches amidst heightened global inflation, rising interest rates, and increased regulatory scrutiny of cryptocurrencies in various jurisdictions. This makes predicting the price impact more challenging than in the past. The previous halvings saw relatively gradual price increases in the period following the event, whereas the current environment suggests greater potential for volatility.
Impact of Macroeconomic Factors on Bitcoin’s Price
Macroeconomic factors, such as inflation and interest rates, exert significant influence on Bitcoin’s price. High inflation can drive investors towards alternative assets like Bitcoin, perceived as a hedge against inflation. Conversely, rising interest rates increase the opportunity cost of holding Bitcoin, potentially reducing demand. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions, for instance, will play a crucial role in shaping investor sentiment and, consequently, Bitcoin’s price. The correlation between Bitcoin’s price and the US Dollar Index is a key indicator to observe. A strengthening dollar could put downward pressure on Bitcoin’s price, while a weakening dollar might have the opposite effect.
Expert Opinions and Market Analyses Regarding Expected Price Volatility
Expert opinions on the 2025 halving’s impact vary widely. Some analysts predict a substantial price surge, pointing to the historical precedent and the inherent scarcity of Bitcoin. Others express caution, highlighting the current macroeconomic uncertainties and potential regulatory headwinds. Market analyses often incorporate sophisticated models that consider various factors, but these models still carry inherent uncertainties. The range of price predictions underscores the inherent volatility of the cryptocurrency market and the difficulty in accurately forecasting future price movements. For example, some analysts have used historical data and on-chain metrics to suggest potential price ranges, while others focus on broader macroeconomic trends and geopolitical events to form their predictions.
The Halving’s Effect on Mining
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event that reduces the block reward paid to miners, significantly impacts the profitability and operational landscape of the Bitcoin mining industry. Understanding these effects is crucial for predicting the future trajectory of the network’s security and decentralization. The 2025 halving, in particular, will be a critical test of the resilience of the mining ecosystem.
The reduction in block rewards directly affects miners’ revenue streams. Prior to the halving, miners receive a certain number of newly minted bitcoins for successfully adding blocks to the blockchain. After the halving, this reward is cut in half. This immediately reduces the income generated per block mined, forcing miners to reassess their operational costs and profitability. This is further complicated by the inherent volatility of Bitcoin’s price, which directly impacts the value of the mined rewards.
Miner Profitability and Operational Challenges
The decreased block reward necessitates a careful evaluation of mining operations. Miners must analyze their energy costs, hardware maintenance, and other operational expenses to determine if they can remain profitable with the reduced income. Those with higher operational costs, less efficient mining hardware, or unfavorable electricity prices will face significant challenges. For example, a miner operating with high electricity costs in a region with less favorable regulatory environments may find it impossible to continue mining profitably after the halving. The resulting pressure on profit margins could lead to the shutdown of less efficient mining operations.
Consequences of a Large-Scale Miner Exodus
A significant exodus of miners could have several negative consequences. Reduced mining activity could lead to a decrease in the network’s hash rate, which is a measure of the computational power securing the blockchain. A lower hash rate increases the vulnerability of the network to 51% attacks, where a malicious actor could control a majority of the network’s hashing power to manipulate the blockchain. Furthermore, a decline in the number of miners could potentially lead to a more centralized network, contradicting Bitcoin’s decentralized ethos. The 2012 and 2016 halvings witnessed periods of decreased hash rate, but the network eventually adapted and recovered, demonstrating resilience. However, the scale of the 2025 halving’s impact remains uncertain.
Miner Adaptation Strategies
Miners will likely employ various strategies to adapt to the reduced rewards. This might include upgrading to more energy-efficient mining hardware, negotiating lower electricity prices, or diversifying revenue streams. Some miners might consolidate operations to achieve economies of scale, while others may explore alternative revenue models such as providing mining-as-a-service or engaging in other crypto-related activities. For instance, a hypothetical scenario could involve a large mining pool consolidating its operations in a region with lower energy costs and investing in the latest generation of ASICs to maximize efficiency. Alternatively, smaller miners might collaborate to share resources and reduce individual operational costs. The ultimate success of these adaptation strategies will depend on various factors, including the price of Bitcoin, the availability of cheap energy, and the regulatory environment.
Long-Term Implications of the 2025 Halving
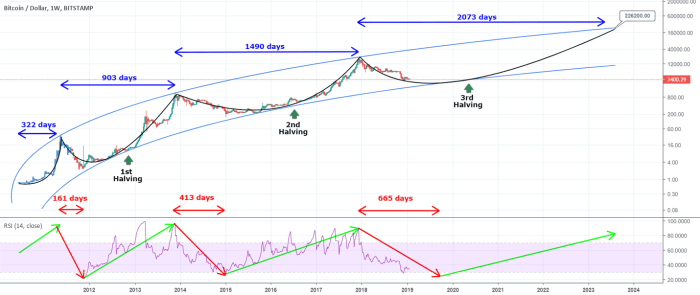
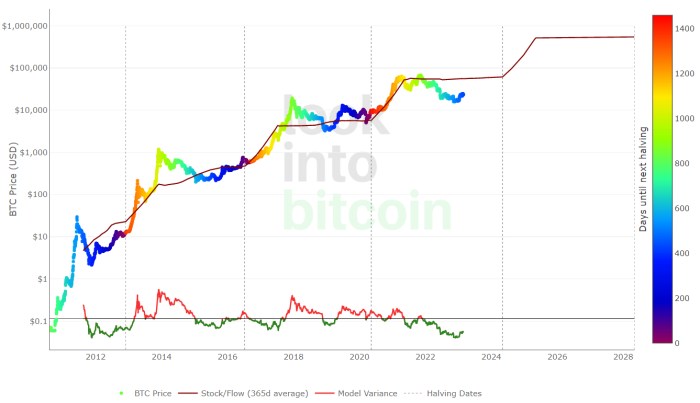
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation by half, presents significant long-term implications for the cryptocurrency’s scarcity, value proposition, and overall market position. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for investors and stakeholders alike, as the event is anticipated to trigger considerable market shifts. The halving’s impact will likely unfold gradually, with its full ramifications becoming apparent over several years.
The halving directly affects Bitcoin’s inherent scarcity, a core tenet of its value proposition. By reducing the supply of newly minted Bitcoin, the halving intensifies the existing scarcity, potentially driving up demand and price. This effect is amplified by the fixed supply limit of 21 million Bitcoin, making it a deflationary asset in a world dominated by inflationary fiat currencies. Historically, Bitcoin’s price has shown a positive correlation with previous halvings, although the magnitude of the price increase varies significantly. For example, the 2012 halving was followed by a substantial price surge, while the 2016 halving’s impact was less dramatic, demonstrating the complexity of market forces influencing price.
Bitcoin’s Adoption and Store of Value
The 2025 halving could accelerate Bitcoin’s adoption as a store of value. The reduced inflation rate, combined with increasing scarcity, makes Bitcoin an attractive alternative to traditional assets, particularly during periods of economic uncertainty or high inflation. This could attract further investment from both retail and institutional investors, strengthening Bitcoin’s position as a hedge against inflation and a safe haven asset. However, broader adoption also hinges on factors beyond the halving, such as regulatory clarity, technological advancements, and overall market sentiment. The growing interest from institutional investors, evident in recent years, suggests a positive trajectory for Bitcoin’s adoption, irrespective of the halving’s immediate impact on price.
Comparison with Other Cryptocurrencies
Unlike Bitcoin, many other cryptocurrencies employ different monetary policies. Some have no fixed supply, while others use different inflation mechanisms. For instance, Ethereum’s transition to proof-of-stake has altered its inflation dynamics. These variations in monetary policy significantly impact the long-term value proposition of each cryptocurrency. The predictability and transparency of Bitcoin’s halving mechanism, however, provides a unique element of stability and scarcity not replicated in many other cryptocurrencies. This predictable scarcity is a key differentiator for Bitcoin and contributes to its perceived value as a long-term store of value.
Institutional Investment Post-Halving
The potential for increased institutional investment in Bitcoin after the 2025 halving is considerable. Several factors could contribute to this. Firstly, the reduced inflation rate enhances Bitcoin’s appeal as a relatively stable asset within diversified portfolios. Secondly, the anticipated increase in price following the halving could make Bitcoin a more attractive investment opportunity for institutions seeking higher returns. Thirdly, regulatory developments and the maturation of the cryptocurrency infrastructure could further encourage institutional participation. Major financial institutions like BlackRock have already expressed significant interest in Bitcoin, indicating a growing acceptance of Bitcoin within the traditional financial ecosystem. This increased institutional participation could lead to a more stable and mature Bitcoin market, reducing volatility and enhancing its overall credibility.
Addressing Common Concerns: Date Of Bitcoin Halving In 2025
The Bitcoin halving, while a significant event in the Bitcoin network’s lifecycle, is often surrounded by misconceptions that can lead to unrealistic expectations. Understanding these common misunderstandings is crucial for navigating the market and making informed decisions. This section clarifies some prevalent myths and explores the complexities involved in predicting Bitcoin’s price behavior.
The halving itself does not automatically translate to a price surge. While historically, price increases have followed previous halvings, this correlation doesn’t imply causation. Numerous other factors, including macroeconomic conditions, regulatory changes, and market sentiment, significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. Attributing price movements solely to the halving oversimplifies a complex interplay of market forces. Furthermore, the timing and magnitude of any price reaction are highly unpredictable.
The Halving’s Impact on Price is Not Guaranteed, Date Of Bitcoin Halving In 2025
It’s a common misconception that the halving *guarantees* a price increase. While reduced supply often leads to increased value in basic economic principles, the cryptocurrency market is far more nuanced. The halving’s impact on price is indirect and depends on several factors. For instance, the 2012 and 2016 halvings were followed by significant price increases, leading many to believe a similar outcome is inevitable in 2025. However, this ignores the unique market conditions prevailing at each time. The 2025 halving will occur in a vastly different macroeconomic environment than its predecessors, impacting investor sentiment and overall market behavior. The decreased inflation rate of new Bitcoins entering circulation might not be enough to offset bearish market trends caused by other external forces.
Predicting Bitcoin’s Price: A Complex Undertaking
Accurately predicting Bitcoin’s price is notoriously difficult. Many factors beyond the halving influence its value, including: global economic conditions, regulatory frameworks in different jurisdictions, technological advancements within the cryptocurrency space, and the overall level of investor confidence. Attempting to predict the price solely based on the halving is like trying to predict the weather based only on the time of year; other significant variables are always at play. For example, the 2017 bull run, while coinciding with the 2016 halving, was also driven by increased mainstream media attention and speculation, factors unrelated to the halving itself.
Frequently Asked Questions about the 2025 Bitcoin Halving
The following table summarizes answers to common questions regarding the 2025 Bitcoin halving:
| Question | Answer | Relevance | Source/Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Will the 2025 halving guarantee a price increase? | No. While historically price increases have followed halvings, this is not guaranteed. Many other factors influence Bitcoin’s price. | High | Analysis of previous halving cycles and market conditions. |
| When exactly will the 2025 halving occur? | The exact date depends on the block generation time, but it’s expected to be around April 2025. | Medium | Bitcoin block explorer data and estimations based on current block times. |
| How will the halving affect Bitcoin miners? | It will reduce their revenue per block, potentially leading to increased mining difficulty and consolidation within the mining industry. | High | Analysis of mining profitability and hashrate dynamics. |
| What are the long-term implications of the halving? | It contributes to Bitcoin’s deflationary nature and could potentially increase its scarcity and long-term value. However, this is not guaranteed. | High | Understanding Bitcoin’s monetary policy and its impact on scarcity. |
Illustrative Examples
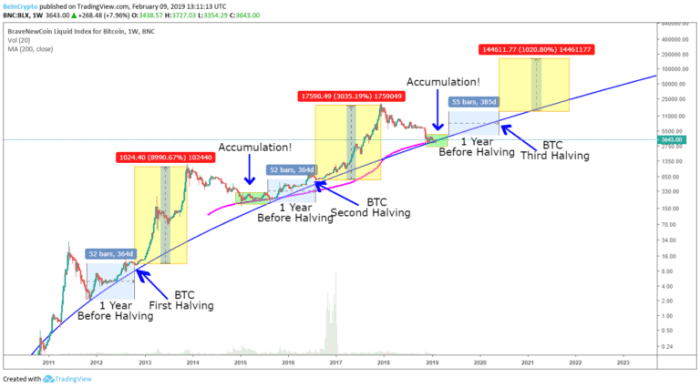
Understanding the mechanics of Bitcoin halving and its subsequent effects requires visualizing the processes involved. The following examples offer simplified representations to clarify the concepts of block reward reduction, inflation rate changes, and mining difficulty adjustments.
Bitcoin Halving and Block Rewards
Imagine a simple line graph. The horizontal axis represents time, marked with the dates of past and future Bitcoin halvings. The vertical axis represents the Bitcoin block reward – the amount of newly minted Bitcoin awarded to miners for successfully adding a block to the blockchain. The graph would show a steadily decreasing step function. Each halving event would be represented by a sharp drop, halving the previous reward. For example, a point at the 2012 halving would show a reward of 25 BTC, then a sharp drop to 12.5 BTC at the 2016 halving, and so on, illustrating the consistent reduction in the reward over time. This visual clearly demonstrates the predictable nature of the halving events.
Bitcoin Halving and Inflation Rate
Consider a pie chart. The entire pie represents the total number of Bitcoins in circulation at a given time. Before a halving, a significant portion of the pie would represent newly minted Bitcoins added during a specific period. After the halving, the portion representing newly minted Bitcoin would be visibly smaller, reflecting the reduced block reward. This illustrates the decrease in Bitcoin’s inflation rate, as the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation is halved. For instance, if the pre-halving inflation rate was 3.5% annually, the post-halving rate might drop to approximately 1.75%, showcasing the direct impact of the halving on the rate of new coin issuance.
Bitcoin Halving and Mining Difficulty
A bar graph would effectively represent the impact of halving on mining difficulty. The horizontal axis would represent time, again marked with the dates of past and future halvings. The vertical axis would represent the mining difficulty. The graph would show an overall upward trend, representing the increasing difficulty of mining Bitcoin over time. However, the graph would also show a noticeable jump in mining difficulty immediately following each halving. This is because, despite the halved reward, miners continue to compete for the reduced block reward, resulting in a sharp increase in the computational power required to successfully mine a block, thus increasing the difficulty. This demonstrates the market’s dynamic response to the halving event and the continuous adaptation within the Bitcoin mining ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Bitcoin halving, a significant event in the cryptocurrency’s lifecycle, often sparks numerous questions. This section addresses some of the most common queries surrounding the anticipated 2025 halving. Understanding these points provides crucial context for navigating the potential impacts on the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The Exact Date of the 2025 Bitcoin Halving
Pinpointing the precise date requires monitoring the Bitcoin blockchain. The halving occurs approximately every four years, after a specific number of blocks have been mined. While we can estimate the date based on the current block mining rate, the actual date can fluctuate slightly depending on the network’s computational power and the time it takes to mine each block. Predicting the precise day months in advance remains challenging. Past halvings have provided some indication, with minor variations from initial projections.
The 2025 Halving’s Effect on Bitcoin’s Price
The impact of a halving on Bitcoin’s price is a complex and hotly debated topic. Historically, halvings have been followed by periods of price appreciation, as the reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin can create upward pressure on demand. However, it’s crucial to remember that numerous other factors influence Bitcoin’s price, including macroeconomic conditions, regulatory developments, and overall market sentiment. The 2012 and 2016 halvings saw subsequent price increases, but these increases were not immediate and were influenced by broader market trends. The 2020 halving, while followed by a price surge, also experienced periods of significant volatility. Therefore, predicting the precise price impact of the 2025 halving is speculative.
Potential Risks Associated with the 2025 Halving
While often associated with positive price movements, halvings also present potential risks. A significant risk is the potential for increased volatility in the lead-up to and following the event. Increased speculation and market manipulation can exacerbate price swings. Furthermore, a decrease in miner profitability due to reduced block rewards could lead to miners exiting the network, potentially impacting the network’s security and hash rate. This scenario, however, is mitigated by the increasing efficiency of mining hardware and the potential for increased transaction fees to compensate for reduced block rewards.
The Halving Mechanism
Bitcoin’s halving mechanism is a built-in feature of its protocol. It dictates that the reward given to Bitcoin miners for successfully adding a block of transactions to the blockchain is halved at regular intervals. This reduction occurs approximately every 210,000 blocks, which translates to roughly four years. The initial block reward was 50 Bitcoin, and it has been halved three times already, bringing the current reward down to 6.25 Bitcoin. The next halving will reduce this reward to 3.125 Bitcoin. This programmed scarcity is a core element of Bitcoin’s design, intended to control inflation and maintain its long-term value.
The Significance of Bitcoin’s Halving Events
Bitcoin’s halving events are significant because they represent a programmed reduction in the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation. This controlled inflation is a key differentiator from traditional fiat currencies and a crucial aspect of Bitcoin’s scarcity model. Halvings are anticipated events that often generate considerable market attention and speculation, impacting investor sentiment and potentially influencing price movements. The halving is a predictable event, embedded within Bitcoin’s code, reinforcing its inherent deflationary nature and contributing to its long-term value proposition.