Bitcoin Halving Explained
The Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. This occurs approximately every four years, or every 210,000 blocks mined. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for comprehending Bitcoin’s long-term price dynamics and its deflationary nature.
Bitcoin’s halving mechanism is designed to control inflation. Every time a halving occurs, the reward miners receive for verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain is cut in half. This directly impacts the supply of new Bitcoins entering circulation, making it a progressively scarcer asset over time. The reduced supply, coupled with (potentially) consistent or increasing demand, can theoretically lead to an increase in price. The interplay between supply and demand is the core principle driving the potential price impact of a halving.
The Impact of Past Halvings
Previous Bitcoin halvings have demonstrated a significant correlation with subsequent price increases, although the timing and magnitude of these increases have varied. While a direct causal link isn’t definitively proven, the halving acts as a significant catalyst influencing market sentiment and potentially driving price appreciation. The reduced supply creates a scarcity narrative that can attract new investors and further bolster demand.
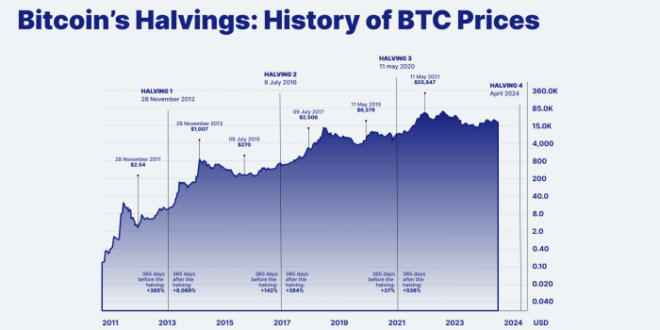
Timeline of Past Halvings and Price Movements
The following table summarizes the historical Bitcoin halvings, highlighting key events and approximate price movements around those dates. Note that these price movements are complex and influenced by various factors beyond the halving itself, including broader market conditions and regulatory changes. It’s crucial to avoid interpreting this as a precise prediction for future events.
| Halving Date | Approximate Bitcoin Price Before Halving (USD) | Approximate Bitcoin Price After Halving (USD) | Key Events/Market Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| November 28, 2012 | ~13 USD | ~1000 USD (approx. 1 year later) | Growing adoption, early market maturity. |
| July 9, 2016 | ~650 USD | ~20,000 USD (approx. 2 years later) | Increased institutional interest, growing global awareness. |
| May 11, 2020 | ~8700 USD | ~65,000 USD (approx. 1 year later) | Mainstream media attention, institutional investment surge, COVID-19 pandemic impact. |
Comparison of Past Halving Effects
Comparing the effects of past halvings reveals a trend of increasing price appreciation after each event. However, the time it takes for the price to significantly rise varies considerably. The first halving saw a gradual increase over a year, while the second and third halvings experienced more rapid, albeit volatile, price appreciation. This variation highlights the influence of external factors and the inherent unpredictability of the cryptocurrency market. It’s important to remember that past performance is not indicative of future results.
Visual Representation of Halvings and Bitcoin Price
Imagine a line graph. The x-axis represents time, showing the dates of the three previous Bitcoin halvings. The y-axis represents the price of Bitcoin in USD. Three distinct points would be plotted on the graph, representing the Bitcoin price around the time of each halving. After each halving point, the line would show a general upward trend, although the slope and timing of the increase would differ for each halving. The graph would clearly illustrate the general correlation between halvings and subsequent price increases, but also the variability in the timing and magnitude of those increases. This visualization would emphasize that while a correlation exists, it’s not a guaranteed or predictable outcome.
Predicting the Next Halving After 2025
Predicting the precise impact of the next Bitcoin halving, expected around 2028, is inherently challenging. While the halving itself is a predictable event – reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation – its effect on price is far from certain and depends on a complex interplay of factors beyond the halving’s programmed scarcity.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price Beyond the Halving
Numerous factors, independent of the halving, significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. These include macroeconomic conditions (inflation rates, interest rates, economic recessions), overall market sentiment (fear, uncertainty, and doubt, or FUD, versus greed), technological advancements within the Bitcoin ecosystem (like the Lightning Network’s adoption), regulatory developments across various jurisdictions, and the actions of large institutional investors. For example, during periods of high inflation, Bitcoin’s price might increase as investors seek a hedge against inflation. Conversely, rising interest rates can divert investment away from riskier assets like Bitcoin. The level of adoption by institutional investors also greatly impacts price volatility.
Technological Advancements and Regulatory Changes
Technological advancements, such as layer-2 scaling solutions like the Lightning Network, can significantly affect Bitcoin’s usability and transaction speed, potentially increasing adoption and driving price appreciation. Conversely, regulatory uncertainty or outright bans in major markets could suppress price growth. For instance, the increasing adoption of Lightning Network for faster and cheaper transactions could boost Bitcoin’s appeal to a wider range of users. Conversely, a sudden crackdown on cryptocurrency exchanges in a major country could negatively affect market sentiment and Bitcoin’s price.
Expert Opinions and Market Analyses
Many market analysts and experts offer diverse predictions regarding the post-2025 halving. Some anticipate a significant price surge due to the reduced supply, mirroring past halving events. Others are more cautious, highlighting the influence of other market factors. For example, some analysts point to the historical price increases following previous halvings as evidence for future price appreciation. However, others emphasize that the market context surrounding each halving is unique, making direct comparisons difficult. It’s crucial to note that these are opinions, not guarantees.
Potential Risks and Uncertainties
Predicting the impact of the halving is fraught with uncertainty. Unforeseen events, such as a major security breach or a significant regulatory shift, could dramatically alter the market’s response. Furthermore, the interplay of various factors makes it difficult to isolate the halving’s specific contribution to price movements. For instance, a major cyberattack targeting a significant Bitcoin exchange could trigger a market sell-off, overshadowing the effects of the halving.
Scenario Analysis: Possible Outcomes
Several scenarios can be envisioned depending on prevailing market conditions. A bullish scenario assumes continued institutional adoption, positive macroeconomic conditions, and successful technological advancements, leading to a substantial price increase post-halving. A neutral scenario suggests a more moderate price increase, reflecting a balance of positive and negative influences. A bearish scenario considers negative macroeconomic conditions, increased regulatory scrutiny, or a significant technological setback, potentially leading to a price decline or stagnation despite the halving. These scenarios illustrate the complexity of predicting the future price of Bitcoin, highlighting the influence of factors beyond the halving itself.
The Halving’s Influence on Bitcoin’s Value: When Is Bitcoin Halving After 2025
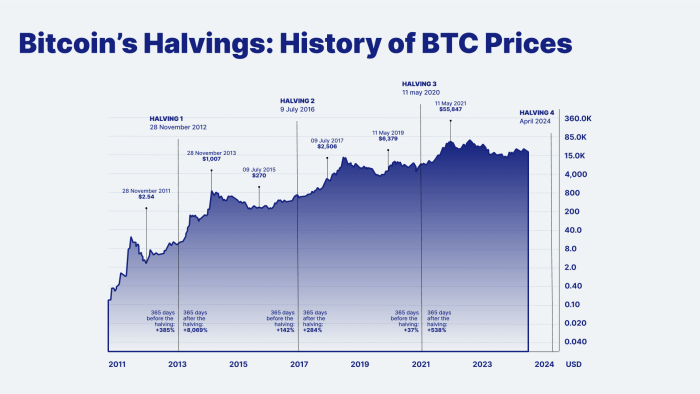
The Bitcoin halving, a programmed event reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation, significantly impacts the cryptocurrency’s value proposition and market dynamics. This reduction in supply, coupled with relatively consistent demand, is theorized to create upward pressure on price, though the actual effect is complex and influenced by various market factors.
The halving’s influence stems primarily from the interplay between Bitcoin’s inherent scarcity and its perceived value. Bitcoin’s fixed supply of 21 million coins is a core tenet of its design, fostering a deflationary model. This inherent scarcity, often cited as a key differentiator from fiat currencies, contributes to its perceived value as a store of value and hedge against inflation.
Bitcoin Scarcity and Perceived Value
The reduction in new Bitcoin entering circulation during a halving event directly amplifies this scarcity. This increased scarcity, all else being equal, tends to make existing Bitcoin more valuable. The psychology of scarcity plays a crucial role; as the supply diminishes, demand may increase, leading to a price rise. This effect is analogous to the value increase of rare collectibles or precious metals. The limited supply creates a sense of exclusivity and desirability, driving up prices.
Supply and Demand Dynamics After a Halving
The halving fundamentally alters the supply and demand equation. While demand may remain relatively constant or even increase due to anticipation, the supply is abruptly halved. This imbalance between a reduced supply and (potentially) increasing demand is a primary driver of price increases after past halving events. However, it’s crucial to note that this effect isn’t immediate or guaranteed. Other market forces, such as overall economic conditions, regulatory changes, and investor sentiment, can significantly influence the actual price trajectory.
Price Volatility Before and After Halving Events
Historically, Bitcoin has exhibited increased price volatility in the periods leading up to halving events. This heightened volatility stems from speculative trading and anticipation of the event’s impact. Investors often engage in price speculation, driving prices up or down depending on their expectations. After the halving, the volatility may initially persist but often settles down as the market adjusts to the new supply dynamics. The period following a halving frequently shows a more gradual price increase, though significant short-term fluctuations can still occur.
Comparative Analysis of Bitcoin’s Price Performance Around Past Halvings
Examining Bitcoin’s price performance around previous halvings provides valuable insight. While past performance is not indicative of future results, it offers a framework for understanding potential trends. In the lead-up to the 2012 and 2016 halvings, we saw periods of price appreciation followed by significant corrections. Following both events, we observed a period of sustained price growth, though the timing and magnitude varied considerably. The 2020 halving showed a similar pattern, with a significant price surge in the following year. These observations suggest a correlation between halvings and long-term price increases, though the precise relationship is far from perfectly predictable.
Potential Impact on Bitcoin’s Long-Term Price Trajectory
The halving’s impact on Bitcoin’s long-term price trajectory is a subject of ongoing debate. Proponents argue that the halving, combined with increasing adoption and institutional investment, will drive Bitcoin’s price significantly higher over the long term. Conversely, skeptics point to the influence of macroeconomic factors, regulatory uncertainty, and the inherent volatility of the cryptocurrency market. Predicting the precise long-term impact remains challenging, but the halving undoubtedly plays a significant role in the ongoing narrative of Bitcoin’s value proposition and its potential for future growth. The long-term impact is likely to be a combination of the factors discussed above.
Beyond the Halving
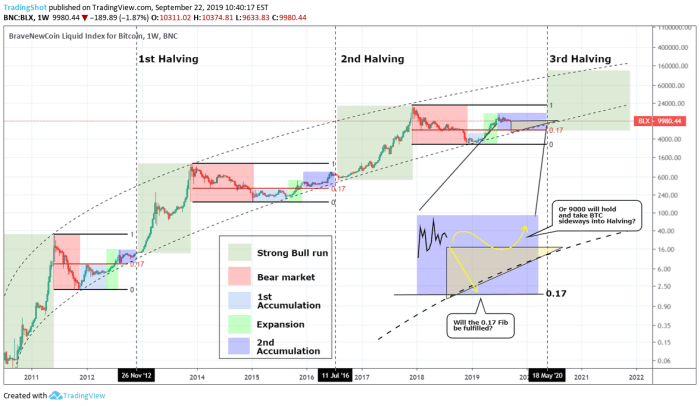
While the Bitcoin halving is a significant event impacting supply and potentially influencing price, it’s crucial to understand that numerous other factors contribute to Bitcoin’s price volatility and overall market adoption. These factors interact in complex ways, making accurate price prediction challenging.
Macroeconomic Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price
Macroeconomic conditions significantly influence Bitcoin’s price. High inflation, for instance, can drive investors towards Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation, increasing demand and potentially pushing prices higher. Conversely, rising interest rates, making traditional investments more attractive, can lead to capital flowing out of Bitcoin, causing price drops. The correlation between Bitcoin’s price and the US dollar’s performance is frequently observed, reflecting the dominance of the US dollar in global finance. For example, periods of US dollar strength have often coincided with Bitcoin price declines, while periods of US dollar weakness have sometimes been associated with Bitcoin price increases. This relationship, however, isn’t always consistent and is influenced by numerous other variables.
Institutional Investment and Regulatory Frameworks
The involvement of institutional investors, such as large corporations and hedge funds, is increasingly impacting Bitcoin’s price and stability. Large-scale investments can inject significant liquidity into the market, potentially driving up prices. Conversely, significant sell-offs by these institutions can lead to sharp price corrections. Regulatory frameworks also play a critical role. Clear and supportive regulations can boost investor confidence and attract further investment, while unclear or restrictive regulations can hinder market growth and depress prices. The differing regulatory approaches across various countries significantly influence Bitcoin’s accessibility and trading volumes in those regions. For example, a country with stringent regulations might see lower trading volumes compared to a country with a more lenient regulatory environment.
Bitcoin’s Performance Relative to Other Assets
Bitcoin’s performance is frequently compared to both other cryptocurrencies and traditional assets like gold and stocks. Its correlation with other cryptocurrencies varies depending on market sentiment and individual project performance. During periods of overall cryptocurrency market growth, Bitcoin often shows positive correlation with altcoins. However, during market downturns, Bitcoin might outperform other cryptocurrencies, acting as a safe haven within the crypto space. Compared to traditional assets, Bitcoin’s performance has shown periods of both outperformance and underperformance. Its volatility is significantly higher than that of gold or established stock indices, making it a riskier but potentially higher-reward investment.
Key Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price
The following table summarizes key factors influencing Bitcoin’s price, categorized by their impact timeframe:
| Factor | Category | Short-Term Impact | Long-Term Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Halving Events | Supply-Side | Potentially Increased Price Volatility | Reduced Inflationary Pressure, Potential Price Appreciation |
| Macroeconomic Conditions (Inflation, Interest Rates) | External | Significant Price Fluctuations | Long-term Correlation, Potential for Diversification |
| Institutional Investment | Demand-Side | Sharp Price Movements | Increased Market Maturity and Liquidity |
| Regulatory Developments | External | Uncertainty and Volatility | Increased or Decreased Market Accessibility |
| Technological Advancements | Internal | Potential for Short-Term Hype | Improved Scalability and Efficiency |
| Market Sentiment and Media Coverage | Demand-Side | Significant Price Swings | Influences Public Perception and Adoption |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section addresses common queries regarding the Bitcoin halving, its impact on price, and other influencing factors. Understanding these aspects is crucial for navigating the complexities of the Bitcoin market.
Bitcoin Halving Explained
The Bitcoin halving is a programmed event in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the reward given to Bitcoin miners for successfully adding new blocks of transactions to the blockchain. This reward, initially 50 BTC per block, is cut in half approximately every four years. This process is designed to control Bitcoin’s inflation rate, ensuring a limited supply of 21 million coins. The halving reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins enter circulation, potentially influencing market dynamics.
The Timing of the Next Bitcoin Halving After 2025
Predicting the exact date of the next halving after 2025 requires careful consideration of the average block time. While the target block time is 10 minutes, variations occur due to network conditions. Based on historical data and assuming an average block time near the target, the next halving is projected to occur sometime in 2028 or early 2029. A precise date can only be determined closer to the event as the actual block generation times continue to accumulate.
The Halving’s Effect on Bitcoin’s Price
Historically, Bitcoin’s price has shown a tendency to increase in the period following a halving event. The 2012 and 2016 halvings were followed by significant price rallies, although the timing and magnitude of these increases varied. This is largely attributed to the reduced supply of newly minted Bitcoins, potentially creating a scarcity effect and increased demand. However, it’s important to note that other factors significantly influence price, as discussed below. The 2020 halving, for example, saw a period of price increase but the effect was not as dramatic as in previous halvings.
Price Rise Guarantees After a Halving: Risk and Uncertainty
There are no guarantees that a Bitcoin halving will automatically lead to a price increase. While historical trends suggest a correlation, it’s not a causal relationship. Market sentiment, regulatory changes, macroeconomic conditions, and technological advancements all play a crucial role. The 2020 halving serves as a reminder that other market forces can override the expected impact of a halving. Investing in Bitcoin carries inherent risk, and relying solely on the halving for price appreciation is unwise.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price Beyond the Halving
Several factors beyond the halving significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. These include:
- Regulatory landscape: Governmental regulations and policies concerning cryptocurrencies can significantly influence investor confidence and market activity.
- Adoption rate: Increased adoption by businesses and individuals fuels demand, potentially pushing prices higher.
- Macroeconomic conditions: Global economic factors like inflation, interest rates, and recessionary fears can influence investment flows into Bitcoin.
- Technological advancements: Developments in blockchain technology and related innovations can affect Bitcoin’s utility and appeal.
- Market sentiment and speculation: Investor sentiment and speculative trading play a significant role in price volatility.
Illustrative Examples
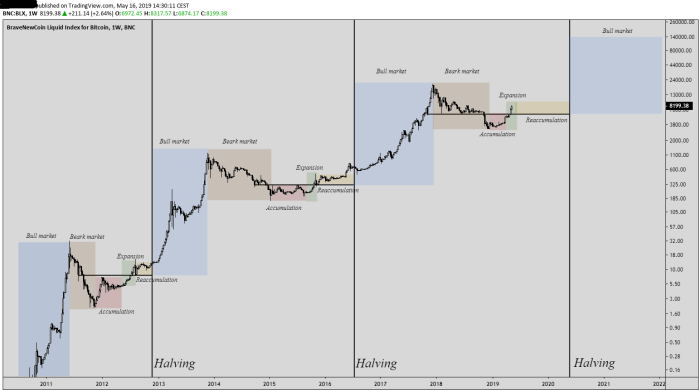
Understanding the impact of a Bitcoin halving requires examining hypothetical scenarios and considering external factors. The following examples illustrate how a halving might play out under different conditions, highlighting the complexities involved in predicting its effect on price.
Hypothetical Halving Impact on Bitcoin Price
Let’s imagine a scenario where the next Bitcoin halving occurs in 2028. Prior to the halving, the price of Bitcoin sits at $50,000, reflecting a relatively stable market with moderate trading volume. The anticipation of the halving begins to build several months beforehand, leading to a gradual price increase, fueled by speculation. By the time of the halving, the price might reach $75,000, a 50% increase driven primarily by market psychology. Following the halving, the reduced supply of newly mined Bitcoin could further boost the price, potentially pushing it towards $100,000 or higher, depending on overall market sentiment and adoption rates. However, this increase isn’t guaranteed. A lack of significant institutional investment or negative news could dampen the price rise, resulting in a more modest increase or even a temporary price correction.
Regulatory Changes Affecting Halving Effects, When Is Bitcoin Halving After 2025
Consider a scenario where a major regulatory body, such as the SEC in the United States, introduces stringent regulations on cryptocurrency exchanges immediately before or after a halving. These regulations could limit access to Bitcoin for some investors, potentially reducing demand and dampening the price increase typically associated with a halving. The regulatory uncertainty could also trigger a sell-off by some investors, leading to a temporary price decline, counteracting the upward pressure from the reduced supply. Conversely, clear and well-defined regulations could foster greater confidence in the market, potentially attracting more institutional investors and mitigating the negative impact of a potential sell-off.
Visual Representation of a Previous Halving
Imagine a line graph charting Bitcoin’s price over a period encompassing a previous halving event. The line would show a relatively flat or slightly upward trending price in the months leading up to the halving. As the halving approaches, the line would begin to curve upwards more steeply, reflecting increased buying pressure and anticipation. At the halving itself, the graph might show a brief pause or slight dip, followed by a period of significant upward movement, potentially showing a sharp incline, as the market reacts to the reduced supply. After reaching a peak, the line might plateau or even dip slightly before resuming a gradual upward trend over the longer term. The overall visual would be a relatively gradual incline initially, followed by a sharper rise around the halving, a period of volatility, and then a more gradual continuation of the upward trend. The visual story would clearly illustrate the anticipation, the immediate impact, and the long-term effects of the halving.
When Is Bitcoin Halving After 2025 – Predicting the precise date of Bitcoin halvings beyond 2025 is challenging due to the inherent complexities of the blockchain. However, understanding the previous halving cycles and their impact on price is crucial. To gain insight into potential price movements, it’s helpful to review analyses like this one on Bitcoin Price At Halving 2025 , which can inform expectations for future halvings.
Ultimately, the timing of future halvings remains dependent on the consistent block generation rate of the Bitcoin network.
Predicting the precise date of Bitcoin halvings beyond 2025 requires careful consideration of the blockchain’s consistent schedule. To understand the potential price impact of the 2025 halving, a useful resource is this analysis of the Halving Bitcoin 2025 Precio , which provides insights into historical trends. Subsequent halvings after 2025 will follow the established four-year pattern, although the exact date may vary slightly depending on block generation times.
Predicting the next Bitcoin halving after 2025 requires understanding the established four-year cycle. To clarify the past, it’s helpful to review the previous halving events; for instance, you can check When Was Bitcoin Halving In 2025 to gain perspective. This historical data helps us extrapolate and better understand the timing of future halvings, allowing for more informed speculation about when the next one might occur.
Determining when the Bitcoin halving occurs after 2025 requires understanding the four-year cycle. To track the progress towards the next halving, you can use a helpful resource like the Bitcoin Halving Countdown 2025 website. This countdown provides a clear visualization of the time remaining until the next halving event, allowing you to easily anticipate the next reduction in Bitcoin’s block reward after 2025.
Determining when the Bitcoin halving occurs after 2025 requires understanding the previous events. To clarify the next halving, we need to first establish the precise date and time of the 2025 halving; you can find this information on this helpful resource: Bitcoin Halving 2025 Date And Time. Once we know the 2025 date, calculating subsequent halvings becomes straightforward, using the four-year interval between each event.
Determining the precise date of Bitcoin halvings beyond 2025 requires careful consideration of the blockchain’s schedule. The next significant event, however, is the Bitcoin Halving April 2025 , which will significantly impact the rate of new Bitcoin creation. Following this, the subsequent halving will occur approximately four years later, based on the established Bitcoin protocol. Therefore, projections suggest a timeframe around 2029 for the next halving after 2025.