Bitcoin Halving 2025: Halving Of Bitcoin 2025
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event occurring approximately every four years, is a significant occurrence in the cryptocurrency’s lifecycle. This event fundamentally alters the rate at which new Bitcoins are added to the circulating supply, impacting various aspects of the Bitcoin ecosystem, from price volatility to miner profitability. The 2025 halving, expected around April, promises to be another pivotal moment.
Bitcoin Halving Mechanics
The Bitcoin halving mechanism is embedded within the Bitcoin protocol. Every 210,000 blocks mined, the reward given to miners for successfully adding a block to the blockchain is cut in half. Initially, the reward was 50 BTC per block. After the first halving, it became 25 BTC, then 12.5 BTC, and the 2025 halving will reduce it to 6.25 BTC. This reduction in the newly minted Bitcoin supply is designed to control inflation and maintain the scarcity of Bitcoin over time. The halving is not a sudden event but a gradual shift in the rate of new Bitcoin emission.
Historical Impact of Bitcoin Halvings
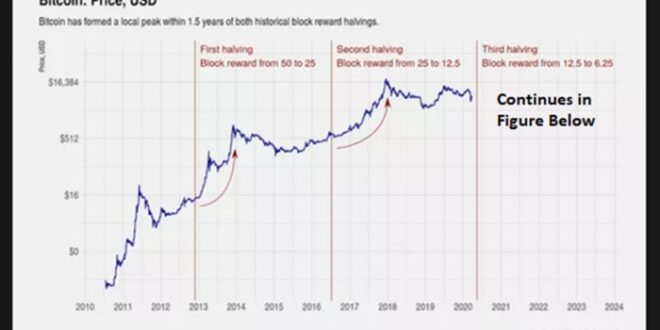
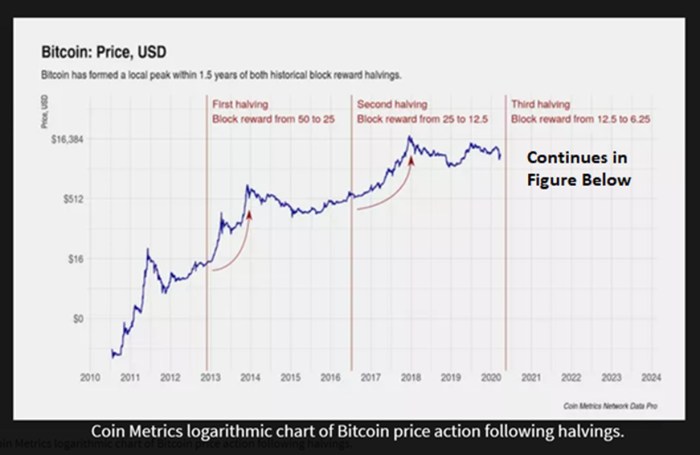
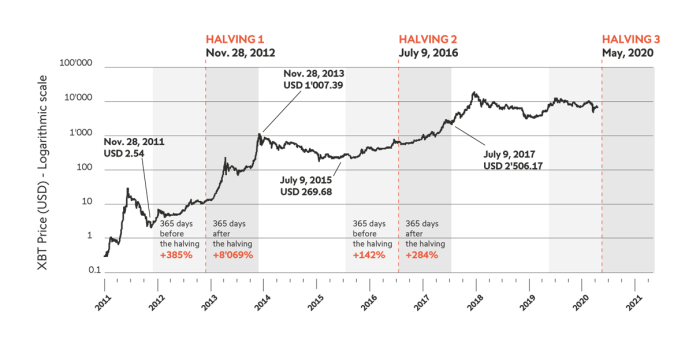
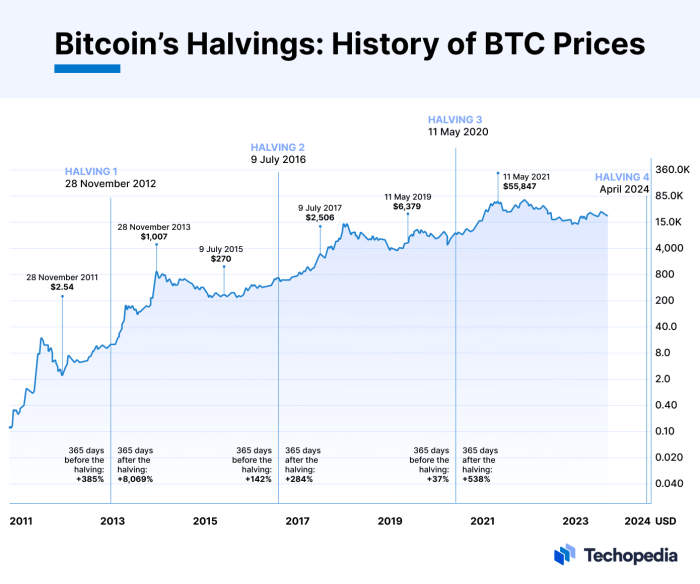
Previous Bitcoin halvings have shown a strong correlation with subsequent price increases. While not a guaranteed predictor, the halving events have historically been followed by periods of increased market price, driven by anticipation and the reduced supply of new Bitcoins entering circulation. The first halving in November 2012 saw Bitcoin’s price rise from approximately $12 to over $1,000 within the following year. Similarly, the second halving in July 2016, saw a price increase from around $650 to nearly $20,000 by the end of 2017. The third halving in May 2020 resulted in a price increase from around $9,000 to over $60,000 in late 2021. These historical trends suggest a potential for upward price pressure following the 2025 halving. However, it’s crucial to remember that other market factors significantly influence Bitcoin’s price.
Expected Supply Reduction in 2025
The 2025 halving will reduce the rate at which new Bitcoins are created by half. This means miners will receive 6.25 BTC per block instead of the current 12.5 BTC. The total supply of Bitcoin is capped at 21 million coins. This fixed supply, combined with the halving events, contributes to Bitcoin’s deflationary nature and perceived scarcity, potentially influencing its long-term value. The reduction in supply is expected to further tighten the market, potentially leading to increased price appreciation.
Timeline of Key Events Surrounding the 2025 Halving
Leading up to the 2025 halving, we can expect increased market speculation and volatility. The anticipation of the event itself often drives price fluctuations. Following the halving, the immediate impact might vary. However, historically, the months and years following halving events have shown periods of significant price appreciation. The exact timing and magnitude of these price movements remain uncertain and are subject to numerous market forces beyond the halving itself. Predicting the exact market response is impossible; however, understanding the historical trends and the mechanics of the halving provides a framework for assessing potential outcomes.
Price Predictions and Market Analysis
The 2025 Bitcoin halving is a significant event expected to impact the cryptocurrency’s price. Predicting the precise effect, however, is challenging due to the interplay of various market forces and inherent volatility. Numerous models attempt to forecast Bitcoin’s price trajectory post-halving, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Analyzing these models, alongside influential external factors, provides a more nuanced understanding of potential price movements.
Bitcoin Price Prediction Models
Several methodologies exist for predicting Bitcoin’s price. Stock-to-flow (S2F) models, for example, focus on the scarcity of Bitcoin relative to its newly mined supply. These models have historically shown some correlation with price movements, suggesting a potential price increase following the halving due to reduced supply. However, S2F models are often criticized for oversimplifying complex market dynamics and failing to account for external factors like regulatory changes or macroeconomic trends. On-chain analysis, which examines data from the Bitcoin blockchain itself, offers another approach. Metrics such as transaction volume, network hash rate, and the number of active addresses can provide insights into market sentiment and potential price shifts. Finally, technical analysis, employing charts and indicators, attempts to identify price patterns and predict future price movements. This method is heavily reliant on historical data and is prone to subjectivity. While each model offers valuable perspectives, relying solely on any one model for accurate prediction is risky.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price Post-Halving
Beyond the halving itself, numerous factors could significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. Regulatory clarity or uncertainty in major markets, such as the US, can dramatically impact investor confidence and market liquidity. Macroeconomic conditions, including inflation rates, interest rates, and overall economic growth, also play a crucial role. A period of high inflation might drive investors towards Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation, potentially boosting its price. Conversely, rising interest rates could divert investment away from riskier assets like Bitcoin. Technological advancements within the Bitcoin ecosystem, such as the development of the Lightning Network or improved scalability solutions, could enhance Bitcoin’s usability and attract more users, thereby influencing its price. Finally, the actions of large institutional investors and whales can trigger significant price swings.
Potential for a “Halving Rally” and Historical Precedent
The concept of a “halving rally” stems from the observation that Bitcoin’s price has historically risen following previous halvings. The halving reduces the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation, potentially increasing its scarcity and driving up demand. However, the magnitude and duration of these rallies have varied. The 2012 halving saw a gradual price increase over several months, while the 2016 halving led to a more pronounced rally. The 2020 halving resulted in a significant price increase followed by a period of consolidation. While historical precedent suggests a potential for a post-halving rally, it’s crucial to understand that past performance is not indicative of future results. Other market forces could outweigh the impact of the halving.
Risks and Uncertainties in Bitcoin Price Predictions
Predicting Bitcoin’s price is inherently uncertain. The cryptocurrency market is known for its volatility, influenced by speculative trading, regulatory changes, and unpredictable news events. Furthermore, the relatively short history of Bitcoin limits the reliability of long-term price predictions. Models may fail to capture unforeseen events, such as a major security breach or a significant change in market sentiment. Therefore, any price prediction should be considered with a healthy dose of skepticism. It’s essential to acknowledge the inherent risks and uncertainties before making any investment decisions based on price predictions. Diversification and risk management strategies are crucial for navigating the volatile nature of the cryptocurrency market.
Mining and Network Security
The 2025 Bitcoin halving will significantly impact the profitability of Bitcoin mining and, consequently, the security and decentralization of the network. Understanding these impacts is crucial for assessing the long-term health and stability of the Bitcoin ecosystem. The reduced block reward will force miners to adapt, potentially leading to shifts in the industry landscape.
The halving reduces the Bitcoin reward miners receive for successfully adding blocks to the blockchain. This directly impacts miners’ profitability, as their revenue stream is halved. This decrease in profitability necessitates miners to adjust their operational strategies to remain solvent. Factors like electricity costs, mining hardware efficiency, and the Bitcoin price all play crucial roles in determining whether miners can continue operating profitably after the halving.
Miner Profitability and Responses
The impact on miner profitability will vary depending on several factors. Miners with access to cheap electricity and efficient hardware will be better positioned to withstand the reduced block reward than those with higher operational costs. Some miners may choose to shut down operations entirely if their margins become unsustainable. Others might seek to increase their hash rate by deploying more efficient hardware or finding cheaper energy sources. This could lead to consolidation within the mining industry, with larger, more efficient operations dominating the landscape. The 2012 and 2016 halvings saw similar trends, with less efficient miners exiting the market and a subsequent increase in the average efficiency of the remaining miners. For example, the transition from ASICs based on older manufacturing processes to newer, more energy-efficient models was accelerated after previous halvings.
Effects on Network Security and Decentralization
The halving’s effect on network security is complex. A decrease in miner profitability could lead to a decline in the network’s hash rate—the total computational power dedicated to securing the Bitcoin blockchain. A lower hash rate makes the network more vulnerable to 51% attacks, where a malicious actor controls more than half of the network’s hash power and could potentially manipulate the blockchain. However, this is unlikely given the significant network effect and the high barriers to entry. Conversely, the increase in mining efficiency after a halving, as seen previously, could potentially offset the reduction in block rewards and maintain or even increase the overall network security. The decentralization of the network could also be affected, as smaller miners might be forced to consolidate or exit the market, leading to greater concentration of hash power among larger players.
Hash Rate Before and After Previous Halvings
Analyzing historical data from previous halvings provides valuable insights. While the immediate impact after each halving showed a temporary dip in the hash rate, the network typically recovered and even exceeded its previous peak within a relatively short period. This is attributed to factors such as the adoption of more efficient mining hardware and the increase in Bitcoin’s price, which ultimately increased miner profitability. For example, after the 2012 halving, the hash rate experienced a temporary decline but subsequently surged to new heights. A similar pattern was observed after the 2016 halving. The resilience of the network and its ability to adapt to these events suggest that the 2025 halving is likely to follow a similar trend.
Changes in Mining Hardware and Energy Consumption
The halving will likely accelerate the adoption of more energy-efficient mining hardware. Miners will be incentivized to invest in newer, more powerful ASICs to maintain profitability. This could lead to a decrease in the overall energy consumption per unit of hash rate, despite the potential increase in total hash rate. However, the overall energy consumption of the Bitcoin network is still likely to increase as more efficient miners come online and expand their operations. This is a continuous process, driven by technological advancements and the economic incentives of mining. The development of more energy-efficient ASICs is a key factor in mitigating the environmental concerns associated with Bitcoin mining.
Investor Sentiment and Market Behavior
Investor sentiment surrounding Bitcoin halvings is a complex interplay of anticipation, speculation, and market forces. Understanding how investors behave leading up to and following these events is crucial for navigating the often volatile cryptocurrency market. Analyzing past halving cycles provides valuable insights into potential future trends, although it’s important to remember that each cycle is unique and influenced by a multitude of factors.
The 2025 halving, like its predecessors, is expected to significantly impact investor sentiment and market behavior. Several key indicators will likely play a significant role in shaping the overall mood.
Key Indicators of Investor Sentiment
Several factors contribute to gauging investor sentiment before a Bitcoin halving. These indicators provide a picture of the overall market mood and investor confidence levels. Analyzing these indicators in conjunction allows for a more nuanced understanding of the market’s expectations.
- On-chain metrics: Analysis of on-chain data, such as the number of active addresses, transaction volume, and miner behavior, can offer valuable clues about investor confidence and network activity. For instance, a rise in the number of active addresses could suggest growing interest and participation in the Bitcoin network.
- Market capitalization and price volatility: Significant fluctuations in Bitcoin’s price and market capitalization leading up to the halving often reflect shifting investor sentiment. Sharp price increases could indicate bullish sentiment, while significant drops may signal growing uncertainty or bearishness. The volatility itself is a key indicator, as higher volatility suggests a market less certain of the outcome.
- Derivatives market activity: The behavior of options and futures markets can offer insights into investor expectations. For example, high open interest in call options (bets on price increases) would suggest a predominantly bullish outlook.
- Social media sentiment analysis: Tracking mentions of Bitcoin and related terms on social media platforms, combined with sentiment analysis tools, can help gauge public opinion and investor confidence. A surge in positive sentiment could suggest growing optimism, while a rise in negative sentiment might indicate concerns.
Common Investor Behaviors Around Previous Halvings
Past halving events have demonstrated consistent patterns in investor behavior. Understanding these trends can help anticipate potential market movements in 2025.
- Price anticipation: Investors often anticipate a price increase following a halving due to the reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin. This anticipation often leads to increased buying pressure in the months leading up to the event.
- Increased volatility: The period surrounding a halving is usually characterized by heightened price volatility as investors react to news, price movements, and changing market conditions.
- Strategic accumulation: Some investors adopt a strategy of accumulating Bitcoin before the halving, anticipating a price appreciation after the event.
- Profit-taking: Conversely, some investors might choose to sell their Bitcoin holdings before or after the halving to secure profits.
Comparison of Current Market Conditions with Past Halvings, Halving Of Bitcoin 2025
While past halvings offer valuable insights, it is crucial to acknowledge the differences between the current market environment and those preceding previous halvings.
The macroeconomic climate, regulatory landscape, and technological advancements all play significant roles in shaping investor sentiment and market behavior. For example, the 2012 halving occurred during a period of nascent cryptocurrency adoption, while the 2020 halving coincided with increased institutional interest. The 2025 halving will undoubtedly be influenced by factors such as inflation, interest rates, and the ongoing development of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Direct comparison is difficult, but identifying key differences helps refine predictions.
The Role of Social Media and News Coverage
Social media and traditional news outlets play a crucial role in shaping investor expectations around Bitcoin halvings. The narratives generated by these channels can significantly impact investor sentiment and market behavior.
Positive news coverage and enthusiastic social media discussions can fuel a bull market, while negative news or fear-mongering can trigger sell-offs.
The amplification effect of social media, particularly among retail investors, can lead to rapid shifts in market sentiment and price volatility. Therefore, discerning credible information from misinformation becomes critical during periods of heightened market activity.
Long-Term Implications and Future Outlook
The 2025 Bitcoin halving, reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation by half, will have profound and lasting effects on the cryptocurrency market and its place in the global financial system. Understanding these long-term implications requires considering its impact on Bitcoin’s price, adoption, and role within a broader economic context. The decreased supply, coupled with potentially sustained or increased demand, could lead to significant price appreciation, but this is not guaranteed and depends heavily on numerous market factors.
The halving’s influence extends beyond simple price fluctuations. It impacts the fundamental nature of Bitcoin, its security, and its potential to become a more widely accepted form of currency or store of value. The long-term implications are complex and intertwined, influencing not only Bitcoin itself but also the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Bitcoin’s Price and Market Volatility
The halving historically correlates with periods of increased Bitcoin price volatility. While past performance doesn’t guarantee future results, the reduced supply post-halving often leads to increased scarcity, potentially driving up demand and price. However, other macroeconomic factors, regulatory changes, and market sentiment significantly influence price movements. For instance, the 2012 and 2016 halvings were followed by substantial price increases, but the market conditions differed significantly between those events and the upcoming 2025 halving. Predicting the exact price trajectory remains impossible, but the halving itself is likely to be a major catalyst for price volatility in the short to medium term.
Bitcoin’s Role in the Global Financial System
The 2025 halving could accelerate Bitcoin’s integration into the global financial system. As a scarce asset with a fixed supply, Bitcoin offers a potential hedge against inflation and a store of value alternative to traditional fiat currencies. Increased institutional adoption, driven in part by the halving-induced scarcity, could further enhance Bitcoin’s role as a global financial asset. This could involve increased usage in cross-border payments, as a reserve asset for institutions, or as a component of diversified investment portfolios. However, widespread institutional adoption depends heavily on regulatory clarity and the continued development of robust infrastructure. Consider, for example, the growing interest from institutional investors in Bitcoin-related products, even before the 2025 halving.
Impact on Bitcoin Adoption and Usage
The halving’s impact on Bitcoin adoption is multifaceted. While the price increase could attract new users, increased transaction fees during periods of high network congestion could hinder adoption. Improved scalability solutions, such as the Lightning Network, will be crucial in facilitating wider adoption and usage. Moreover, the halving could further solidify Bitcoin’s position as a digital gold, attracting investors seeking a store of value rather than a transactional currency. The long-term impact on adoption depends on the successful implementation of solutions addressing scalability and usability challenges, coupled with favorable regulatory environments globally.
A Potential Future for Bitcoin Beyond 2025
One potential scenario sees Bitcoin solidifying its position as a significant global asset, akin to digital gold. Increased institutional adoption and regulatory clarity could lead to higher liquidity and broader acceptance. Technological advancements in scalability and usability could overcome current limitations, driving widespread adoption as a medium of exchange. However, alternative cryptocurrencies and technological innovations could also challenge Bitcoin’s dominance. In this scenario, Bitcoin’s value could be driven by its scarcity, store-of-value properties, and its established network effect, potentially reaching levels significantly higher than current valuations. However, this scenario hinges on continued technological development and a positive regulatory landscape. Another, less optimistic scenario involves regulatory crackdowns or significant technological disruption that could impact Bitcoin’s price and adoption negatively. The future is inherently uncertain, but the 2025 halving will be a pivotal event shaping Bitcoin’s trajectory in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
This section addresses common queries regarding Bitcoin halvings, their impact on price, and associated risks. Understanding these aspects is crucial for informed decision-making in the cryptocurrency market.
Bitcoin Halving Explained
A Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created and added to the circulating supply. This occurs approximately every four years, or every 210,000 blocks mined. The halving cuts the block reward in half, meaning miners receive fewer Bitcoins for successfully verifying and adding transactions to the blockchain. This mechanism is integral to Bitcoin’s deflationary nature and long-term scarcity.
Bitcoin Halving’s Effect on Price
Historically, Bitcoin halvings have been followed by periods of significant price appreciation. The previous halvings in 2012, 2016, and 2020 all showed a substantial increase in Bitcoin’s price in the months and years following the event. However, it’s crucial to understand that correlation does not equal causation. While the halving reduces the supply of newly minted Bitcoin, the actual price movement is influenced by numerous other factors, including market sentiment, regulatory changes, technological advancements, and overall macroeconomic conditions. For example, the 2020 halving was followed by a bull market, but the price increase wasn’t solely attributable to the halving itself. Other factors, such as increased institutional adoption and growing public interest, played a significant role.
Timing of the Next Bitcoin Halving
The next Bitcoin halving is expected to occur in April 2024. The precise date will depend on the time it takes to mine the 210,000 blocks leading up to the event. This date is determined by the Bitcoin protocol’s inherent algorithm and is not subject to change or manipulation.
Risks Associated with Investing in Bitcoin Around a Halving
Investing in Bitcoin, particularly around a halving, carries inherent risks. The price volatility of Bitcoin is well-known, and significant price swings can occur both before and after a halving. The anticipation of a price increase can lead to speculative bubbles, potentially resulting in sharp corrections. Furthermore, regulatory uncertainty, technological vulnerabilities, and macroeconomic factors can significantly impact Bitcoin’s price irrespective of the halving. There’s no guarantee that a halving will automatically lead to a price surge. Investors should conduct thorough research, understand their risk tolerance, and only invest what they can afford to lose. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
Illustrative Data Presentation
Understanding the historical trends of key Bitcoin metrics surrounding previous halving events provides valuable context for anticipating potential outcomes in 2025. Analyzing these trends helps to form more informed predictions about price movements, network security, and overall market behavior. The following data and visualization aim to illuminate these historical patterns.
Historical Halving Metrics Comparison
The table below compares key metrics from the previous Bitcoin halvings. Note that these are approximate figures, and the exact values may vary slightly depending on the data source.
| Halving Event | Approximate Date | Block Reward (BTC) | Approximate Price Before Halving (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Halving | November 2012 | 50 | ~13 |
| Second Halving | July 2016 | 25 | ~650 |
| Third Halving | May 2020 | 12.5 | ~9000 |
Bitcoin Halving Schedule and Price History Visualization
A visual representation of Bitcoin’s halving schedule and price history would ideally be a line graph. The x-axis would represent time, spanning from Bitcoin’s inception to the present day. The y-axis would represent Bitcoin’s price in USD. Two distinct lines would be overlaid on this graph. The first line would be a price line, showing the historical price fluctuations of Bitcoin. This line would show periods of significant growth and decline. The second line would represent the halving events. These would be marked by vertical dashed lines at the dates of each halving, potentially labeled with the block reward at that time. The graph would clearly show the price trend before, during, and after each halving. Importantly, the visual would demonstrate that while halvings have historically been followed by periods of price appreciation, the extent of that appreciation has varied significantly. The graph would highlight the relationship between the halving events and subsequent price movements, but would also emphasize that other factors significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. For example, periods of increased regulatory scrutiny or market sentiment shifts could be observed to impact the price trajectory independently of the halving events. The graph would not suggest a direct causal relationship, but rather a correlation that warrants further analysis and consideration. The visual would serve to illustrate the complex interplay of factors affecting Bitcoin’s price, highlighting the halving events as a significant, but not sole, contributing factor.