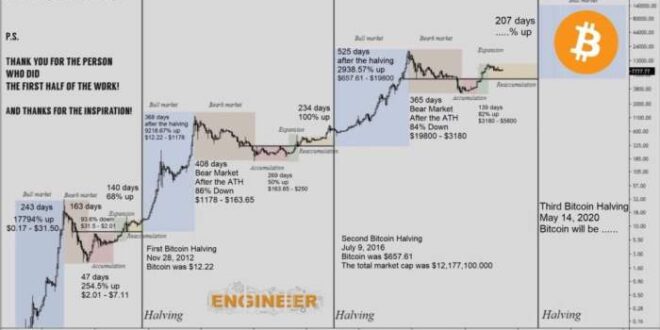
Understanding Bitcoin Halving 2025 (Apa itu Bitcoin Halving 2025?)
Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. This occurs approximately every four years, and it’s designed to control inflation and maintain the scarcity of Bitcoin. The halving cuts the block reward – the amount of Bitcoin miners receive for verifying transactions and adding them to the blockchain – in half. This directly impacts the supply of new Bitcoin entering circulation.
Bitcoin Halving: Impact on Supply
The halving mechanism is crucial for Bitcoin’s long-term economic model. By reducing the supply of new Bitcoins over time, the halving aims to maintain its value and prevent hyperinflation. Each halving event reduces the rate of Bitcoin inflation, making it a deflationary asset in the long run. This controlled inflation is a key differentiator from traditional fiat currencies. The halving doesn’t directly affect the total number of Bitcoins that will ever exist (currently capped at 21 million), but it does slow down the rate at which that cap is reached.
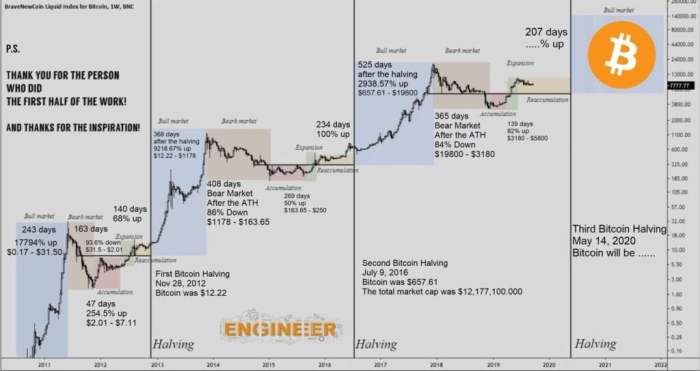
Historical Impact of Bitcoin Halvings on Price and Market Sentiment
Previous Bitcoin halvings have been followed by periods of significant price appreciation, although the exact timing and magnitude of price increases vary. This is often attributed to the reduced supply of new Bitcoins creating increased scarcity and potentially driving up demand. However, it’s important to note that other market factors, such as regulatory changes, technological advancements, and overall market sentiment, also play significant roles in Bitcoin’s price. The increase in price is not guaranteed and shouldn’t be interpreted as a direct causal effect solely from the halving. Market psychology and speculation also play a major role.
Timeline of Past Halvings and Subsequent Price Movements
The following table summarizes the past Bitcoin halvings and the approximate price movements in the periods following each event. Note that these are approximations and the actual price movements are complex and influenced by numerous factors. Charts illustrating these price movements would show a general upward trend after each halving, but with significant volatility and periods of both price increases and decreases.
| Halving Date | Block Reward Before Halving | Block Reward After Halving | Approximate Price Movement (12-18 months post-halving) |
|---|---|---|---|
| November 28, 2012 | 50 BTC | 25 BTC | Significant increase |
| July 9, 2016 | 25 BTC | 12.5 BTC | Substantial increase |
| May 11, 2020 | 12.5 BTC | 6.25 BTC | Significant increase followed by a correction |
Comparison of Past Halvings and Projections for 2025
The table below compares key metrics from past halvings and provides projections for the 2025 halving. It’s important to remember that these are estimations, and the actual figures may vary. The difficulty adjustment mechanism in Bitcoin dynamically adjusts the mining difficulty to maintain a consistent block generation time (approximately 10 minutes), which impacts the profitability of mining and the overall network security.
| Halving | Block Reward (BTC) | Circulating Supply (BTC) (approximate) | Estimated Difficulty (relative) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 50 -> 25 | 10.5 Million | Low |
| 2016 | 25 -> 12.5 | 15.5 Million | Medium |
| 2020 | 12.5 -> 6.25 | 18.5 Million | High |
| 2025 (Projected) | 6.25 -> 3.125 | 19.5 Million (estimated) | Very High (projected) |
Predicting the Impact of the 2025 Halving
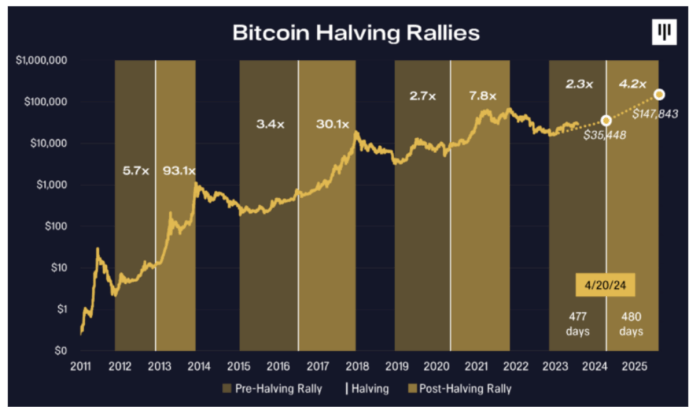
The Bitcoin halving, a pre-programmed event reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation, is anticipated to significantly impact the cryptocurrency’s price, though the extent and nature of this impact remain a subject of ongoing debate among analysts. Understanding the potential effects requires considering both the direct consequences of reduced supply and the influence of external factors.
Predicting the precise price movement following the 2025 halving is inherently challenging, as numerous interconnected variables come into play. While historically, halvings have been followed by periods of price appreciation, the market’s response is not guaranteed to be consistent.
Short-Term and Long-Term Price Effects
The immediate aftermath of a halving often sees increased price volatility. The reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin can create upward pressure on demand, particularly if investor sentiment remains positive. However, short-term price fluctuations are influenced by numerous factors, including speculative trading and broader market sentiment. In the long term, a decreased inflation rate associated with the halving could contribute to Bitcoin’s perceived value as a store of value, potentially driving sustained price increases. However, this effect might be countered by other economic factors or changes in regulatory environments. For example, the 2012 and 2016 halvings were followed by significant price rallies, but the timing and magnitude varied considerably.
Factors Beyond the Halving
Several external factors significantly influence Bitcoin’s price trajectory, independent of the halving. Regulatory developments, such as the adoption of clearer regulatory frameworks in major economies, could positively or negatively impact investor confidence and liquidity. Macroeconomic conditions, like inflation rates, interest rates, and global economic growth, also play a crucial role. A global recession, for instance, could negatively affect the price of risk assets, including Bitcoin, irrespective of the halving. Similarly, increased institutional adoption or significant technological advancements could drive price appreciation independently of the supply-side changes brought about by the halving.
Comparison of Market Predictions
Various market analysts and research firms offer contrasting predictions regarding the 2025 halving’s impact. Some predict a significant price surge, drawing parallels with previous halving cycles. Others express more cautious optimism, emphasizing the influence of external factors and the potential for market corrections. For example, some analysts suggest a price range of $100,000 to $200,000 by the end of 2025, while others offer more conservative estimates, citing potential macroeconomic headwinds. These differing perspectives highlight the inherent uncertainty associated with predicting future price movements. Reputable sources for such predictions include CoinMetrics, Glassnode, and various financial news outlets, but it’s crucial to note that these are forecasts, not guarantees.
Scenario Analysis of Price Movements
To illustrate potential price outcomes, we can Artikel a few scenarios:
Scenario 1: Positive Macroeconomic Conditions & Strong Institutional Adoption: In a scenario where global economic growth remains robust, inflation is controlled, and institutional adoption continues to accelerate, the 2025 halving could trigger a significant price increase, potentially exceeding previous post-halving rallies. This could lead to a price range significantly above previous all-time highs.
Scenario 2: Neutral Macroeconomic Conditions & Moderate Institutional Adoption: If macroeconomic conditions remain relatively stable, but institutional adoption progresses at a moderate pace, the price increase following the halving might be less pronounced than in the optimistic scenario. The price could still see significant growth, but perhaps not to the same extent.
Scenario 3: Negative Macroeconomic Conditions & Reduced Investor Confidence: In a scenario characterized by a global recession, high inflation, and reduced investor confidence in risk assets, the impact of the halving could be muted or even overshadowed by negative market sentiment. Price appreciation might be minimal, or the market could even experience a significant price correction.
These scenarios are illustrative and do not encompass all possible outcomes. The actual price movement will depend on the complex interplay of various factors.
The Role of Miner Economics in the Halving: Halving Bitcoin 2025 Là Gì
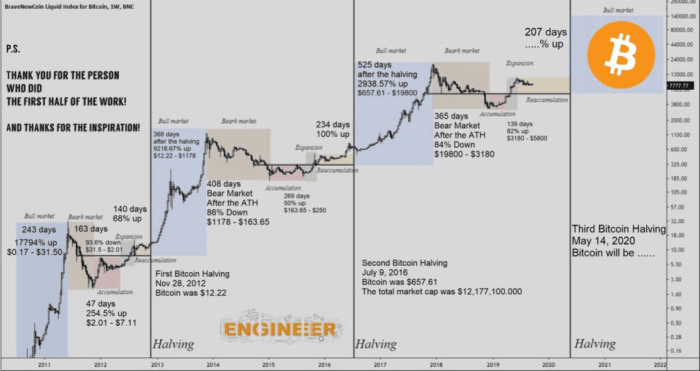
The Bitcoin halving, a pre-programmed event reducing the block reward miners receive for validating transactions, significantly impacts the economics of Bitcoin mining. This event creates a ripple effect across the entire ecosystem, influencing miner profitability, operational strategies, and ultimately, Bitcoin’s price. Understanding these economic dynamics is crucial for comprehending the long-term sustainability of Bitcoin mining.
The halving directly affects miners’ revenue by cutting the block reward in half. Before the halving, miners receive a certain number of Bitcoins for each block they successfully mine. After the halving, this reward is halved, reducing their immediate income. This reduction necessitates adjustments in their operational strategies to maintain profitability. Many miners will respond by increasing their efficiency, upgrading their hardware, or seeking out cheaper energy sources.
Miner Profitability and Operational Strategies
Miners must adapt to the reduced block reward to remain profitable. Strategies employed might include transitioning to more energy-efficient mining hardware (e.g., adopting newer ASIC chips with improved hash rates), negotiating lower electricity costs by relocating to regions with abundant and cheaper renewable energy, or consolidating operations to achieve economies of scale. Those unable to adapt risk becoming unprofitable and exiting the market. This dynamic is not new; it has occurred in previous halving cycles. For instance, after the 2020 halving, many less efficient miners were forced to shut down, leading to a period of consolidation within the mining industry.
Increased Competition and Potential Consolidation
The halving intensifies competition among miners. With reduced block rewards, miners are incentivized to maximize their hash rate to secure a larger share of the newly minted Bitcoin. This competition can lead to increased operational costs as miners invest in more efficient equipment or seek out cheaper energy. This competitive pressure often results in market consolidation, where larger, more efficient mining operations absorb smaller, less profitable ones. This leads to a more concentrated mining landscape, potentially impacting the decentralization of Bitcoin’s network. A hypothetical scenario post-2025 halving could see a significant reduction in the number of active mining pools, with a few dominant players controlling a larger percentage of the network’s hashrate.
Miner Behavior and Bitcoin Price Volatility
Miner behavior significantly influences Bitcoin’s price volatility around the halving. Anticipation of the halving can lead to increased Bitcoin price before the event, as investors speculate on the reduced supply and potential impact on scarcity. However, after the halving, if miner profitability drops substantially, some miners might sell their Bitcoin holdings to offset losses, potentially creating downward pressure on the price. Conversely, if the price remains high or increases despite the reduced reward, it can signal a strong belief in Bitcoin’s long-term value, leading to continued mining activity. The 2016 and 2020 halvings demonstrated a period of price volatility surrounding the events, with the price increasing significantly in the period following each halving.
Sustainability of Bitcoin Mining in the Long Term, Halving Bitcoin 2025 Là Gì
The long-term sustainability of Bitcoin mining hinges on the interplay between Bitcoin’s price, mining costs, and the halving mechanism. As halvings continue to reduce block rewards, the profitability of mining will increasingly depend on the price of Bitcoin and the efficiency of mining operations. While the halving mechanism is designed to control inflation and maintain the scarcity of Bitcoin, the sustainability of the network relies on miners remaining profitable enough to secure the network. Technological advancements in mining hardware and the exploration of renewable energy sources are crucial factors influencing the long-term sustainability of Bitcoin mining. A potential scenario for long-term sustainability involves a continued increase in Bitcoin’s value, which could offset the reduced block rewards and maintain profitability for efficient mining operations.
Investing and Trading Strategies Around the Halving
The Bitcoin halving, a significant event reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation, historically has preceded periods of price appreciation. However, this is not guaranteed, and various investment strategies exist, each with its own risk profile and potential reward. Understanding these strategies and their inherent risks is crucial for navigating the market around a halving event.
Buy-and-Hold Strategy
This classic approach involves purchasing Bitcoin and holding it for an extended period, regardless of short-term price fluctuations. The rationale is that the halving’s deflationary pressure will eventually drive up the price. The primary risk is the potential for prolonged periods of price stagnation or even decline before the anticipated price increase materializes. The reward, however, can be substantial if the historical trend continues. For example, investors who bought and held Bitcoin before previous halvings experienced significant gains in the following years.
Day Trading and Short-Term Strategies
Day trading involves attempting to profit from short-term price movements, often leveraging leverage and technical analysis. This approach requires significant market expertise and risk tolerance, as rapid price swings can lead to substantial losses. While the potential for quick profits is high, the probability of losses is equally significant. The volatility around the halving event presents both opportunity and extreme risk for day traders. Successful day trading necessitates constant monitoring and a deep understanding of market sentiment.
Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA)
Dollar-cost averaging mitigates risk by investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the price. This strategy reduces the impact of market volatility, as purchases are made both during periods of high and low prices. While DCA may not yield the highest returns in a consistently bullish market, it significantly reduces the risk of investing a large sum at a market peak. This approach is generally considered less risky than attempting to time the market perfectly.
Bitcoin vs. Other Cryptocurrencies
Investing in Bitcoin versus other cryptocurrencies involves a comparative analysis of their potential returns and risk profiles. Bitcoin, as the most established cryptocurrency, often exhibits lower volatility than altcoins (alternative cryptocurrencies). However, altcoins can potentially offer higher returns but with significantly increased risk. The halving’s impact on altcoins is less predictable than its effect on Bitcoin, as their price movements are often influenced by factors unrelated to Bitcoin’s supply dynamics. For example, some altcoins might experience increased demand due to speculation around their potential use cases, independent of the Bitcoin halving.
Sample Investment Strategy Flowchart
This flowchart illustrates a simplified investment strategy, emphasizing risk tolerance and time horizon.
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would start with a decision node: “High Risk Tolerance & Long Time Horizon?” A “Yes” branch would lead to “Invest in Bitcoin & Altcoins using a combination of Buy-and-Hold and DCA strategies.” A “No” branch would lead to “Invest in Bitcoin using primarily DCA, with a smaller portion in stablecoins”.]The flowchart would visually represent the decision-making process based on individual risk tolerance and investment timeframe. For instance, a risk-averse investor with a long time horizon might allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to Bitcoin via DCA, while a more risk-tolerant investor might diversify into altcoins, but still utilizing risk mitigation strategies like DCA. The key is tailoring the strategy to individual circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
This section addresses some common questions surrounding the 2025 Bitcoin halving, clarifying the process, impacts, and associated risks. Understanding these aspects is crucial for informed decision-making regarding Bitcoin investments.
Expected Date of the 2025 Bitcoin Halving
The Bitcoin halving occurs approximately every four years. The exact date is determined by the blockchain’s block generation time. Miners add blocks to the blockchain, and a block is typically added every 10 minutes. The halving event is triggered when a specific number of blocks have been mined since the previous halving (approximately 210,000 blocks). Therefore, while we can estimate the date based on the average block time, slight variations are possible due to fluctuations in mining difficulty. Predicting the precise date requires monitoring the blockchain’s progress closely as the halving approaches. While estimations place the 2025 halving in the Spring or early Summer, precise confirmation requires monitoring the blockchain’s actual block count.
Impact of the Halving on Bitcoin’s Scarcity
The Bitcoin halving directly impacts its scarcity by reducing the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. Each halving cuts the block reward received by miners in half. Initially, the reward was 50 BTC per block. After the first halving, it became 25 BTC, then 12.5 BTC, and the 2025 halving will reduce it to 6.25 BTC. This reduction in the rate of new Bitcoin creation, coupled with the fixed maximum supply of 21 million Bitcoins, increases the scarcity of the cryptocurrency over time. This controlled scarcity is a fundamental element of Bitcoin’s design and a key factor in its perceived value.
Will the 2025 Halving Definitely Cause a Price Increase?
While historically Bitcoin’s price has tended to increase following halving events, it’s crucial to understand that this is not guaranteed. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Numerous factors influence Bitcoin’s price, including macroeconomic conditions, regulatory changes, technological advancements, and overall market sentiment. A halving primarily impacts the supply side of the equation; demand-side factors are equally, if not more, significant in determining price movements. For example, the 2020 halving was followed by a significant price increase, but various other market forces were also at play. The 2025 halving’s impact on price will depend on a complex interplay of these various factors.
Risks of Investing in Bitcoin Before and After the Halving
Investing in Bitcoin, regardless of the halving, carries inherent risks. Bitcoin’s price is highly volatile, subject to significant fluctuations in short periods. Before the halving, investors face the risk of price declines before the anticipated price increase. After the halving, the price might not rise as expected, or a subsequent price drop could occur. Furthermore, regulatory uncertainty, security breaches, and technological disruptions can all negatively impact Bitcoin’s value. The potential for significant losses exists. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research, understand your risk tolerance, and only invest what you can afford to lose. Diversification of your investment portfolio is also recommended to mitigate risk.
Illustrative Example: Bitcoin Halving Price Impact
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, reducing the block reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC, presents a complex scenario with potential for significant price movements. Predicting the exact impact is impossible, but a hypothetical example can illustrate the interplay of factors influencing Bitcoin’s price.
This example considers a simplified model, acknowledging that real-world events and market sentiment will significantly affect the outcome. We will examine a hypothetical price trajectory post-halving, taking into account both bullish and bearish pressures.
Hypothetical Price Movement Post-Halving
Let’s imagine Bitcoin’s price is $30,000 at the time of the halving. The immediate aftermath could see a period of consolidation or even a slight dip as some investors take profits or wait to see the impact of reduced miner rewards. This is partially due to the immediate decrease in the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation. This initial period of uncertainty might last for several weeks or even months.
Following this, we might see a gradual increase in price as the reduced supply begins to exert upward pressure on demand. This increase, however, won’t be linear. We could see periods of volatility where prices fluctuate based on macroeconomic conditions, regulatory announcements, and general market sentiment.
Imagine a graph depicting this scenario. The X-axis represents time (months post-halving), and the Y-axis represents Bitcoin’s price in USD. The line starts at $30,000, dips slightly to around $28,000 in the first month, then gradually climbs over the next six months, reaching approximately $40,000. However, this upward trend isn’t smooth; it features several minor dips and peaks, reflecting the volatile nature of the cryptocurrency market. After six months, the price might consolidate around $40,000 for a period before resuming a more pronounced upward trend, potentially reaching $50,000 or higher within a year. The graph would visually represent this fluctuation, showing a general upward trend punctuated by periods of correction and consolidation. This upward movement would be attributed to a combination of reduced supply, increased institutional investment, and growing adoption of Bitcoin as a store of value. However, unforeseen negative events, such as a major regulatory crackdown or a significant market crash in traditional assets, could cause significant downward deviations from this hypothetical trajectory.
Factors Influencing the Hypothetical Scenario
Several factors contribute to this hypothetical price movement. The reduced supply, as mentioned, is a primary driver. However, other elements, such as increased institutional adoption, growing regulatory clarity (or lack thereof), and overall market sentiment play crucial roles. A positive regulatory environment could boost investor confidence, while negative news could trigger a sell-off. Similarly, a broader market downturn could negatively impact Bitcoin’s price regardless of the halving. Conversely, increased institutional investment, driven by factors like inflation hedging strategies, could significantly bolster Bitcoin’s price. This complex interplay of factors makes precise price prediction nearly impossible.